Page 29 - ONLINE – Nursing Matters October 2020_Vol 11
P. 29
SOUTH AFRICAN ART CLINICAL GUIDELINES 2019 Contact the TOLL-FREE National
NEED HELP?
clinical guidance
HIV & TB Health Care Worker Hotline
(Infants and children < 10 years or < 35kg) 0800 212 506 / 021 - 406 6782
First edition February 2020 Alternatively “WhatsApp” or send an SMS or “Please Call Me” to 071 840 1572
www.mic.uct.ac.za
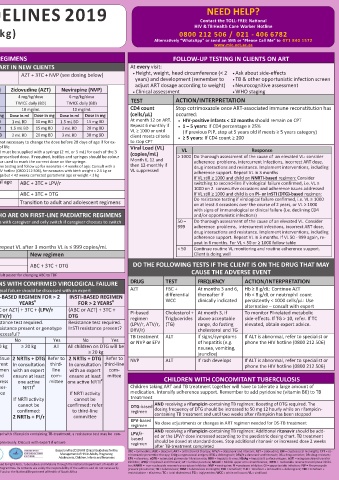
ART ELIGIBILITY AND DETERMINING THE TIMEFRAME FOR ART INITIATION REGIMENS FOLLOW-UP TESTING IN CLIENTS ON ART
WHO IS ELIGIBLE? FIRST-LINE ART IN NEW CLIENTS At every visit:
#
Neonates until 28 days of age AZT + 3TC + NVP (see dosing below) • Height, weight, head circumference (< 2 • Ask about side-effects
(with birth weight ≥ 2.5 kg) years) and development (remember to • TB & other opportunistic infection screen
adjust ART dosage according to weight)
Lamivudine (3TC) Zidovudine (AZT) Nevirapine (NVP) • Clinical assessment • Neurocognitive assessment
• WHO staging
REASONS TO DEFER STARTING ART WHEN TO START ART* Target dose 2 mg/kg/dose 4 mg/kg/dose 6 mg/kg/dose
TB symptoms (cough, fever, recent weight loss, No TB: Same day or within 7 days TWICE daily (BD) TWICE daily (BD) TWICE daily (BD) TEST ACTION/INTERPRETATION
fatigue/always tired) Confirmed DS-TB at non-neurological site: Available formulation 10 mg/mL 10 mg/mL 10 mg/mL CD4 count Stop cotrimoxazole once ART-associated immune reconstitution has
CD4 < 50 cells/μL: within 2 weeks of starting TB treatment Weight (kg) Dose in ml Dose in mg Dose in ml Dose in mg Dose in ml Dose in mg (cells/µL) occurred:
CD4 ≥ 50 cells/μL: within 8 weeks after starting TB treatment ≥ 2.5 - < 3 0.5 mL BD 5 mg BD 1 mL BD 10 mg BD 1.5 mL BD 15 mg BD At month 12 on ART. • HIV-positive infants < 12 months should remain on CPT
Repeat 6 monthly if
Confirmed DR-TB at non-neurological site: ≥ 3 - < 4 0.8 mL BD 8 mg BD 1.5 mL BD 15 mg BD 2 mL BD 20 mg BD VL ≥ 1000 or until • 1 – 5 years: If CD4 percentage ≥ 25%
Start ART 2 weeks after TB treatment, once symptoms ≥ 4 - < 5 1 mL BD 10 mg BD 2 mL BD 20 mg BD 3 mL BD 30 mg BD client meets criteria (If previous PJP, stop at 5 years old if meets ≥ 5 years category)
improved and TB treatment tolerated • ≥ 5 years: If CD4 count ≥ 200
Signs and symptoms of meningitis (headache, Investigate for meningitis before starting ART • Dosing is based on the birth weight of the child. It is not necessary to change the dose before 28 days of age if for ex- to stop CPT
ample the weight decreases in the first week or two of life
confusion, fever, neck stiffness or coma) TBM (DS or DR): 4 - 8 weeks after starting TB treatment • Caregivers administering ARV medication to the child must be supplied with a syringe (2 mL or 5 mL) for each of the 3 Viral Load (VL) VL Response
CM: 4 - 6 weeks after starting antifungal treatment ARVs and shown how to prepare and administer the prescribed dose. If required, bottles and syringes should be colour (copies/mL) ≥ 1000 Do thorough assessment of the cause of an elevated VL: consider
Serum CrAg-positive with no symptoms or 2 weeks after starting fluconazole coded with stickers and a sticker of the relevant colour used to mark the correct dose on the syringe. Month 6, 12 and adherence problems, intercurrent infections, incorrect ART dose,
signs of meningitis # See protocol in the 2019 ART Clinical Guidelines for baseline testing and follow up for neonates < 4 weeks of age; Consult with a then 12-monthly if drug interactions and resistance. Implement interventions, including
VL suppressed
clinician experienced in paediatric ARV prescribing or the HIV hotline (0800 212 506), for neonates with birth weight < 2.5 kg or
Other acute illnesses e.g. Pneumocystis Defer ART for 1 - 2 weeks after commencing gestational age < 35 weeks, as well as infants ≥ 28 days of age but < 42 weeks corrected gestational age or weight < 3 kg adherence support. Repeat VL in 3 months
jirovecii pneumonia or bacterial pneumonia treatment for the infection ≥ 4 weeks of age, and ≥ 42 weeks gestational age If VL still ≥ 1000 and child on NNRTI-based regimen: Consider
