Page 54 - SAHCS HIVMed Journal Vol 20 No 1 2019
P. 54
Page 25 of 26 Guideline
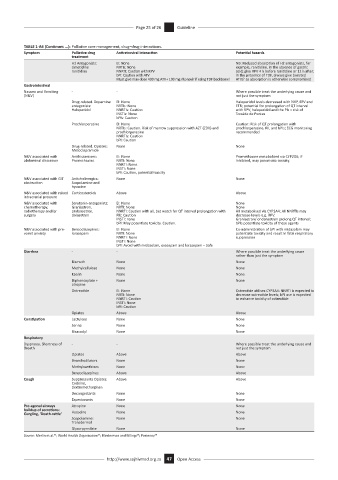
TABLE 1-A6 (Continues ...): Palliative care management, drug–drug interactions.
Symptom Palliative drug Antiretroviral interaction Potential hazards
treatment
H2 Antagonists: EI: None NB: Reduced absorption of H2 antagonists, for
cimetidine NRTIs: None example, ranitidine, in the absence of gastric
ranitidine NNRTI: Caution with RPV acid; give RPV 4 h before ranitidine or 12 h after;
bPI: Caution with ATV in the presence of TDF, always give boosted
Must give max dose 400 mg ATV+ 100 mg ritonavir if using TDF backbone! ATV/r as absorption is otherwise compromised
Gastrointestinal
Nausea and Vomiting - - Where possible treat the underlying cause and
(N&V) not just the symptom
Drug-related. Dopamine EI: None Haloperidol levels decreased with NVP, EFV and
antagonists: NRTIs: None ETR; potential for prolongation of QT interval
Haloperidol NNRTIs: Caution with RPV, haloperidol and the PIs = risk of
INSTIs: None Torsáde de Pontes
bPIs: Caution
Prochlorperazine EI: None Caution: Risk of QT prolongation with
NRTIs: Caution. Risk of marrow suppression with AZT (ZDV) and prochlorperazine, RIL and bPIs; ECG monitoring
prochlorperazine recommended
NNRTIs: Caution
bPI: Caution
Drug-related. Opiates: None None
Metoclopramide
N&V associated with Antihistamines: EI: None Promethazine metabolised via CYP2D6; if
abdominal distention Promethazine NRTI: None inhibited, may potentiate toxicity.
NNRTI: None
INSTI: None
bPI: Caution, potential toxicity
N&V associated with GIT Anticholinergics: None None
obstruction Scopolamine and
hyoscine
N&V associated with raised Corticosteroids Above Above
intracranial pressure
N&V associated with Serotonin-antagonists: EI: None None
chemotherapy, Granisetron, NRTI: None None
radiotherapy and/or ondansetron, NNRTI: Caution with all, but watch for QT interval prolongation with All metabolised via CYP3A4; All NNRTIs may
surgery dolasetron RIL: Caution decrease levels e.g. RPV.
INSTI: none Granisetron/ ondansetron prolong QT interval;
bPI: May potentiate toxicity. Caution. bPIs potentiate toxicity of these agents
N&V associated with pre- Benzodiazepines: EI: None Co-administration of bPI with midazolam may
vomit anxiety lorazepam NRTI: None potentiate toxicity and result in fatal respiratory
NNRTI: None suppression
INSTI: None
bPI: Avoid with midazolam, oxazepam and lorazepam – Safe
Diarrhea - - Where possible treat the underlying cause
rather than just the symptom
Bismuth None None
Methylcellulose None None
Kaolin None None
Diphenoxylate + None None
atropine
Octreotide EI: None Octreotide utilises CYP3A4: NNRTI is expected to
NRTI: None decrease octreotide levels; bPI use is expected
NNRTI: Caution to enhance toxicity of octreotide
INSTI: None
bPI: Caution
Opiates Above Above
Constipation Lactulose None None
Senna None None
Bisacodyl None None
Respiratory
Dyspnoea, Shortness of - - Where possible treat the underlying cause and
Breath not just the symptom
Opiates Above Above
Bronchodilators None None
Methylxanthines None None
Benzodiazepines Above Above
Cough Suppressants Opiates: Above Above
Codeine,
dextromethorphan
Decongestants None None
Expectorants None None
Pre-agonal airways Atropine None None
buildup of secretions: Hyoscine None None
Gurgling, ‘Death-rattle’
Scopolamine: None None
Transdermal
Glyco-pyrrolate None None
38
33
Source: Merlin et al. ; World Health Organization ; Blinderman and Billings ; Portenoy 40
37
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 47 Open Access