Page 32 - ONLINE – Nursing Matters October 2020_Vol 11
P. 32
useful resources
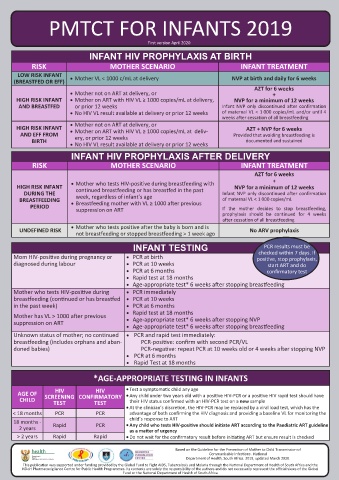
PMTCT FOR INFANTS 2019
EMGuidance digital platform
First version April 2020
INFANT HIV PROPHYLAXIS AT BIRTH
RISK MOTHER SCENARIO INFANT TREATMENT
LOW RISK INFANT EMGuidance (short for Essential Medical Follow these two steps to access the green button to ‘downLoad seLected
(BREASTFED OR EFF) • Mother VL < 1000 c/mL at delivery NVP at birth and daily for 6 weeks Guidance) is a mobile- and web-based 2019 guidelines: GuideLines’ will appear on the
AZT for 6 weeks medi cines and treatment platform for bottom of the screen.
• Mother not on ART at delivery, or +
HIGH RISK INFANT • Mother on ART with HIV VL ≥ 1000 copies/mL at delivery, NVP for a minimum of 12 weeks medical professionals. We are pleased 1. Sign up to access EMGuidance on
AND BREASTFED or prior 12 weeks Infant NVP only discontinued after confirmation to announce that we have partnered Google Play, the Apple App Store For more information, read the following
• No HIV VL result available at delivery or prior 12 weeks of maternal VL < 1 000 copies/mL and/or until 4 with the National Department of or via Web: articles applicable to your device:
weeks after cessation of all breastfeeding Health to launch the 2019 guidelines • Google Play: https://play. • Android:
• Mother not on ART at delivery, or
HIGH RISK INFANT AZT + NVP for 6 weeks for antiretroviral therapy (ART) and the google.com/store/apps/ https://intercom.help/essential-medical-
AND EFF FROM • Mother on ART with HIV VL ≥ 1000 copies/mL at deliv- Provided that avoiding breastfeeding is prevention of mother-to-child transmission details?id=emguidance. guidance/en/articles/3529816-how-
ery, or prior 12 weeks
BIRTH documented and sustained to-download-the-latest-guidelines-on-the-
• No HIV VL result available at delivery or prior 12 weeks of communicable infections (PMTCT) on tompsa&hl=en_ZA
the EMGuidance platform. • App Store: https:// emguidance-platform-for-an-android-device
INFANT HIV PROPHYLAXIS AFTER DELIVERY apps.apple.com/za/app/ • iOS:
RISK MOTHER SCENARIO INFANT TREATMENT About EMGuidance essential-medical-guidance/ https://intercom.help/essential-medical-
guidance/en/articles/3529793-how-
AZT for 6 weeks id789625087 to-download-the-latest-guidelines-on-the-
+
HIGH RISK INFANT • Mother who tests HIV-positive during breastfeeding with NVP for a minimum of 12 weeks EMGuidance offers free access to • Web: http://emguidance.com emguidance-platform-for-an-ios-device
comprehensive, up-to-date, locally
continued breastfeeding or has breastfed in the past
DURING THE week, regardless of infant’s age Infant NVP only discontinued after confirmation relevant, evidence-based medicines 2. Download the latest guidelines:
BREASTFEEDING • Breastfeeding mother with VL ≥ 1000 after previous of maternal VL < 1 000 copies/mL information and guidelines at the touch Tap on the ‘Library’ icon on the home
PERIOD suppression on ART If the mother decides to stop breastfeeding, Should you have any feedback
prophylaxis should be continued for 4 weeks of a button. The platform is accessible screen. Select the ‘GuideLines’ tab, or queries for our team regarding
after cessation of all breastfeeding via your desktop or smartphone. followed by the ‘+’ icon. Browse these guidelines or use of the
• Mother who tests positive after the baby is born and is The platform is used by over 26 000 through the available guidelines platform, feel free to contact us at:
UNDEFINED RISK No ARV prophylaxis
not breastfeeding or stopped breastfeeding > 1 week ago healthcare professionals across South and select the relevant guidelines
Africa. View this video to see how it you want to download by checking [email protected]
INFANT TESTING PCR results must be works: https://youtu.be/rGRefOK8-y4 the box next to the guideline title. A
checked within 7 days. If
Mom HIV-positive during pregnancy or • PCR at birth positive, stop prophylaxis,
diagnosed during labour • PCR at 10 weeks start ART and do
• PCR at 6 months confirmatory test
• Rapid test at 18 months
• Age-appropriate test* 6 weeks after stopping breastfeeding
Mother who tests HIV-positive during • PCR immediately
breastfeeding (continued or has breastfed • PCR at 10 weeks
in the past week) • PCR at 6 months
• Rapid test at 18 months
Mother has VL > 1000 after previous • Age-appropriate test* 6 weeks after stopping NVP
suppression on ART
• Age-appropriate test* 6 weeks after stopping breastfeeding
Unknown status of mother; no continued • PCR and rapid test immediately:
breastfeeding (includes orphans and aban- PCR-positive: confirm with second PCR/VL
doned babies) PCR-negative: repeat PCR at 10 weeks old or 4 weeks after stopping NVP
• PCR at 6 months
• Rapid Test at 18 months
*AGE-APPROPRIATE TESTING IN INFANTS
HIV
HIV
AGE OF SCREENING CONFIRMATORY • Test a symptomatic child any age
• Any child under two years old with a positive HIV-PCR or a positive HIV rapid test should have
CHILD TEST TEST their HIV status confirmed with an HIV-PCR test on a new sample
• At the clinician’s discretion, the HIV-PCR may be replaced by a viral load test, which has the
< 18 months PCR PCR advantage of both confirming the HIV diagnosis and providing a baseline VL for monitoring the
18 months - child’s response to ART Free instant access to Medicines Medicines Interaction checker
2 years Rapid PCR • Any child who tests HIV-positive should initiate ART according to the Paediatric ART guideline locally relevant medicines, South Africa’s most Each medicine has a Improve the safety and
as a matter of urgency
> 2 years Rapid Rapid • Do not wait for the confirmatory result before initiating ART but ensure result is checked info and clinical guidelines. comprehensive, evidence- detailed monograph. effectiveness of prescribed
based medicines resource. medicines.
HIV Nursing Matters | October 2020 | page 30 Based on the Guideline for the Prevention of Mother to Child Transmission of HIV Nursing Matters | October 2020 | page 31
Communicable Infections . National
Department of Health, South Africa. 2019, updated March 2020.
This publication was supported under funding provided by the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria through the National Department of Health of South Africa and the
NDoH Pharmacovigilance Centre for Public Health Programmes. Its contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the Global
Fund or the National Department of Health of South Africa