Page 200 - SAHCS HIVMed Journal Vol 20 No 1 2019
P. 200
Page 4 of 10 Original Research
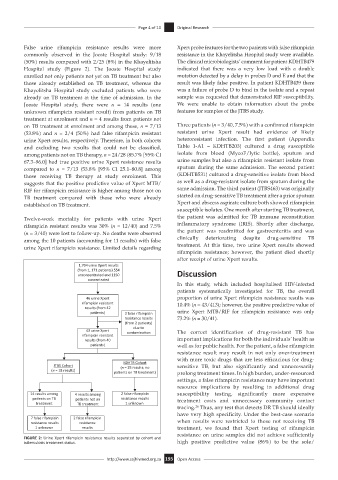
False urine rifampicin resistance results were more Xpert probe features for the two patients with false rifampicin
commonly observed in the Jooste Hospital study: 9/18 resistance in the Khayelitsha Hospital study were available.
(50%) results compared with 2/25 (8%) in the Khayelitsha The clinical microbiologists’ comment for patient KDHTB479
Hospital study (Figure 2). The Jooste Hospital study indicated that there was a very low load with a double
enrolled not only patients not yet on TB treatment but also mutation detected by a delay in probes D and E and that the
those already established on TB treatment, whereas the result was likely false positive. In patient KDHTB439 there
Khayelitsha Hospital study excluded patients who were was a failure of probe D to bind in the isolate and a repeat
already on TB treatment at the time of admission. In the sample was requested that demonstrated RIF susceptibility.
Jooste Hospital study, there were n = 14 results (one We were unable to obtain information about the probe
unknown rifampicin resistant result) from patients on TB features for samples of the JTBS study.
treatment at enrolment and n = 4 results from patients not
on TB treatment at enrolment and among these, n = 7/13 Three patients (n = 3/40, 7.5%) with a confirmed rifampicin
(53.8%) and n = 2/4 (50%) had false rifampicin resistant resistant urine Xpert result had evidence of likely
urine Xpert results, respectively. Therefore, in both cohorts heteroresistant infection. The first patient (Appendix
and excluding two results that could not be classified, Table 1-A1 – KDHTB203) cultured a drug susceptible
among patients not on TB therapy, n = 24/28 (85.7% [95% CI isolate from blood (MycoF/lytic bottle), sputum and
67.3–96.0] had true positive urine Xpert resistance results urine samples but also a rifampicin resistant isolate from
compared to n = 7/13 (53.8% [95% CI 25.1–80.8] among sputum during the same admission. The second patient
those receiving TB therapy at study enrolment. This (KDHTB531) cultured a drug-sensitive isolate from blood
suggests that the positive predictive value of Xpert MTB/ as well as a drug-resistant isolate from sputum during the
RIF for rifampicin resistance is higher among those not on same admission. The third patient (JTBS463) was originally
TB treatment compared with those who were already started on drug-sensitive TB treatment after a prior sputum
established on TB treatment. Xpert and abscess aspirate culture both showed rifampicin
susceptible isolates. One month after starting TB treatment,
Twelve-week mortality for patients with urine Xpert the patient was admitted for TB immune reconstitution
rifampicin resistant results was 30% (n = 12/40) and 7.5% inflammatory syndrome (IRIS). Shortly after discharge,
(n = 3/40) were lost to follow-up. No deaths were observed the patient was readmitted for gastroenteritis and was
among the 10 patients (accounting for 11 results) with false clinically deteriorating despite drug-sensitive TB
urine Xpert rifampicin resistance. Limited details regarding treatment. At this time, two urine Xpert results showed
rifampicin resistance; however, the patient died shortly
after receipt of urine Xpert results.
1,704 urine Xpert results
(from 1, 171 pa
ents) 554
unconcentrated and 1150 Discussion
concentrated
In this study, which included hospitalised HIV-infected
patients systematically investigated for TB, the overall
46 urine Xpert proportion of urine Xpert rifampicin resistance results was
rifampicin resistant 10.4% (n = 43/413); however, the positive predictive value of
results (from 42
pa
ents) 3 false rifampicin urine Xpert MTB/RIF for rifampicin resistance was only
resistance results 73.2% (n = 30/41).
(from 2 pa
ents)
due to
43 urine Xpert contamina
on The correct identification of drug-resistant TB has
rifampicin resistant
results (from 40 important implications for both the individuals’ health as
pa
ents) well as for public health. For the patient, a false rifampicin
resistance result may result in not only over-treatment
with more toxic drugs that are less efficacious for drug-
KDHTB Cohort
JTBS Cohort (n = 25 results; no sensitive TB, but also significantly and unnecessarily
(n = 18 results)
pa
ents on TB treatment) prolong treatment times. In high burden, under-resourced
settings, a false rifampicin resistance may have important
resource implications by resulting in additional drug
14 results among 4 results among 2 false rifampicin susceptibility testing, significantly more expensive
pa
ents on TB pa
ents not on resistance results treatment costs and unnecessary community contact
treatment TB treatment 1 unknown
26
tracing. Thus, any test that detects DR TB should ideally
have very high specificity. Under the best-case scenario
7 false rifampicin 2 false rifampicin
resistance results resistance when results were restricted to those not receiving TB
1 unknown results treatment, we found that Xpert testing of rifampicin
resistance on urine samples did not achieve sufficiently
FIGURE 2: Urine Xpert rifampicin resistance results separated by cohort and
tuberculosis treatment status. high positive predictive value (86%) to be the sole/
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 193 Open Access