Page 27 - ONLINE – Nursing Matters October 2020_Vol 11
P. 27
clinical guidance
SOUTH AFRICAN ART CLINICAL GUIDELINES 2019 Contact the TOLL-FREE National HIV & TB Health Care Worker Hotline
NEED HELP?
0800 212 506 / 021 406 6782
ADOLESCENTS (≥ 10 YEARS) AND ADULTS Alternatively “WhatsApp” or send an SMS or “Please Call Me”
Second version April 2020 www.mic.uct.ac.za
to 071 840 1572
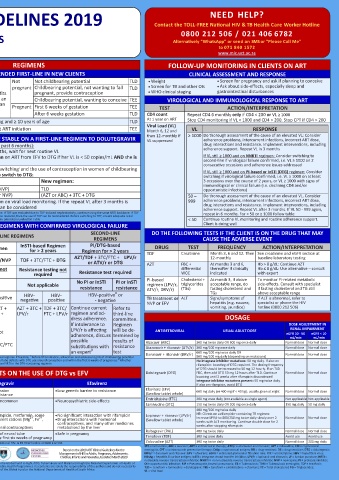
ART ELIGIBILITY AND DETERMINING THE TIMEFRAME FOR ART INITIATION REGIMENS FOLLOW-UP MONITORING IN CLIENTS ON ART
WHO IS ELIGIBLE? RECOMMENDED FIRST-LINE IN NEW CLIENTS CLINICAL ASSESSMENT AND RESPONSE
Adult women and adolescent girls Not Not childbearing potential TLD • Weight • Screen for pregnancy and ask if planning to conceive
≥ 35 kg and ≥ 10 years pregnant Childbearing potential, not wanting to fall TLD • Screen for TB and other OIs • Ask about side-effects, especially sleep and
REASONS TO DEFER STARTING ART WHEN TO START ART* Provide information on risks and benefits pregnant, provide contraception • WHO clinical staging gastrointestinal disturbances
TB symptoms (cough, night sweats, No TB: Same day or within 7 days of TEE and TLD to allow client to make an Childbearing potential, wanting to conceive TEE VIROLOGICAL AND IMMUNOLOGICAL RESPONSE TO ART
fever, recent weight loss) Confirmed DS-TB at non-neurological site: informed choice. Document that woman Pregnant First 6 weeks of gestation TEE
ACTION/INTERPRETATION
CD4 < 50 cells/μL: within 2 weeks of starting TB treatment has been counselled and consents to After 6 weeks gestation TLD TEST Repeat CD4 6 monthly only if CD4 < 200 or VL ≥ 1000
CD4 ≥ 50 cells/μL: 8 weeks after starting TB treatment receive DTG CD4 count
At 1 year on ART
Confirmed DR-TB at non-neurological site: Adult men and adolescent boys ≥ 35 kg and ≥ 10 years of age TLD Stop CD4 monitoring if VL < 1000 and CD4 > 200. Stop CPT if CD4 > 200
Start ART 2 weeks after TB treatment, once symptoms improved Client currently on DS-TB treatment at ART initiation TEE Viral Load (VL) VL RESPONSE
and TB treatment tolerated Month 6, 12 and ≥ 1000 Do thorough assessment of the cause of an elevated VL: Consider
Signs and symptoms of meningitis (headache, Investigate for meningitis before starting ART SWITCHING CLIENTS WHO ARE STABLE ON A FIRST-LINE REGIMEN TO DOLUTEGRAVIR then 12-monthly if adherence problems, intercurrent infections, incorrect ART dose,
VL suppressed
confusion, fever, neck stiffness or coma) TBM (DS or DR): 4 - 8 weeks after starting TB treatment Latest VL (copies/mL) result (within the past 6 months): drug interactions and resistance. Implement interventions, including
CM: 4 - 6 weeks after starting antifungal treatment • If VL not done within the past 6 months, wait for next routine VL adherence support. Repeat VL in 3 months
CrAg-positive with no symptoms or signs of meningitis 2 weeks after starting fluconazole • Only switch a stable pregnant woman on ART from EFV to DTG if her VL is < 50 copies/mL AND she is If VL still ≥ 1000 and on NNRTI regimen: Consider switching to
Other acute illnesses e.g. PJP or bacterial pneumonia Defer ART for 1 - 2 weeks after commencing treatment for the more than 6 weeks pregnant second-line if virological failure confirmed, i.e. VL ≥ 1000 on 2
infection VL < 50 Discuss benefits and risks of switching and the use of contraception in women of childbearing consecutive occasions and adherence issues addressed
