Page 351 - HIVMED_v21_i1.indb
P. 351
Page 5 of 7 Original Research
TABLE 3: Pregnant women living with human immunodeficiency virus assessed for antiretroviral therapy eligibility and initiated on treatment at 13 healthcare
facilities in Soweto, 2005–2015.
Indicator 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015
n % n % n % n % n % n % n % n % n % n % n %
Newly diagnosed HIV-positive 8721 - 8872 - 8850 - 8774 - 8130 - 6243 - 5062 - 4536 - 4121 - 3575 - 2659 -
Known PWLHIV not on ART - - - - - - - - - - 295 - 213 - 112 - 199 - 277 - 128 -
CD4 counts done† 4453 51.1 8767 98.8 8912 100.7 8775 100.0 8163 100.4 6741 103.1 5525 104.7 4811 103.5 4299 99.5 3694 95.9 - -
CD4 < 200 719 16.2 1489 17.0 1272 14.3 1511 17.2 1353 16.6 973 14.4 906 16.4 740 15.4 - - - - - -
CD4 ≤ 350 - - - - - - - - - - 2513 37.3 2209 40.0 1795 37.3 - - - - - -
Initiated on ART‡ - - 96 6.5 300 23.6 495 32.8 505 37.3 1836 73.1 1949 88.2 1528 85.1 2830 65.5 3185 82.7 3187 114.3
HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; PWLHIV, pregnant women living with HIV; ART, antiretroviral therapy.
†, Represents aggregate data of the total number of CD4 counts’ first tests done.
‡, Aggregate data on the total number initiated on ART and the denominator is the total number eligible for ART, based on the eligibility criteria at the time.
-, Indicates that data for the indicator were not collected during that period.
progress has been made in the prevention of new HIV
ART-eligible Ini ated on ART MTCT rate
infections among women of reproductive age, an important
8
ART-eligible/ini ated on ART 4000 6 5 4 3 2 MTCT rate (%) reproductive age globally in the period 2009–2015, and this is
5000
aspect of PMTCT. South Africa is reported to have had the
2
Op on B+
Op on B
Op on A
4500
7
highest number of new HIV infections among women of
3500
3000
reflected in the high HIV prevalence among pregnant women,
2500
a consistent finding throughout the review period in our
2000
The finding of a consistently high HIV prevalence is
study.
2,29
1500
1000
500
HIV prevalence surveys that have been conducted in South
0
2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 1 0 similar to figures reported in the national antenatal sentinel
Africa since 1990. Pregnant women in South Africa as a
29
whole still present at an advanced gestational age for their
Year first antenatal visit, with just over 50% reported to have
ART, antiretroviral therapy; MTCT, mother-to-child transmission of HIV. presented before 20 weeks in 2014, albeit this being an increase
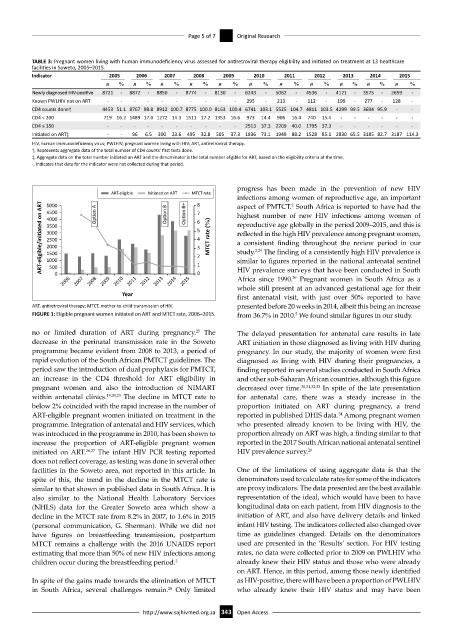
FIGURE 1: Eligible pregnant women initiated on ART and MTCT rate, 2006–2015. from 36.7% in 2010. We found similar figures in our study.
5
no or limited duration of ART during pregnancy. The The delayed presentation for antenatal care results in late
25
decrease in the perinatal transmission rate in the Soweto ART initiation in those diagnosed as living with HIV during
programme became evident from 2008 to 2013, a period of pregnancy. In our study, the majority of women were first
rapid evolution of the South African PMTCT guidelines. The diagnosed as living with HIV during their pregnancies, a
period saw the introduction of dual prophylaxis for PMTCT, finding reported in several studies conducted in South Africa
an increase in the CD4 threshold for ART eligibility in and other sub-Saharan African countries, although this figure
pregnant women and also the introduction of NIMART decreased over time. 30,31,32,33 In spite of the late presentation
within antenatal clinics. 19,20,23 The decline in MTCT rate to for antenatal care, there was a steady increase in the
below 2% coincided with the rapid increase in the number of proportion initiated on ART during pregnancy, a trend
ART-eligible pregnant women initiated on treatment in the reported in published DHIS data. Among pregnant women
34
programme. Integration of antenatal and HIV services, which who presented already known to be living with HIV, the
was introduced in the programme in 2010, has been shown to proportion already on ART was high, a finding similar to that
increase the proportion of ART-eligible pregnant women reported in the 2017 South African national antenatal sentinel
initiated on ART. 26,27 The infant HIV PCR testing reported HIV prevalence survey. 29
does not reflect coverage, as testing was done in several other
facilities in the Soweto area, not reported in this article. In One of the limitations of using aggregate data is that the
spite of this, the trend in the decline in the MTCT rate is denominators used to calculate rates for some of the indicators
similar to that shown in published data in South Africa. It is are proxy indicators. The data presented are the best available
also similar to the National Health Laboratory Services representation of the ideal, which would have been to have
(NHLS) data for the Greater Soweto area which show a longitudinal data on each patient, from HIV diagnosis to the
decline in the MTCT rate from 8.2% in 2007, to 1.6% in 2015 initiation of ART, and also have delivery details and linked
(personal communication, G. Sherman). While we did not infant HIV testing. The indicators collected also changed over
have figures on breastfeeding transmission, postpartum time as guidelines changed. Details on the denominators
MTCT remains a challenge with the 2016 UNAIDS report used are presented in the ‘Results’ section. For HIV testing
estimating that more than 50% of new HIV infections among rates, no data were collected prior to 2009 on PWLHIV who
children occur during the breastfeeding period. 2 already knew their HIV status and those who were already
on ART. Hence, in this period, among those newly identified
In spite of the gains made towards the elimination of MTCT as HIV-positive, there will have been a proportion of PWLHIV
in South Africa, several challenges remain. Only limited who already knew their HIV status and may have been
28
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 343 Open Access