Page 356 - HIVMED_v21_i1.indb
P. 356
Page 3 of 4 Scientific Letter
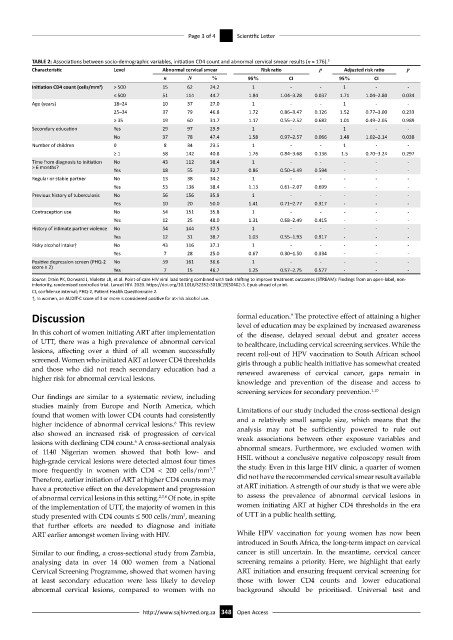
TABLE 2: Associations between socio-demographic variables, initiation CD4 count and abnormal cervical smear results (n = 176). 5
Characteristic Level Abnormal cervical smear Risk ratio p Adjusted risk ratio p
n N % 95% CI 95% CI
Initiation CD4 count (cells/mm ) 3 > 500 15 62 24.2 1 - - 1 - -
≤ 500 51 114 44.7 1.84 1.04–3.28 0.037 1.71 1.04–2.80 0.034
Age (years) 18–24 10 37 27.0 1 - - 1 - -
25–34 37 79 46.8 1.72 0.86–3.47 0.126 1.52 0.77–3.00 0.233
≥ 35 19 60 31.7 1.17 0.55–2.52 0.682 1.01 0.49–2.05 0.989
Secondary education Yes 29 97 29.9 1 - - 1 - -
No 37 78 47.4 1.58 0.97–2.57 0.066 1.48 1.02–2.14 0.038
Number of children 0 8 34 23.5 1 - - 1 - -
≥ 1 58 142 40.8 1.76 0.84–3.68 0.136 1.5 0.70–3.24 0.297
Time from diagnosis to initiation No 43 112 38.4 1 - - - - -
> 6 months?
Yes 18 55 32.7 0.86 0.50–1.49 0.594 - - -
Regular or stable partner No 13 38 34.2 1 - - - - -
Yes 53 138 38.4 1.13 0.61–2.07 0.699 - - -
Previous history of tuberculosis No 56 156 35.9 1 - - - - -
Yes 10 20 50.0 1.41 0.71–2.77 0.317 - - -
Contraception use No 54 151 35.8 1 - - - - -
Yes 12 25 48.0 1.31 0.68–2.49 0.415 - - -
History of intimate partner violence No 54 144 37.5 1 - - - - -
Yes 12 31 38.7 1.03 0.55–1.93 0.917 - - -
Risky alcohol intake† No 43 116 37.1 1 - - - - -
Yes 7 28 25.0 0.67 0.30–1.50 0.334 - - -
Positive depression screen (PHQ-2 No 59 161 36.6 1 - - - - -
score ≥ 2)
Yes 7 15 46.7 1.25 0.57–2.75 0.577 - - -
Source: Drain PK, Dorward J, Violette LR, et al. Point-of-care HIV viral load testing combined with task shifting to improve treatment outcomes (STREAM): Findings from an open-label, non-
inferiority, randomised controlled trial. Lancet HIV. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2352-3018(19)30402-3. Epub ahead of print.
CI, confidence interval; PHQ-2, Patient Health Questionnaire 2.
†, In women, an AUDIT-C score of 3 or more is considered positive for at-risk alcohol use.
Discussion formal education. The protective effect of attaining a higher
9
level of education may be explained by increased awareness
In this cohort of women initiating ART after implementation of the disease, delayed sexual debut and greater access
of UTT, there was a high prevalence of abnormal cervical to healthcare, including cervical screening services. While the
lesions, affecting over a third of all women successfully recent roll-out of HPV vaccination to South African school
screened. Women who initiated ART at lower CD4 thresholds girls through a public health initiative has somewhat created
and those who did not reach secondary education had a renewed awareness of cervical cancer, gaps remain in
higher risk for abnormal cervical lesions.
knowledge and prevention of the disease and access to
screening services for secondary prevention. 1,10
Our findings are similar to a systematic review, including
studies mainly from Europe and North America, which Limitations of our study included the cross-sectional design
found that women with lower CD4 counts had consistently and a relatively small sample size, which means that the
higher incidence of abnormal cervical lesions. This review analysis may not be sufficiently powered to rule out
6
also showed an increased risk of progression of cervical
lesions with declining CD4 count. A cross-sectional analysis weak associations between other exposure variables and
6
of 1140 Nigerian women showed that both low- and abnormal smears. Furthermore, we excluded women with
high-grade cervical lesions were detected almost four times HSIL without a conclusive negative colposcopy result from
more frequently in women with CD4 < 200 cells/mm . the study. Even in this large HIV clinic, a quarter of women
3 7
Therefore, earlier initiation of ART at higher CD4 counts may did not have the recommended cervical smear result available
have a protective effect on the development and progression at ART initiation. A strength of our study is that we were able
of abnormal cervical lesions in this setting. 2,3,8 Of note, in spite to assess the prevalence of abnormal cervical lesions in
of the implementation of UTT, the majority of women in this women initiating ART at higher CD4 thresholds in the era
3
study presented with CD4 counts ≤ 500 cells/mm , meaning of UTT in a public health setting.
that further efforts are needed to diagnose and initiate
ART earlier amongst women living with HIV. While HPV vaccination for young women has now been
introduced in South Africa, the long-term impact on cervical
Similar to our finding, a cross-sectional study from Zambia, cancer is still uncertain. In the meantime, cervical cancer
analysing data in over 14 000 women from a National screening remains a priority. Here, we highlight that early
Cervical Screening Programme, showed that women having ART initiation and ensuring frequent cervical screening for
at least secondary education were less likely to develop those with lower CD4 counts and lower educational
abnormal cervical lesions, compared to women with no background should be prioritised. Universal test and
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 348 Open Access