Page 309 - HIVMED_v21_i1.indb
P. 309
Page 3 of 8 Original Research
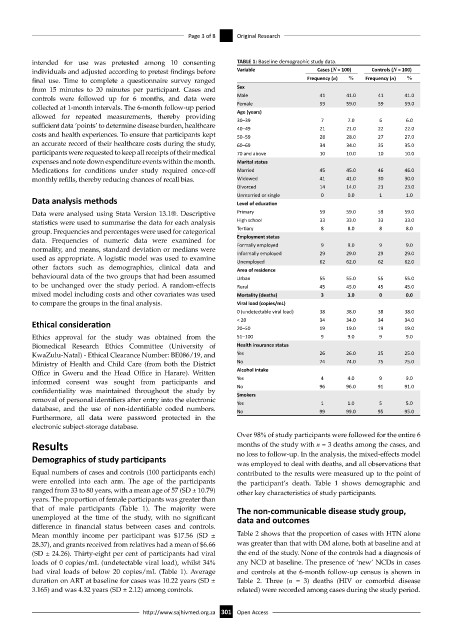
intended for use was pretested among 10 consenting TABLE 1: Baseline demographic study data.
individuals and adjusted according to pretest findings before Variable Cases (N = 100) Controls (N = 100)
final use. Time to complete a questionnaire survey ranged Frequency (n) % Frequency (n) %
from 15 minutes to 20 minutes per participant. Cases and Sex
controls were followed up for 6 months, and data were Male 41 41.0 41 41.0
collected at 1-month intervals. The 6-month follow-up period Female 59 59.0 59 59.0
Age (years)
allowed for repeated measurements, thereby providing 30–39 7 7.0 6 6.0
sufficient data ‘points’ to determine disease burden, healthcare 40–49 21 21.0 22 22.0
costs and health experiences. To ensure that participants kept 50–59 28 28.0 27 27.0
an accurate record of their healthcare costs during the study, 60–69 34 34.0 35 35.0
participants were requested to keep all receipts of their medical 70 and above 10 10.0 10 10.0
expenses and note down expenditure events within the month. Marital status
Medications for conditions under study required once-off Married 45 45.0 46 46.0
monthly refills, thereby reducing chances of recall bias. Widowed 41 41.0 30 30.0
Divorced 14 14.0 23 23.0
Unmarried or single 0 0.0 1 1.0
Data analysis methods Level of education
Data were analysed using Stata Version 13.1®. Descriptive Primary 59 59.0 59 59.0
statistics were used to summarise the data for each analysis High school 33 33.0 33 33.0
group. Frequencies and percentages were used for categorical Tertiary 8 8.0 8 8.0
data. Frequencies of numeric data were examined for Employment status
9
9.0
9.0
9
normality, and means, standard deviation or medians were Formally employed 29 29.0 29 29.0
Informally employed
used as appropriate. A logistic model was used to examine Unemployed 62 62.0 62 62.0
other factors such as demographics, clinical data and Area of residence
behavioural data of the two groups that had been assumed Urban 55 55.0 55 55.0
to be unchanged over the study period. A random-effects Rural 45 45.0 45 45.0
mixed model including costs and other covariates was used Mortality (deaths) 3 3.0 0 0.0
to compare the groups in the final analysis. Viral load (copies/mL)
0 (undetectable viral load) 38 38.0 38 38.0
Ethical consideration < 20 34 34.0 34 34.0
19.0
20–50
19
19.0
19
Ethics approval for the study was obtained from the 51–100 9 9.0 9 9.0
Biomedical Research Ethics Committee (University of Health insurance status
KwaZulu-Natal) - Ethical Clearance Number: BE086/19, and Yes 26 26.0 25 25.0
Ministry of Health and Child Care (from both the District No 74 74.0 75 75.0
Office in Gweru and the Head Office in Harare). Written Alcohol intake
informed consent was sought from participants and Yes 4 4.0 9 9.0
confidentiality was maintained throughout the study by No 96 96.0 91 91.0
removal of personal identifiers after entry into the electronic Smokers 1 1.0 5 5.0
Yes
database, and the use of non-identifiable coded numbers. No 99 99.0 95 95.0
Furthermore, all data were password protected in the
electronic subject-storage database.
Over 98% of study participants were followed for the entire 6
Results months of the study with n = 3 deaths among the cases, and
Demographics of study participants no loss to follow-up. In the analysis, the mixed-effects model
was employed to deal with deaths, and all observations that
Equal numbers of cases and controls (100 participants each) contributed to the results were measured up to the point of
were enrolled into each arm. The age of the participants the participant’s death. Table 1 shows demographic and
ranged from 33 to 80 years, with a mean age of 57 (SD ± 10.79) other key characteristics of study participants.
years. The proportion of female participants was greater than
that of male participants (Table 1). The majority were The non-communicable disease study group,
unemployed at the time of the study, with no significant data and outcomes
difference in financial status between cases and controls.
Mean monthly income per participant was $17.56 (SD ± Table 2 shows that the proportion of cases with HTN alone
28.37), and grants received from relatives had a mean of $6.66 was greater than that with DM alone, both at baseline and at
(SD ± 24.26). Thirty-eight per cent of participants had viral the end of the study. None of the controls had a diagnosis of
loads of 0 copies/mL (undetectable viral load), whilst 34% any NCD at baseline. The presence of ‘new’ NCDs in cases
had viral loads of below 20 copies/mL (Table 1). Average and controls at the 6-month follow-up census is shown in
duration on ART at baseline for cases was 10.22 years (SD ± Table 2. Three (n = 3) deaths (HIV or comorbid disease
3.165) and was 4.32 years (SD ± 2.12) among controls. related) were recorded among cases during the study period.
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 301 Open Access