Page 100 - HIVMED_v21_i1.indb
P. 100
Page 9 of 34 Guideline
BOX 10: Key components of brief interventions. 50
Screen 1. Providing information and feedback about screening results
2. Understanding the patients’ views of their use and then coaching the patients
to change their perceptions about their use
Moderate to Severe risk/ 3. Encouraging the patients to discuss their views on how their use led to
No risk Low risk their injury, their likes and dislikes about use and how they may consider
high risk dependency
changing
4. Advising patients in clear but respectful terms to decrease or abstain from
Brief Brief substances
No further intervention intervention 5. Teaching behaviour change skills that will reduce substance use as well as
intervention Brief advice/ (e.g. motivational and referral the chances of negative consequences
beyond psycho- interviewing and to specialised 6. Establishing a method for follow-up with the patient; follow-up can be done
information education problem-solving assessment in another visit or telephonically
sharing
therapy and
combination) treatment
TABLE 10: Stages of change and recommended brief intervention elements.
Stage Definition Brief intervention elements to
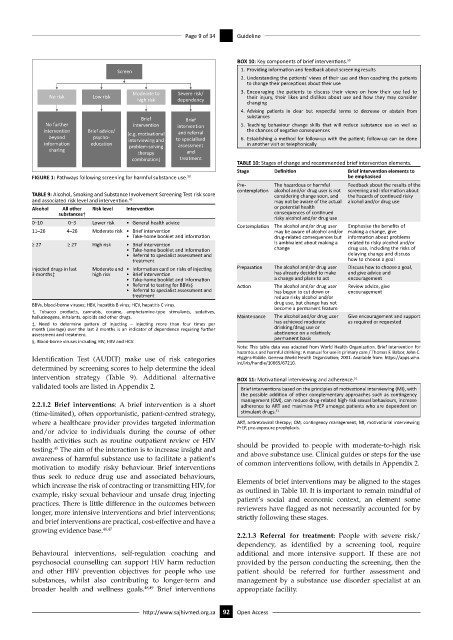
FIGURE 1: Pathways following screening for harmful substance use. 50 be emphasised
Pre- The hazardous or harmful Feedback about the results of the
contemplation alcohol and/or drug user is not screening and information about
TABLE 9: Alcohol, Smoking and Substance Involvement Screening Test risk score considering change soon, and the hazards of continued risky
and associated risk level and intervention. 45 may not be aware of the actual alcohol and/or drug use
Alcohol All other Risk level Intervention or potential health
substances† consequences of continued
risky alcohol and/or drug use
0–10 0–3 Lower risk • General health advice Contemplation The alcohol and/or drug user Emphasise the benefits of
11–26 4–26 Moderate risk • Brief intervention may be aware of alcohol and/or making a change, give
• Take-home booklet and information drug-related consequences but information about problems
≥ 27 ≥ 27 High risk • Brief intervention is ambivalent about making a related to risky alcohol and/or
• Take-home booklet and information change drug use, including the risks of
• Referral to specialist assessment and delaying change and discuss
treatment how to choose a goal
Injected drugs in last Moderate and • Information card on risks of injecting Preparation The alcohol and/or drug user Discuss how to choose a goal,
3 months‡ high risk • Brief intervention has already decided to make and give advice and
• Take-home booklet and information a change and plans to act encouragement
• Referral to testing for BBVs§ Action The alcohol and/or drug user Review advice, give
• Referral to specialist assessment and has begun to cut down or encouragement
treatment reduce risky alcohol and/or
BBVs, blood-borne viruses; HBV, hepatitis B virus; HCV, hepatitis C virus. drug use, but change has not
†, Tobacco products, cannabis, cocaine, amphetamine-type stimulants, sedatives, become a permanent feature
hallucinogens, inhalants, opioids and other drugs. Maintenance The alcohol and/or drug user Give encouragement and support
‡, Need to determine pattern of injecting – injecting more than four times per has achieved moderate as required or requested
month (average) over the last 3 months is an indicator of dependence requiring further drinking/drug use or
assessment and treatment. abstinence on a relatively
§, Blood-borne viruses including HIV, HBV and HCV. permanent basis
Note: This table data was adapted from World Health Organization. Brief intervention for
hazardous and harmful drinking: A manual for use in primary care / Thomas F. Babor, John C.
Identification Test (AUDIT) make use of risk categories Higgins-Biddle. Geneva:World Health Organization; 2001. Available from: https://apps.who.
int/iris/handle/10665/67210.
determined by screening scores to help determine the ideal
intervention strategy (Table 9). Additional alternative BOX 11: Motivational interviewing and adherence. 51
validated tools are listed in Appendix 2. Brief interventions based on the principles of motivational interviewing (MI), with
the possible addition of other complementary approaches such as contingency
management (CM), can reduce drug-related high-risk sexual behaviours, increase
2.2.1.2 Brief interventions: A brief intervention is a short adherence to ART and maximise PrEP amongst patients who are dependent on
(time-limited), often opportunistic, patient-centred strategy, stimulant drugs. 51
where a healthcare provider provides targeted information ART, antiretroviral therapy; CM, contingency management; MI, motivational interviewing;
and/or advice to individuals during the course of other PrEP, pre-exposure prophylaxis.
health activities such as routine outpatient review or HIV should be provided to people with moderate-to-high risk
45
testing. The aim of the interaction is to increase insight and and above substance use. Clinical guides or steps for the use
awareness of harmful substance use to facilitate a patient’s
motivation to modify risky behaviour. Brief interventions of common interventions follow, with details in Appendix 2.
thus seek to reduce drug use and associated behaviours,
which increase the risk of contracting or transmitting HIV, for Elements of brief interventions may be aligned to the stages
as outlined in Table 10. It is important to remain mindful of
example, risky sexual behaviour and unsafe drug injecting patient’s social and economic context, an element some
practices. There is little difference in the outcomes between
longer, more intensive interventions and brief interventions; reviewers have flagged as not necessarily accounted for by
and brief interventions are practical, cost-effective and have a strictly following these stages.
growing evidence base. 46,47
2.2.1.3 Referral for treatment: People with severe risk/
dependency, as identified by a screening tool, require
Behavioural interventions, self-regulation coaching and additional and more intensive support. If these are not
psychosocial counselling can support HIV harm reduction provided by the person conducting the screening, then the
and other HIV prevention objectives for people who use patient should be referred for further assessment and
substances, whilst also contributing to longer-term and management by a substance use disorder specialist at an
broader health and wellness goals. 48,49 Brief interventions appropriate facility.
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 92 Open Access