Page 311 - HIVMED_v21_i1.indb
P. 311
Page 5 of 8 Original Research
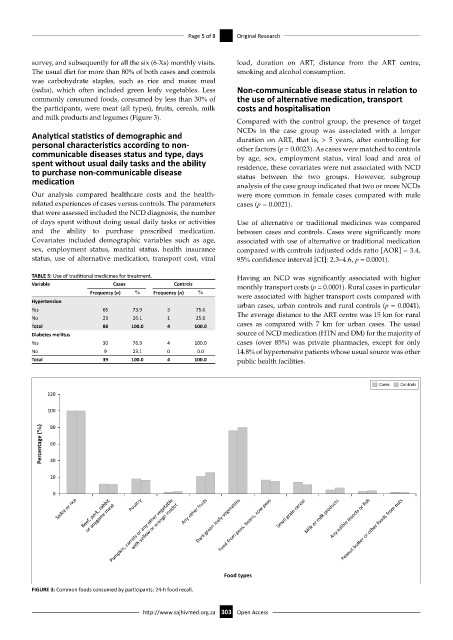
survey, and subsequently for all the six (6-Xs) monthly visits. load, duration on ART, distance from the ART centre,
The usual diet for more than 80% of both cases and controls smoking and alcohol consumption.
was carbohydrate staples, such as rice and maize meal
(sadza), which often included green leafy vegetables. Less Non-communicable disease status in relation to
commonly consumed foods, consumed by less than 30% of the use of alternative medication, transport
the participants, were meat (all types), fruits, cereals, milk costs and hospitalisation
and milk products and legumes (Figure 3).
Compared with the control group, the presence of target
NCDs in the case group was associated with a longer
Analytical statistics of demographic and duration on ART, that is, > 5 years, after controlling for
personal characteristics according to non- other factors (p = 0.0023). As cases were matched to controls
communicable diseases status and type, days by age, sex, employment status, viral load and area of
spent without usual daily tasks and the ability residence, these covariates were not associated with NCD
to purchase non-communicable disease status between the two groups. However, subgroup
medication
analysis of the case group indicated that two or more NCDs
Our analysis compared healthcare costs and the health- were more common in female cases compared with male
related experiences of cases versus controls. The parameters cases (p = 0.0021).
that were assessed included the NCD diagnosis, the number
of days spent without doing usual daily tasks or activities Use of alternative or traditional medicines was compared
and the ability to purchase prescribed medication. between cases and controls. Cases were significantly more
Covariates included demographic variables such as age, associated with use of alternative or traditional medication
sex, employment status, marital status, health insurance compared with controls (adjusted odds ratio [AOR] = 3.4,
status, use of alternative medication, transport cost, viral 95% confidence interval [CI]: 2.3–4.6, p = 0.0001).
TABLE 5: Use of traditional medicines for treatment. Having an NCD was significantly associated with higher
Variable Cases Controls monthly transport costs (p = 0.0001). Rural cases in particular
Frequency (n) % Frequency (n) % were associated with higher transport costs compared with
Hypertension urban cases, urban controls and rural controls (p = 0.0041).
Yes 65 73.9 3 75.0
No 23 26.1 1 25.0 The average distance to the ART centre was 15 km for rural
Total 88 100.0 4 100.0 cases as compared with 7 km for urban cases. The usual
Diabetes mellitus source of NCD medication (HTN and DM) for the majority of
Yes 30 76.9 4 100.0 cases (over 85%) was private pharmacies, except for only
No 9 23.1 0 0.0 14.8% of hypertensive patients whose usual source was other
Total 39 100.0 4 100.0 public health facilities.
Cases Controls
120
100
80
Percentage (%) 60
40
20
0
Dark green leafy vegetables
Peanut buer or other foods from nuts
Poultry
Sadza or rice Beef, pork, rabbit Pumpkin, carrots or any other vegetable Any other fruits Food from peas, beans, cow peas Small grain cereal Milk or milk products Any edible insects or fish
with yellow or orange insidet
or anygame meat
Food types
FIGURE 3: Common foods consumed by participants: 24-h food recall.
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 303 Open Access