Page 57 - SAHCS HIVMed Journal Vol 20 No 1 2019
P. 57
Page 2 of 10 Review Article
definitions of LTFU and retention, as well as the bias in Search strategy and information sources
reporting interruptions in care. 10,11,12 If patient retention is to By use of a broad search strategy (Appendix 1), one
be used as a key indicator of ART programme effectiveness, investigator (S.K.) worked independently to search MEDLINE
there should be a standardised definition of LTFU so that
ART programmes can be more accurately compared within via PubMed, EMBASE via Scopus, Web of Science, CINAHL
and between countries. and Africa-Wide databases from 01 January 2011 to date of
search. PubMed was searched on 05 October 2015, Scopus and
Africa-Wide on 07 October 2015, Web of Science on 14 October
The aims of this systematic review were to identify all
studies published in South Africa from 2011 to 2015 that 2015 and CINAHL on 15 October 2015. Information specialists
used LTFU as an indicator or outcome, to describe the at the University of Cape Town Medical Library assisted
variation and diversity of definitions as justification for with the literature search process. After obtaining lists of
establishing a single standardised definition going forward, abstracts meeting the search criteria from each database,
to summarise the findings using meta-analysis and to two investigators (S.K. and K.S.N.) reviewed the abstracts
provide suggestions for ways to use LTFU as an indicator in independently in duplicate and met to achieve consensus
a standardised fashion. Reporting standards have evolved on final inclusions of full-text review. S.K. and K.S.N.
since ART began to be provided in the South African public supplemented database searches by screening bibliographies
sector in 2004, as have treatment guidelines. This review of all full-text articles screened for the review. Figure 1 details
focuses on the 5 years between 2011 and 2015, when there the article selection process.
were more stringent requirements to start ART; those who
started had lower CD4 counts. Since 2015, universal test and Data extraction
treat has been adopted in South Africa and even more Data were extracted independently in duplicate (S.K., K.S.N.)
patients have been enrolled in ART. Based on the findings of using a standardised extraction form. Data collection forms
this review, we provide suggestions for ways to use ‘LTFU’ were crosschecked by both reviewers, and the reviewers
as an indicator in a standardised fashion with an increasing discussed discrepancies, with differences resolved by a third
population of patients on ART.
investigator (G.M.). Data were extracted on study design,
Methods dates, description and context of intervention, if applicable,
participant characteristics (age, baseline CD4 count),
This systematic review was designed, conducted and programme characteristics (cohort size, number of clinics,
reported in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items eligibility criteria), length of follow-up, definition of outcomes,
for Systematic Reviews (PRISMA) statement. The protocol outcomes, missing data and study limitations.
13
was registered on PROSPERO International Prospective
Register of Systematic Reviews as #CRD42015026466 (http:// Primary outcomes were LTFU and mortality. If a study
www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO). reported these outcomes by sub-cohort instead of aggregate,
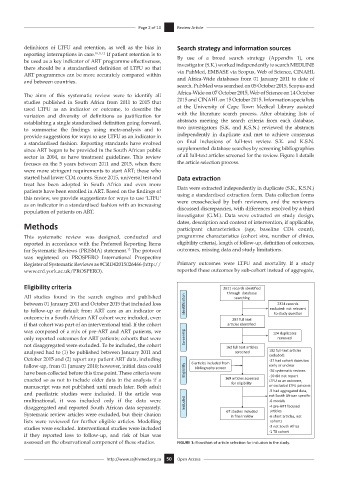
Eligibility criteria 2611 records iden fied
through database
All studies found in the search engines and published searching
between 01 January 2011 and October 2015 that included loss Iden fiva on Iden fica on 2324 records
to follow-up or default from ART care as an indicator or excluded: not relevant
to study ques on
outcome in a South African ART cohort were included, even 287 full text
if that cohort was part of an interventional trial. If the cohort ar cles iden fied
was composed of a mix of pre-ART and ART patients, we 124 duplicates
only reported outcomes for ART patients; cohorts that were Screening removed
not disaggregated were excluded. To be included, the cohort 163 full text ar cles
analysed had to (1) be published between January 2011 and screened 102 full-text ar cles
excluded:
October 2015 and (2) report any patient ART data, including -37 had cohort dates too
follow-up, from 01 January 2010; however, initial data could 6 ar cles included from early or unclear
bibliography screen
have been collected before this time point. These criteria were Eligibility Eligibility -26 systema c reviews
-10 did not report
enacted so as not to include older data in the analysis if a 169 ar cles assessed LTFU as an outcome,
for eligibility
manuscript was not published until much later. Both adult or excluded LTFU pa ents
and paediatric studies were included. If the article was -9 had aggregated data,
not South African specific
multinational, it was included only if the data were Included -6 models
disaggregated and reported South African data separately. Included -4 pre-ART focused
Systematic review articles were excluded, but their citation 67 studies included ar cles
in final review
-6 short ar cles, not
lists were reviewed for further eligible articles. Modelling cohorts
studies were excluded. Interventional studies were included -3 not South Africa
if they reported loss to follow-up, and risk of bias was -1 TB cohort
assessed on the observational component of these studies. FIGURE 1: Flowchart of article selection for inclusion in the study.
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 50 Open Access