Page 53 - SAHCS HIVMed Journal Vol 20 No 1 2019
P. 53
Page 24 of 26 Guideline
Appendix 6: Palliative care management: Drugs used for symptom control in
HIV palliation
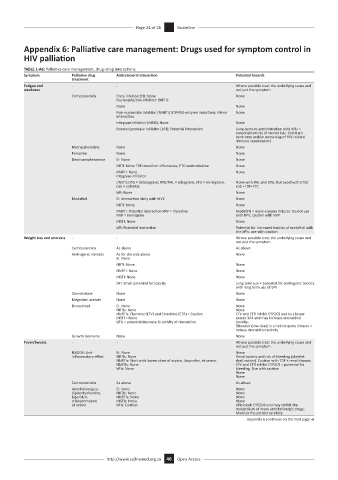
TABLE 1-A6: Palliative care management, drug–drug interactions.
Symptom Palliative drug Antiretroviral interaction Potential hazards
treatment
Fatigue and - - Where possible treat the underlying cause and
weakness not just the symptom
Corticosteroids Entry inhibitor(EI): None None
Nucleoside/tide inhibitor (NRTI):
None None
Non-nucleoside inhibitor (NNRTI) (CYP450 enzyme induction): Minor None
interaction
Integrase inhibitor (INSTI): None None
Boosted protease inhibitor (bPI): Potential interaction Long-term co-administration with bPIs =
potential toxicity of steroid (viz. Cushing’s
syndrome and/or worsening of HIV-related
immune suppression)
Methylphenidate None None
Pemoline None None
Dextroamphetamine EI: None None
NRTI: None TDF=tenofovir difumarate, FTC=emtricitabine None
NNRTI: None None
Integrase inhibitor
(INSTI):DTG = dolutegravir, RTG/RAL = raltegravir, ETG = elvitegravir, None with RAL and DTG, but avoid with ETG/
cob = cobisitat cob +TDF+FTC
bPI: None None
Modafinil EI: Interaction likely with MVC None
NRTI: None None
NNRTI: Potential interaction RPV = rilpivirine Modafinil = weak enzyme inducer. Do not use
NVP = nevirapine with RPV, caution with NVP
INSTI: None None
bPI: Potential interaction Potential for increased toxicity of modafinil with
the bPIs: use with caution
Weight loss and anorexia - - Where possible treat the underlying cause and
not just the symptom
Corticosteroids As above As above
Androgenic steroids As for steroids above None
EI: None
NRTI: None None
NNRTI: None None
INSTI: None None
bPI: Small potential for toxicity Long term use = potential for androgenic toxicity
with long term use of bPI
Oxandrolone None None
Megestrol acetate None None
Dronabinol EI: None None
NRTIs: None None
NNRTIs: Efavirenz (EFV) and Etravirine (ETR) = Caution EFV and ETR inhibit CYP2C9 and to a lesser
INSTI = None extent 3A4 and may increase dronabinol
bPIs = potential decrease in activity of dronabinol toxicity;
Ritonavir (low-dose) is a mild enzyme inducer =
reduce dronabinol activity
Growth hormone None None
Fever/Sweats - - Where possible treat the underlying cause and
not just the symptom
NSAIDS: Anti- EI: None None
inflammatory effect NRTIs: None Renal toxicity and risk of bleeding (platelet
NNRTIs: Start with lowest dose of aspirin, ibuprofen, et cetera. dysfunction). Caution with TDF + renal disease.
NNSTIs: None EFV and ETR inhibit CYP2C9 = potential for
bPIs: None bleeding. Use with caution
None
None
Corticosteroids As above As above
Anticholinergics: EI: None None
diphenhydramine, NRTIs: None None
biperiden, NNRTIs: None None
chlorpromazine INSTIs: None None
et cetera. bPIs: Caution bPIs block CYP2D6 and may inhibit the
metabolism of many anticholinergic drugs;
Monitor the patient carefully
Appendix 6 continues on the next page →
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 46 Open Access