*
Clinical symptoms or signs of liver disease Confirm liver disease using ALT and bilirubin. ALT > 120 IU/L with potential. If client chooses to switch to DTG: If VL still ≥ 1000 and on PI-based or InSTI (DTG) regimen: Consider
symptoms of hepatitis (nausea, vomiting, upper quadrant pain) switching if virological failure confirmed, i.e. VL ≥ 1000 on at least
and/or total serum bilirubin concentrations > 40 µmol/L: Current regimen: New regimen: 3 occasions over the course of 2 years, or VL ≥ 1000 with signs of
immunological or clinical failure (i.e. declining CD4 and/or
investigate and manage possible causes before starting ART TDF + (FTC or 3TC) + (EFV or NVP) TLD opportunistic infections)
¥
*Clients already on ART should NOT have their treatment interrupted upon diagnosis of the above conditions (AZT or ABC) + 3TC + (EFV or NVP) (AZT or ABC) + 3TC + DTG 50 – Do thorough assessment of the cause of an elevated VL. Consider
BASELINE CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS VL ≥ 50 Do not switch. Refer to section on viral load monitoring. If the repeat VL after 3 months is 999 adherence problems, intercurrent infections, incorrect ART dose,
drug interactions and resistance. Implement interventions, including
≤ 999, then a switch to DTG can be considered
• Recognise the client with respiratory, • Mental health issues/substance abuse ¥ was excluded due to non-TDF related renal failure that has since resolved, then the use of TDF can be reconsidered. Before switching to TDF, ensure adequate renal adherence support. Repeat VL after 3 months. If VL 50 - 999 again,
Assess the reason for exclusion of TDF from the NRTI backbone. If TDF was excluded due to TDF-induced nephrotoxicity, continue using the same NRTI backbone. If TDF
repeat in 6 months. For < 50 or ≥ 1000 follow table
neurological, or abdominal danger signs • Major chronic non-communicable diseases (NCDs) function by checking eGFR/creatinine as outlined in the Baseline Laboratory Evaluation Table < 50 Continue routine VL monitoring and routine adherence support.
• e.g. diabetes, hypertension, epilepsy SECOND- AND THIRD-LINE REGIMENS WITH CONFIRMED VIROLOGICAL FAILURE Client is doing well
• Pregnancy or planning to conceive SECOND-LINE DO THE FOLLOWING TESTS IF THE CLIENT IS ON THE DRUG THAT MAY
• • Symptom screen for sexually transmitted infections FIRST-LINE REGIMENS REGIMENS CAUSE THE ADVERSE EVENT
• Meningitis • WHO clinical stage InSTI-based Regimen PI/DTG-based
REGIMEN NNRTI-based Regimen for > 2 years Regimen for > 2 years DRUG TEST FREQUENCY ACTION/INTERPRETATION
BASELINE LABORATORY EVALUATION TDF + 3TC/FTC + EFV/NVP TDF + 3TC/FTC + DTG AZT/TDF + 3TC/FTC + LPV/r TDF Creatinine Month 3, 6 and 12. Then See creatinine and eGFR section at
12-monthly
baseline laboratory testing
TEST AND PURPOSE INTERPRETATION / ACTION RESISTANCE Resistance testing not Resistance testing not or ATV/r or DTG AZT FBC + At months 3 and 6, Hb > 8 g/dL: Continue AZT
thereafter if clinically
Hb ≤ 8 g/dL: Use alternative – consult
differential
Confirm HIV test result Ensure that the national testing algorithm has been followed TESTING required required Resistance test required WCC indicated with expert
To confirm HIV status for those RESISTANCE No PI or InSTI PI or InSTI PI-based Cholesterol + At month 3, if above To monitor PI-related metabolic
