Page 199 - SAHCS HIVMed Journal Vol 20 No 1 2019
P. 199
Page 3 of 10 Original Research
HIV-infected patients requiring medical admission and had The majority of rifampicin resistance results (n = 30/43; 69.8%
detailed TB investigations performed. Urine Xpert rifampicin [95% CI 53.9–82.8]) were classified as true urine Xpert
resistance results were classified by two authors rifampicin resistance based on the results from other
independently by first assessing all available microbiological independent clinical samples. Eleven (11/43, 25.6% [95% CI
results (including culture, Xpert and line probe assay) on all 13.5–41.2]) results were classified as false rifampicin
clinical samples. In cases where it was not possible to classify resistance and two further results (one from each study)
urine Xpert rifampicin resistance results by assessing could not be classified. Thus, by the most conservative
microbiological results from other clinical samples, the estimate (excluding 2 unknown results), n = 30/41 results
type of TB treatment, response to treatment and vital status were confirmed as true urine Xpert rifampicin resistant
at 12 weeks were also considered. All patients with urine results, for a positive predictive value of 73.2% (95% CI 57.1–
Xpert rifampicin resistant results were assigned to one of the 85.8). Comprehensive details for each patient with urine
three mutually exclusive groups: (1) true rifampicin resistant Xpert rifampicin resistance were reported in Appendix
urine Xpert (patients who had rifampicin-resistant TB Table 1-A1.
confirmed by culture or Xpert on other clinical samples)
(2) false rifampicin resistant urine Xpert (patients who did TABLE 1: Baseline characteristics of Jooste Hospital tuberculosis study and
not have rifampicin-resistant TB present on additional Khayelitsha Hospital tuberculosis study patients.
clinical samples and had a clinical course that was not Variable Jooste Hospital study Khayelitsha Hospital study
compatible with drug-resistant TB), (3) unknown (insufficient n (n = 585) n (n = 586)
microbiological and clinical evidence to classify a patient’s Sex % or IQR % or IQR
urine Xpert rifampicin resistant result). Furthermore, Female 338 57.8 307 52.4
patients with true urine Xpert rifampicin resistance were Male 247 42.2 279 47.6
classified as having heteroresistance if additional Age, years 35.3 28.9, 41.4 35.9 30.8, 43.9
independent sample/s from the same clinical episode ART status
demonstrated both a rifampicin-susceptible and a rifampicin- Defaulted ART 113 19.3 140 24.1
resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) isolate, i.e. ART naive 209 35.7 222 38.3
discordant results from two different clinical specimens in Currently on ART 263 45.0 218 37.6
the same patient. Two patients (contributing three urine TB history
Xpert rifampicin resistance results) were determined to have Previous TB 263 45.1 268 45.7
false urine Xpert rifampicin resistance; this occurred within Unknown TB history 2 0.3 23 3.9
66
3 months of initiating the first study, and was prior to the CD4, cells/mL 134 53, 275 5.2 24, 138
4.2
HIV viral load, log copies/mL
1.6, 5.5
3.8, 5.7
introduction of single use disposable bedpans (see details Established on TB 158 27 - -
above). This led to the introduction of single-use disposable treatment at enrolment
bedpans and avoided further such cases. ART, Antiretroviral therapy; TB, Tuberculosis.
Continuous variables presented as median and interquartile range and categorical variables
as number and percentage.
Ethical consideration
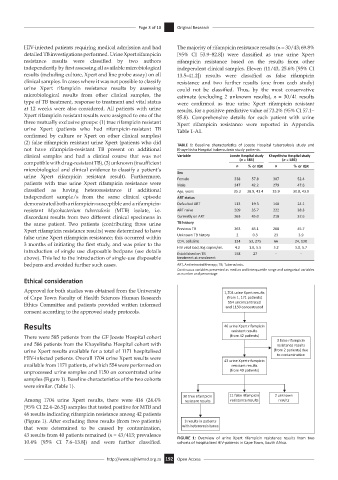
Approval for both studies was obtained from the University 1,704 urine Xpert results
of Cape Town Faculty of Health Sciences Human Research (from 1, 171 pa
ents)
554 unconcentrated
Ethics Committee and patients provided written informed and 1150 concentrated
consent according to the approved study protocols.
Results 46 urine Xpert rifampicin
resistant results
There were 585 patients from the GF Jooste Hospital cohort (from 42 pa
ents) 3 false rifampicin
and 586 patients from the Khayelitsha Hospital cohort with resistance results
urine Xpert results available for a total of 1171 hospitalised (from 2 pa
ents) due
HIV-infected patients. Overall 1704 urine Xpert results were 43 urine Xpert rifampicin to contamina
on
available from 1171 patients, of which 554 were performed on resistant results
unprocessed urine samples and 1150 on concentrated urine (from 40 pa
ents)
samples (Figure 1). Baseline characteristics of the two cohorts
were similar. (Table 1).
30 true rifampicin 11 false rifampicin 2 unknown
Among 1704 urine Xpert results, there were 416 (24.4% resistant results resistance results results
[95% CI 22.4–26.5]) samples that tested positive for MTB and
46 results indicating rifampicin resistance among 42 patients
(Figure 1). After excluding three results (from two patients) 3 results in pa
ents
that were determined to be caused by contamination, with heteroresisitance
43 results from 40 patients remained (n = 43/413; prevalence FIGURE 1: Overview of urine Xpert rifampicin resistance results from two
10.4% [95% CI 7.6–13.8]) and were further classified. cohorts of hospitalised HIV-patients in Cape Town, South Africa.
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 192 Open Access