Page 368 - HIVMED_v21_i1.indb
P. 368
Page 6 of 8 Original Research
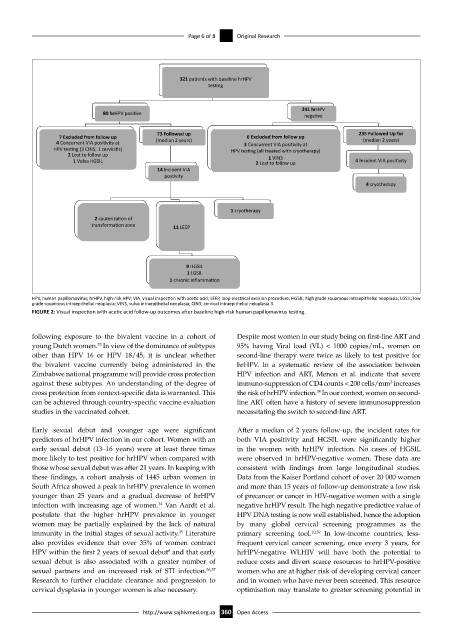
321 pa ents with baseline hrHPV
tes ng
241 hrHPV
80 hrHPV posi ve nega ve
73 Followed up 235 Followed Up for
7 Excluded from follow up 6 Excluded from follow up
4 Concurrent VIA posi vity at (median 2 years) 3 Concurrent VIA posi vity at (median 2 years)
HPV tes ng (3 CINS, 1 cervici s) HPV tes ng (all treated with cryotherapy)
2 Lost to follow up
1 VIN3
1 Vulva HGSIL 2 Lost to follow up 4 Incident VIA posi vity
14 Incident VIA
pos vity
4 cryotherapy
1 cryotherapy
2 cauteriza on of
transforma on zone 11 LEEP
9 HGSIL
1 LGSIL
1 chronic inflamma on
HPV, human papillomavirus; hrHPV, high-risk HPV; VIA, visual inspection with acetic acid; LEEP, loop electrical excision procedure; HGSIL, high grade squamous intraepithelial neoplasia; LGSIL, low
grade squamous intraepithelial neoplasia; VIN3, vulva intraepithelial neoplasia; CIN3, cervical intraepithelial neioplasia 3.
FIGURE 2: Visual inspection with acetic acid follow-up outcomes after baseline high-risk human papillomavirus testing.
following exposure to the bivalent vaccine in a cohort of Despite most women in our study being on first-line ART and
young Dutch women. In view of the dominance of subtypes 95% having Viral load (VL) < 1000 copies/mL, women on
33
other than HPV 16 or HPV 18/45, it is unclear whether second-line therapy were twice as likely to test positive for
the bivalent vaccine currently being administered in the hrHPV. In a systematic review of the association between
Zimbabwe national programme will provide cross protection HPV infection and ART, Menon et al. indicate that severe
3
against these subtypes. An understanding of the degree of immuno-suppression of CD4 counts < 200 cells/mm increases
cross protection from context-specific data is warranted. This the risk of hrHPV infection. In our context, women on second-
38
can be achieved through country-specific vaccine evaluation line ART often have a history of severe immunosuppression
studies in the vaccinated cohort. necessitating the switch to second-line ART.
Early sexual debut and younger age were significant After a median of 2 years follow-up, the incident rates for
predictors of hrHPV infection in our cohort. Women with an both VIA positivity and HGSIL were significantly higher
early sexual debut (13–16 years) were at least three times in the women with hrHPV infection. No cases of HGSIL
more likely to test positive for hrHPV when compared with were observed in hrHPV-negative women. These data are
those whose sexual debut was after 21 years. In keeping with consistent with findings from large longitudinal studies.
these findings, a cohort analysis of 1445 urban women in Data from the Kaiser Portland cohort of over 20 000 women
South Africa showed a peak in hrHPV prevalence in women and more than 15 years of follow-up demonstrate a low risk
younger than 25 years and a gradual decrease of hrHPV of precancer or cancer in HIV-negative women with a single
infection with increasing age of women. Van Aardt et al. negative hrHPV result. The high negative predictive value of
34
postulate that the higher hrHPV prevalence in younger HPV DNA testing is now well established, hence the adoption
women may be partially explained by the lack of natural by many global cervical screening programmes as the
immunity in the initial stages of sexual activity. Literature primary screening tool. 10,39 In low-income countries, less-
35
also provides evidence that over 35% of women contract frequent cervical cancer screening, once every 3 years, for
HPV within the first 2 years of sexual debut and that early hrHPV-negative WLHIV will have both the potential to
8
sexual debut is also associated with a greater number of reduce costs and divert scarce resources to hrHPV-positive
sexual partners and an increased risk of STI infection. 36,37 women who are at higher risk of developing cervical cancer
Research to further elucidate clearance and progression to and in women who have never been screened. This resource
cervical dysplasia in younger women is also necessary. optimisation may translate to greater screening potential in
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 360 Open Access