without documented HIV status TEST RESULTS Not applicable Not applicable resistance resistance regimen (LPV/r, triglycerides acceptable range, do side-effects. Consult with specialist
CD4 count (cells/µL) Initiate CPT if CD4 < 200 or WHO stage 2, 3 or 4 # ATV/r, DRV/r) (TGs) fasting cholesterol and if fasting cholesterol and TG still
above acceptable range
TGs
To identify eligibility for CPT If CD4 < 100 a reflex CrAg screening will be done automatically HBV CO- HBV- HBV-positive HBV- HBV- HBV-positive or TB treatment or ALT Signs/symptoms of If ALT is abnormal, refer to
and CrAg screening CrAg-negative: no fluconazole therapy required. Start ART INFECTION negative negative positive - negative NVP or EFV hepatitis (e.g. nausea, specialist or phone the HIV
CrAg-positive: the client will require treatment of the infection. All clients, including AZT + 3TC + TDF + AZT + AZT + 3TC + TDF + 3TC/ Continue current Refer to vomiting, jaundice) hotline (0800 212 506)
pregnant women, should be referred for a LP. Defer ART as above DTG 3TC/FTC + LPV/r FTC + LPV/r regimen and ad- third-line
∞
∞
Cervical cancer screening At baseline and thereafter every three years if normal. If lesions present, refer for DTG dress adherence. committee. DOSAGE
To identify women with cervical colposcopy and manage accordingly NEW If DTG not If intolerance to Regimen DOSE ADJUSTMENT IN
RENAL IMPAIRMENT
lesions REGIMEN suitable: If DTG not LPV/r is affecting will be de- ANTIRETROVIRAL USUAL ADULT DOSE eGFR 10 - 50 eGFR < 10
adherence, discuss termined by
HBsAg If positive, TDF-containing regimen is preferred. Exercise caution when stopping TDF due AZT + 3TC + suitable: possible results of mL/min mL/min
Identify hepatitis B co-infection to risk of hepatitis flares LPV/r TDF + 3TC/FTC substitutions with resistance Abacavir (ABC) 300 mg twice daily OR 600 mg once daily Normal dose Normal dose
β
Creatinine and eGFR Serum creatinine (SCr) is a waste product filtered by the kidneys used to determine eGFR + LPV/r an expert test Atazanavir + ritonavir (ATV/r) 300 mg/100 mg once daily Normal dose Normal dose
600 mg/100 mg twice daily OR
To detect renal insufficiency, Age/Pregnancy status What must be measured? Safe to use TDF # Ideally clients who are HBsAg-positive should be on a TDF-based regimen if feasible; Before DTG initiation, all women and adolescent girls of childbearing potential Darunavir + ritonavir (DRV/r) 800 mg/100 mg daily (depending on mutations) Normal dose Normal dose
∞
β
and eligibility for TDF must be appropriately counselled on the potential risk of neural tube defects with DTG use around conception and within the first 6 weeks of pregnancy; Whether No integrase inhibitor mutations: 50 mg daily. If also on
remaining on DTG, or switching to DTG, ensure at least one active NRTI in the DTG-containing regimen
#
2
≥ 10 and < 16 years eGFR using Counahan Barratt formula > 80 mL/min/1.73 m rifampicin: boosting of DTG required. The dosing frequency
of DTG should be increased to 50 mg 12 hourly. If on TLD
Adult and adolescent eGFR using MDRD equation as 2 KEY POINTS ON THE USE OF DTG vs EFV Dolutegravir (DTG) FDC, then add DTG 50 mg 12 hours after TLD. Continue Normal dose Normal dose
≥ 16 years provided by the laboratory > 50 mL/min/1.73m boosting until 2 weeks after rifampicin discontinued
Integrase inhibitor mutations present: 50 mg twice daily.
