Page 55 - SAHCS HIVMed Journal Vol 20 No 1 2019
P. 55
Page 26 of 26 Guideline
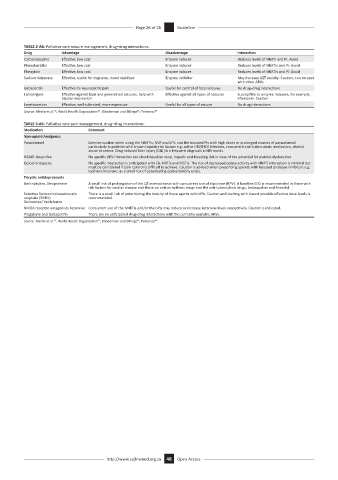
TABLE 2-A6: Palliative care seizure management, drug–drug interactions.
Drug Advantage Disadvantage Interaction
Carbamazepine Effective, low cost Enzyme inducer Reduces levels of NNRTI and PI: Avoid
Phenobarbital Effective, low cost Enzyme inducer Reduces levels of NNRTIs and PI: Avoid
Phenytoin Effective, low cost Enzyme inducer Reduces levels of NNRTIs and PI: Avoid
Sodium Valproate Effective, useful for migraine, mood stabiliser Enzyme inhibitor May increase AZT toxicity: Caution; can be used
with other ARVs
Gabapentin Effective for neuropathic pain Useful for control of focal seizures No drug–drug interactions
Lamotrigine Effective against focal and generalised seizures, help with Effective against all types of seizures Susceptible to enzyme inducers, for example,
bipolar depression rifampicin: Caution
Levetiracetam Effective, well-tolerated, more expensive Useful for all types of seizure No drug interactions
Source: Merlin et al. ; World Health Organization ; Blinderman and Billings ; Portenoy 40
38
37
33
TABLE 3-A6: Palliative care pain management, drug–drug interactions.
Medication Comment
Non-opioid Analgesics
Paracetamol Exercise caution when using the NNRTIs, NVP and EFV. and the boosted PIs with high doses or prolonged courses of paracetamol
particularly in patients with known hepatic risk factors e.g. active HBV/HCV infection, concurrent anti-tuberculosis medication, alcohol
abuse et cetera. Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a frequent diagnosis in HIV wards.
NSAID: Ibuprofen No specific ARV interaction but check baseline renal, hepatic and bleeding risk in view of the potential for platelet dysfunction
Opioid analgesics No specific interaction is anticipated with EIs, NRTIs and INSTIs. The risk of decreased opiate activity with NNRTI interaction is minimal but
must be considered if pain control is difficult to achieve. Caution is advised when prescribing opioids with boosted protease inhibitors e.g.
lopinavir/ritonavir, as a small risk of potentiating opiate toxicity exists.
Tricyclic antidepressants
Amitriptyline, Desipramine A small risk of prolongation of the QT interval exists with concurrent use of rilpivirine (RPV). A baseline ECG is recommended in those with
risk factors for cardiac disease and those on anti-arrhythmic drugs and the anti-tuberculosis drugs, bedaqualine and linezolid.
Selective Serotonin/noradrenalin There is a small risk of potentiating the toxicity of these agents with bPIs. Caution and starting with lowest possible effective dose levels is
reuptake (SNRIs) recommended.
Duloxetine/ Venlafaxine
NMDA receptor antagonists Ketamine Concurrent use of the NNRTIs and/or the bPIs may reduce or increase ketamine levels respectively. Caution is indicated.
Pregabalin and Gabapentin There are no anticipated drug-drug interactions with the currently available ARVs.
Source: Merlin et al. ; World Health Organization ; Blinderman and Billings ; Portenoy .
40
38
33
37
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 48 Open Access