Clinical symptoms or signs of liver disease Do ALT and bilirubin. Investigate and manage possible causes and ≥ 3 kg, but < 20 kg ABC + 3TC + LPV/r switching to second-line if virological failure confirmed, i.e. VL ≥
1000 on 2 consecutive occasions and adherence issues addressed
before starting ART ≥ 20 kg to < 35 kg or < 10 years of age ABC + 3TC + DTG If VL still ≥ 1000 and child is on PI- or InSTI (DTG)-based regimen:
SOCIAL CONSIDERATIONS ≥ 35 kg and ≥ 10 years of age Transition to adult and adolescent regimens Do resistance testing if virological failure confirmed, i.e. VL ≥ 1000
The following points are important to maximise adherence: on at least 3 occasions over the course of 2 years, or VL ≥ 1000
• One named, responsible primary caregiver able to administer ART to the child with signs of immunological or clinical failure (i.e. declining CD4
• Disclosure to another adult living in the same house able to supervise the child’s ART when primary caregiver is unavailable SWITCHING TO DTG IN CHILDREN WHO ARE ON FIRST-LINE PAEDIATRIC REGIMENS and/or opportunistic infections)
*Clients already on ART should NOT have their treatment interrupted upon diagnosis of the above conditions Before switching to DTG, discuss risks and benefits with caregiver and only switch if caregiver chooses to switch 50 – Do thorough assessment of the cause of an elevated VL. Consider
999
adherence problems, intercurrent infections, incorrect ART dose,
To switch, client must:
Ѱ
BASELINE CLINICAL EVALUATION • Weigh ≥ 20 kg , and drug interactions and resistance. Implement interventions, including
adherence support. Repeat VL in 3 months. If VL 50 - 999 again, re-
• VL < 50 (in the last 6 months) or peat in 6 months. For VL < 50 or ≥ 1000 follow table
TEST AND PURPOSE INTERPRETATION/ACTION • VL 50 – 999 in the last 6 months and on repeat VL after 3 months VL is ≤ 999 copies/mL < 50 Continue routine VL monitoring and routine adherence support.
Recognise the client with respiratory, Identify danger signs as classified in the IMCI Chart Current regimen New regimen Client is doing well
neurological or abdominal danger signs booklet. Refer if needed ABC + 3TC + LPV/r
Height, weight, head circumference (< 2 Use the Road to Health Booklet (RTHB) as tool ABC + 3TC + EFV ABC + 3TC + DTG DO THE FOLLOWING TESTS IF THE CLIENT IS ON THE DRUG THAT MAY
years), and measure MUAC ѰIf child is ≥ 35 kg and ≥ 10 years: refer to adolescent and adult poster for changing ABC to TDF CAUSE THE ADVERSE EVENT
Nutritional assessment to monitor growth, develop-
mental stage and determine correct dosing of ART SECOND- AND THIRD-LINE REGIMENS WITH CONFIRMED VIROLOGICAL FAILURE DRUG TEST FREQUENCY ACTION/INTERPRETATION
Screen for symptoms of meningitis Identify symptoms of headache, confusion or visual All children with confirmed virological failure should be discussed with an expert AZT FBC + At months 3 and 6, Hb ≥ 8 g/dL: Continue AZT
Hb < 8 g/dL or neutrophil count
thereafter if
differential
To diagnose and treat clients with cryptococcal and disturbances. Other symptoms may include fever, neck NNRTI-BASED REGIMEN PI-BASED REGIMEN FOR > 2 INSTI-BASED REGIMEN WCC clinically indicated persistently < 1000 cells/µL: Use
¥
¥
other forms of meningitis and reduce associated stiffness or coma. Refer the client for a lumbar puncture. YEARS FOR > 2 YEARS alternative – consult with expert
morbidity and mortality Defer ART if meningitis is confirmed Regimen (ABC or AZT) + 3TC + (EFV (ABC or AZT) + 3TC + (LPV/r (ABC or AZT) + 3TC + PI-based Cholesterol + At month 3, if To monitor PI-related metabolic
Screen for TB Suspect TB in clients with the following symptoms: cough- or NVP) or ATV/r) DTG regimen Triglycerides above acceptable side-effects. If TG > 10, refer. If TC
To identify TB/HIV co-infection and eligibility for ing, night sweats, fever, unexplained weight loss, then Resistance Resistance test not required Resistance test required. Resistance test required. (LPV/r, ATV/r, (TG) range, do fasting elevated, obtain expert advice.
tuberculosis preventive therapy (TPT) confirm or exclude TB. Do GeneXpert in clients with Testing PI resistance present or genotype InSTI resistance present? DRV/r) cholesterol and TG
a positive TB symptom screen unsuccessful?