Pregnant Absolute creatinine level < 85 μmol/L Dolutegravir Efavirenz If also on rifampicin, avoid DTG
Resistance • Provides rapid viral suppression • Low genetic barrier to resistance Efavirenz (EFV) 600 mg daily (or 400 mg if < 40 kg); usually given at night Normal dose Normal dose
(Swallow tablet whole)
• High genetic barrier to resistance
Side-effects • Side-effects are mild and uncommon • Neuropsychiatric side-effects Emtricitabine (FTC) 200 mg once daily (not available as single agent) Not applicable Not applicable
eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m ) = height [cm] x 40 • Weight gain Lamivudine (3TC) 150 mg twice daily OR 300 mg once daily 150 mg daily 50 mg daily
2
creatinine [μmol/L] • Insomnia 400 mg/100 mg twice daily
ϖ
Interactions • Drug interactions with rifampicin, metformin, some • No significant interaction with rifampicin Lopinavir + ritonavir (LPV/r) NB: Clients on a rifampicin-containing TB regimen: Normal dose Normal dose
Increase LPV/r to 800/200 mg twice daily slowly over 2
2+
2+
Haemoglobin (Hb) Adults and Pregnant women anticonvulsants and polyvalent cations (Mg , Fe , • Drug interactions with hormonal (Swallow tablet whole) weeks with ALT monitoring. Continue double dose for 2
2+
2+
3+
Ca , Al , Zn )
contraceptives, and many other medicines
To detect anaemia adolescents • No interaction with hormonal contraceptives metabolised by the liver weeks after stopping rifampicin
If Hb < 10 do FBC, and follow If Hb < 10 initiate iron supplementation • DTG may increase the risk of neural tube • Safe in pregnancy Raltegravir (RAL) 400 mg twice daily Normal dose Normal dose
Primary Care Standard Refer if: Hb < 8 with symptoms of anaemia, or Pregnancy defects (NTDs) if used in the first six weeks of pregnancy Tenofovir (TDF) 300 mg once daily Avoid use Avoid use
Treatment guidelines anaemia and ≥ 36 weeks pregnant, or no response to iron ϖ For more information on drug-drug interactions contact the National HIV- & TB HCW hotline at 0800 212 506 Zidovudine (AZT) 300 mg twice daily Normal dose 300 mg daily
If Hb < 8 avoid AZT Take note of DTG drug interactions under key points 3TC = lamivudine; ABC = abacavir; ART = antiretroviral therapy; ATV/r = atazanavir and ritonavir; AZT = zidovudine; CM = cryptococcal
HIV Nursing Matters | October 2020 | page 25
HIV Nursing Matters | October 2020 | page 24 Based on the 2019 ART Clinical Guidelines for the meningitis; CPT = cotrimoxazole preventive therapy; CrAg = cryptococcal antigen; DR = drug-resistant; DS = drug-sensitive; DTG = dolutegravir;
GeneXpert Adults and adolescents Pregnant women Management of HIV in Adults, Pregnancy, Adolescents, DRV/r = darunavir and ritonavir; EFV = efavirenz; eGFR = estimated glomerular filtration rate; FTC = emtricitabine; HBV = hepatitis B virus;
Children, Infants and Neonates, Updated March 2020
HBsAg = hepatitis B surface antigen; InSTI = Integrase strand transfer inhibitor; LPV/r = lopinavir and ritonavir; LP = lumbar puncture; NRTI =
To diagnose TB Do GeneXpert only if client Routinely done at first antenatal visit, regardless of This publication was supported under funding provided by the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria through the National Department of Health of nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor; NNRTI = non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor; NVP = nevirapine; PI = protease inhibitor;
has symptoms of TB symptoms South Africa and the NDoH Pharmacovigilance Centre for Public Health Programmes. Its contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily OI = opportunistic infection; PJP = Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia; TB = Tuberculosis; TBM = Tuberculosis meningitis; TDF = tenofovir;
TLD = tenofovir + lamivudine + dolutegravir; TEE = tenofovir + emtricitabine + efavirenz; TC = Total cholesterol; TG = Triglycerides;
represent the official views of the Global Fund or the National Department of Health of South Africa VL = viral load