Page 105 - HIVMED_v21_i1.indb
P. 105
Page 14 of 34 Guideline
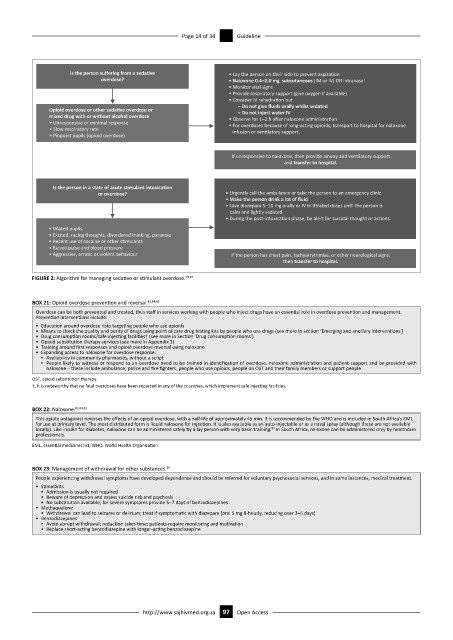
Is the person suffering from a seda
ve • Lay the person on their side to prevent aspira on
overdose? • Naloxone 0.4–2.0 mg subcutaneous (IM or IV) OR intranasal
• Monitor vital signs
• Provide respiratory support (give oxygen if available)
• Consider IV rehydra on but
– Do not give fluids orally whilst sedated
Opioid overdose or other seda
ve overdose or – Do not inject water IV
mixed drug with or without alcohol overdose • Observe for 1–2 h aer naloxone administra on
• Unresponsive or minimal response • For overdoses because of long-ac ng opioids, transport to hospital for naloxone
• Slow respiratory rate infusion or ven latory support.
• Pinpoint pupils (opioid overdose)
If unresponsive to naloxone, then provide airway and ven latory support
and transfer to hospital.
Is the person in a state of acute s
mulant intoxica
on
or overdose? • Urgently call the ambulance or take the person to an emergency clinic
• Make the person drink a lot of fluid
• Give diazepam 5–10 mg orally or IV in trated doses un l the person is
calm and lightly sedated.
• During the post-intoxica on phase, be alert for suicidal thought or ac ons.
• Dilated pupils
• Excited, racing thoughts, disordered thinking, paranoia
• Recent use of cocaine or other s mulants
• Raised pulse and blood pressure
• Aggressive, erra c or violent behaviour If the person has chest pain, tachyarrythmias, or other neurological signs,
then transfer to hospital.
FIGURE 2: Algorithm for managing sedative or stimulant overdose. 19,87
BOX 21: Opioid overdose prevention and reversal. 83,84,85
Overdose can be both prevented and treated, thus staff in services working with people who inject drugs have an essential role in overdose prevention and management.
Prevention interventions include:
• Education around overdose risks targeting people who use opioids
• Means to check the quality and purity of drugs using point of care drug testing kits by people who use drugs (see more in section ‘Emerging and ancillary interventions’)
• Drug consumption rooms/safe injecting facilities† (see more in Section ‘Drug consumption rooms’)
• Opioid substitution therapy services (see more in Appendix 3)
• Training around first responses and opioid overdose reversal using naloxone
• Expanding access to naloxone for overdose response:
▪ Availability in community pharmacies, without a script
▪ People likely to witness or respond to an overdose need to be trained in identification of overdose, naloxone administration and patient support and be provided with
naloxone – these include ambulance, police and fire fighters, people who use opioids, people on OST and their family members or support people
OST, opioid substitution therapy.
†, It is noteworthy that no fatal overdoses have been reported in any of the countries, which implement safe injecting facilities.
BOX 22: Naloxone. 83,84,85
This opiate antagonist reverses the effects of an opioid overdose, with a half-life of approximately 45 min. It is recommended by the WHO and is included in South Africa’s EML
for use at primary level. The most distributed form is liquid naloxone for injection. It is also available as an auto-injectable or as a nasal spray (although these are not available
locally). Like insulin for diabetes, naloxone can be administered safely by a lay person with very basic training. In South Africa, naloxone can be administered only by healthcare
84
professionals.
EML, essential medicines list; WHO, World Health Organization.
BOX 23: Management of withdrawal for other substances. 88
People experiencing withdrawal symptoms have developed dependence and should be referred for voluntary psychosocial services, and in some instances, medical treatment.
• Stimulants
• Admission is usually not required
• Beware of depression and assess suicide risk and psychosis
• No substitution available; for severe symptoms provide 5–7 days of benzodiazepines
• Methaqualone
• Withdrawal can lead to seizures or delirium; treat if symptomatic with diazepam (oral 5 mg 8-hourly, reducing over 3–5 days)
• Benzodiazepines
• Avoid abrupt withdrawal; reduction takes time; patients require monitoring and motivation
• Replace short-acting benzodiazepine with longer-acting benzodiazepine
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 97 Open Access