WHO clinical staging See eligibility for CPT under CD4 count section in baseline No Yes No Yes TB treatment ALT If signs/symptoms If ALT is abnormal, refer to specialist or
of hepatitis (e.g.
phone the HIV hotline (0800 212 506)
or NVP or EFV
To determine immune status, priority of initiating laboratory evaluation, below Weight < 20 kg ≥ 20 kg < 20 kg ≥ 20 kg All All children on DTG will be nausea, vomiting,
ART and need for cotrimoxazole preventive therapy ≥ 20 kg
(CPT) New (AZT or ABC) 2 NRTIs + DTG Continue 2 NRTIs + DTG Refer to 2 NRTIs + DTG Refer to jaundice)
Screen for depression in older children and Be aware of and monitor for potential drug regimen + 3TC + In consultation current In consultation third- In consultation third-line NVP ALT If rash develops If ALT is abnormal, refer to specialist or
phone the HIV hotline (0800 212 506)
epilepsy in all ages interactions and neuropsychiatric side effects of LPV/r with an expert regimen with an expert line with an expert com-
To exclude drug-drug and drug-disease interactions efavirenz and dolutegravir ensure at least and ensure at least com- ensure at least mittee
#
Neurodevelopmental screen Refer the child to the next level of care if child has not one active address one active mittee one active NRTI CHILDREN WITH CONCOMITANT TUBERCULOSIS
#
#
To identify neurocognitive or developmental delays achieved the age-appropriate developmental NRTI adher- NRTI Children taking ART and TB treatment together will have to tolerate a large amount of
milestone. Screening tool is available in RTHB ence If NRTI activity medication. Intensify adherence support. Remember to add pyridoxine (vitamin B6) to TB
If NRTI activity If NRTI activity cannot be treatment
BASELINE LABORATORY EVALUATION (> 1 MONTH OLD) cannot be cannot be confirmed: refer DTG-based AND receiving a rifampicin-containing TB regimen: Boosting of DTG required. The
confirmed: confirmed: to third-line regimen dosing frequency of DTG should be increased to 50 mg 12 hourly while on rifampicin-
TEST AND PURPOSE INTERPRETATION/ACTION 2 NRTIs + PI/r 2 NRTIs + PI/r committee containing TB treatment and until two weeks after rifampicin has been stopped
Confirm HIV test result Ensure that the national testing algorithm has been followed EFV-based No dose adjustments or changes in ART regimen needed for DS-TB treatment
regimen
To confirm HIV status for those without AND receiving a rifampicin-containing TB regimen: Additional ritonavir should be add-
documented HIV status ¥ In some cases, for example where LPV/r wasn’t dose adjusted with rifampicin containing TB-treatment, a resistance test may be con- LPV/r- ed or the LPV/r dose increased according to the paediatric dosing chart. TB treatment
Haemoglobin (Hb) Can use AZT if Hb ≥ 8 g/dL sidered sooner. Discuss with an expert; based should be dosed at standard doses. Stop additional ritonavir or increased dose 2 weeks
#
AZT can be used if the client has only been exposed to ABC previously. Discuss with expert if unsure
regimen
To identify anaemia and eligibility for AZT Treat anaemia according to Primary Health Care EML Based on the 2019 ART Clinical Guidelines for the after TB-treatment completed
HIV Nursing Matters | October 2020 | page 27
HIV Nursing Matters | October 2020 | page 26
CD4 cell count Eligibility for CPT: Management of HIV in Adults, Pregnancy, 3TC = lamivudine; ABC = abacavir; ART = antiretroviral therapy; ATV/r = atazanavir and ritonavir; AZT = zidovudine; CM = cryptococcal meningitis; CPT = co-
trimoxazole preventive therapy; CrAg = cryptococcal antigen; DTG = dolutegravir; DRV/r = darunavir and ritonavir; DS = drug-sensitive; DR: drug-resistant;
To determine eligibility for cotrimoxazole · All HIV-positive children ≥ 4 weeks and < 1 year Adolescents, Children, Infants and Neonates EFV = efavirenz; eGFR = estimated glomerular filtration rate; HBV = hepatitis B virus; HBsAg = hepatitis B surface antigen; InSTI = integrase strand transfer
inhibitor; LPR/r = lopinavir and ritonavir; LP = lumbar puncture; MUAC = Middle upper arm circumference; NRTI = nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibi-
This publication was supported under funding provided by the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria through the National Department of Health of
preventive therapy (CPT) · HIV-positive child 1 - 5 years with WHO stage 2, 3 or 4, or CD4 ≤ 25% South Africa and the NDoH Pharmacovigilance Centre for Public Health Programmes. Its contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily tor; NNRTI = non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor; NVP = nevirapine; PI = protease inhibitor; OI = opportunistic infection; PJP = Pneumocystis
· HIV-positive child > 5 years with WHO stage 2, 3 or 4, or CD4 ≤ 200 represent the official views of the Global Fund or the National Department of Health of South Africa jirovecii pneumonia; TB = tuberculosis; TBM = tuberculosis meningitis; TDF = tenofovir; TLD = tenofovir + lamivudine + dolutegravir; TEE = tenofovir +
emtricitabine + efavirenz; TC = total cholesterol; TG = triglycerides; WCC = white cell count; VL = viral load