Page 361 - HIVMED_v21_i1.indb
P. 361
Page 4 of 5 Original Research
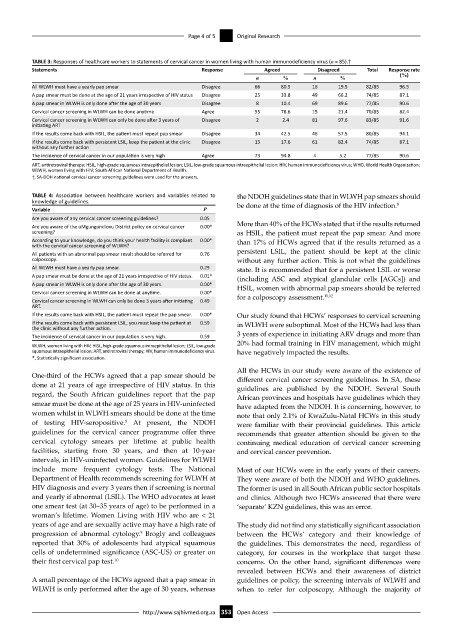
TABLE 3: Responses of healthcare workers to statements of cervical cancer in women living with human immunodeficiency virus (n = 85).†
Statements Response Agreed Disagreed Total Response rate
n % n % (%)
All WLWH must have a yearly pap smear Disagree 66 80.5 16 19.5 82/85 96.5
A pap smear must be done at the age of 21 years irrespective of HIV status Disagree 25 33.8 49 66.2 74/85 87.1
A pap smear in WLWH is only done after the age of 30 years Disagree 8 10.4 69 89.6 77/85 90.6
Cervical cancer screening in WLWH can be done anytime Agree 55 78.6 15 21.4 70/85 82.4
Cervical cancer screening in WLWH can only be done after 3 years of Disagree 2 2.4 81 97.6 83/85 91.6
initiating ART
If the results come back with HSIL, the patient must repeat pap smear Disagree 34 42.5 46 57.5 80/85 94.1
If the results come back with persistent LSIL, keep the patient at the clinic Disagree 13 17.6 61 82.4 74/85 87.1
without any further action
The incidence of cervical cancer in our population is very high Agree 73 94.8 4 5.2 77/85 90.6
ART, antiretroviral therapy; HSIL, high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion; LSIL, low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; WHO, World Health Organization;
WLWH, women living with HIV; South African National Department of Health.
†, SA-DOH national cervical cancer screening guidelines were used for the answers.
TABLE 4: Association between healthcare workers and variables related to the NDOH guidelines state that in WLWH pap smears should
knowledge of guidelines. be done at the time of diagnosis of the HIV infection.
8
Variable P
Are you aware of any cervical cancer screening guidelines? 0.05
Are you aware of the uMgungundlovu District policy on cervical cancer 0.00* More than 40% of the HCWs stated that if the results returned
screening? as HSIL, the patient must repeat the pap smear. And more
According to your knowledge, do you think your health facility is compliant 0.00* than 17% of HCWs agreed that if the results returned as a
with the cervical cancer screening of WLWH?
All patients with an abnormal pap smear result should be referred for 0.76 persistent LSIL, the patient should be kept at the clinic
colposcopy. without any further action. This is not what the guidelines
All WLWH must have a yearly pap smear. 0.29 state. It is recommended that for a persistent LSIL or worse
A pap smear must be done at the age of 21 years irrespective of HIV status. 0.01* (including ASC and atypical glandular cells [AGCs]) and
A pap smear in WLWH is only done after the age of 30 years. 0.00* HSIL, women with abnormal pap smears should be referred
Cervical cancer screening in WLWH can be done at anytime. 0.00* 11,12
Cervical cancer screening in WLWH can only be done 3 years after initiating 0.49 for a colposcopy assessment.
ART.
If the results come back with HSIL, the patient must repeat the pap smear. 0.00* Our study found that HCWs’ responses to cervical screening
If the results come back with persistent LSIL, you must keep the patient at 0.59 in WLWH were suboptimal. Most of the HCWs had less than
the clinic without any further action.
The incidence of cervical cancer in our population is very high. 0.59 3 years of experience in initiating ARV drugs and more than
20% had formal training in HIV management, which might
WLWH, women living with HIV; HISL, high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion; LSIL, low-grade
squamous intraepithelial lesion; ART, antiretroviral therapy; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus. have negatively impacted the results.
*, Statistically significant association.
All the HCWs in our study were aware of the existence of
One-third of the HCWs agreed that a pap smear should be different cervical cancer screening guidelines. In SA, these
done at 21 years of age irrespective of HIV status. In this guidelines are published by the NDOH. Several South
regard, the South African guidelines report that the pap African provinces and hospitals have guidelines which they
smear must be done at the age of 25 years in HIV-uninfected have adapted from the NDOH. It is concerning, however, to
women whilst in WLWH smears should be done at the time note that only 2.1% of KwaZulu-Natal HCWs in this study
of testing HIV-seropositive. At present, the NDOH were familiar with their provincial guidelines. This article
8
guidelines for the cervical cancer programme offer three recommends that greater attention should be given to the
cervical cytology smears per lifetime at public health continuing medical education of cervical cancer screening
facilities, starting from 30 years, and then at 10-year and cervical cancer prevention.
intervals, in HIV-uninfected women. Guidelines for WLWH
include more frequent cytology tests. The National Most of our HCWs were in the early years of their careers.
Department of Health recommends screening for WLWH at They were aware of both the NDOH and WHO guidelines.
HIV diagnosis and every 3 years then if screening is normal The former is used in all South African public sector hospitals
and yearly if abnormal (LSIL). The WHO advocates at least and clinics. Although two HCWs answered that there were
one smear test (at 30–35 years of age) to be performed in a ‘separate’ KZN guidelines, this was an error.
woman’s lifetime. Women Living with HIV who are < 21
years of age and are sexually active may have a high rate of The study did not find any statistically significant association
progression of abnormal cytology. Brogly and colleagues between the HCWs’ category and their knowledge of
9
reported that 30% of adolescents had atypical squamous the guidelines. This demonstrates the need, regardless of
cells of undetermined significance (ASC-US) or greater on category, for courses in the workplace that target these
their first cervical pap test. 10 concerns. On the other hand, significant differences were
revealed between HCWs and their awareness of district
A small percentage of the HCWs agreed that a pap smear in guidelines or policy, the screening intervals of WLWH and
WLWH is only performed after the age of 30 years, whereas when to refer for colposcopy. Although the majority of
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 353 Open Access