Page 326 - HIVMED_v21_i1.indb
P. 326
Page 5 of 8 Original Research
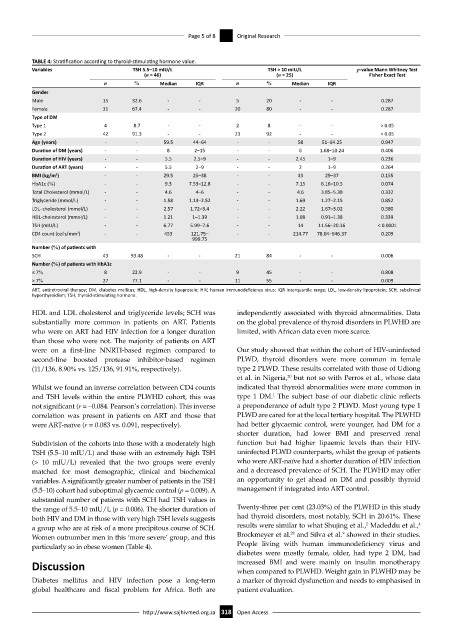
TABLE 4: Stratification according to thyroid-stimulating hormone value.
Variables TSH 5.5–10 mIU/L TSH > 10 mIU/L p-value Mann Whitney Test
(n = 46) (n = 25) Fisher Exact Test
n % Median IQR n % Median IQR
Gender
Male 15 32.6 - - 5 20 - - 0.287
Female 31 67.4 - - 20 80 - - 0.287
Type of DM
Type 1 4 8.7 - - 2 8 - - > 0.05
Type 2 42 91.3 - - 23 92 - - > 0.05
Age (years) - - 59.5 44–64 - - 58 51–64.25 0.947
Duration of DM (years) - - 8 2–15 - - 6 1.68–10.24 0.406
Duration of HIV (years) - - 5.5 2.5–9 - - 2.45 1–9 0.236
Duration of ART (years) - - 5.5 2–9 - - 2 1–9 0.264
BMI (kg/m ) 2 - - 29.5 25–38 - - 33 29–37 0.155
HbA1c (%) - - 9.3 7.53–12.8 - - 7.15 6.16–10.5 0.074
Total Cholesterol (mmol/L) - - 4.6 4–6 - - 4.6 3.85–5.38 0.332
Triglyceride (mmol/L) - - 1.58 1.14–2.52 - - 1.69 1.27–2.15 0.852
LDL- cholesterol (mmol/L) - - 2.57 1.72–3.4 - - 2.22 1.67–3.02 0.580
HDL-cholesterol (mmol/L) - - 1.21 1–1.39 - - 1.08 0.91–1.38 0.339
TSH (mIU/L) - - 6.77 5.99–7.6 - - 14 11.56–20.36 < 0.0001
CD4 count (cells/mm ) 3 - - 453 121.75– - - 214.77 78.04–646.37 0.209
999.75
Number (%) of patients with
SCH 43 93.48 - - 21 84 - - 0.006
Number (%) of patients with HbA1c
≤ 7% 8 22.9 - - 9 45 - - 0.808
> 7% 27 77.1 - - 11 55 - - 0.009
ART, antiretroviral therapy; DM, diabetes mellitus; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; IQR interquartile range; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; SCH, subclinical
hyperthyroidism; TSH, thyroid-stimulating hormone.
HDL and LDL cholesterol and triglyceride levels; SCH was independently associated with thyroid abnormalities. Data
substantially more common in patients on ART. Patients on the global prevalence of thyroid disorders in PLWHD are
who were on ART had HIV infection for a longer duration limited, with African data even more scarce.
than those who were not. The majority of patients on ART
were on a first-line NNRTI-based regimen compared to Our study showed that within the cohort of HIV-uninfected
second-line boosted protease inhibitor-based regimen PLWD, thyroid disorders were more common in female
(11/136, 8.90% vs. 125/136, 91.91%, respectively). type 2 PLWD. These results correlated with those of Udiong
et al. in Nigeria, but not so with Perros et al., whose data
20
Whilst we found an inverse correlation between CD4 counts indicated that thyroid abnormalities were more common in
1
and TSH levels within the entire PLWHD cohort, this was type 1 DM. The subject base of our diabetic clinic reflects
not significant (r = ‒0.084. Pearson’s correlation). This inverse a preponderance of adult type 2 PLWD. Most young type 1
correlation was present in patients on ART and those that PLWD are cared for at the local tertiary hospital. The PLWHD
were ART-naïve (r = 0.083 vs. 0.091, respectively). had better glycaemic control, were younger, had DM for a
shorter duration, had lower BMI and preserved renal
Subdivision of the cohorts into those with a moderately high function but had higher lipaemic levels than their HIV-
TSH (5.5–10 mIU/L) and those with an extremely high TSH uninfected PLWD counterparts, whilst the group of patients
(> 10 mIU/L) revealed that the two groups were evenly who were ART-naïve had a shorter duration of HIV infection
matched for most demographic, clinical and biochemical and a decreased prevalence of SCH. The PLWHD may offer
variables. A significantly greater number of patients in the TSH an opportunity to get ahead on DM and possibly thyroid
(5.5–10) cohort had suboptimal glycaemic control (p = 0.009). A management if integrated into ART control.
substantial number of patients with SCH had TSH values in
the range of 5.5–10 mIU/L (p = 0.006). The shorter duration of Twenty-three per cent (23.03%) of the PLWHD in this study
both HIV and DM in those with very high TSH levels suggests had thyroid disorders, most notably, SCH in 20.61%. These
4
2
a group who are at risk of a more precipitous course of SCH. results were similar to what Shujing et al., Madeddu et al.,
28
9
Women outnumber men in this ‘more severe’ group, and this Brockmeyer et al. and Silva et al. showed in their studies.
particularly so in obese women (Table 4). People living with human immunodeficiency virus and
diabetes were mostly female, older, had type 2 DM, had
Discussion increased BMI and were mainly on insulin monotherapy
when compared to PLWHD. Weight gain in PLWHD may be
Diabetes mellitus and HIV infection pose a long-term a marker of thyroid dysfunction and needs to emphasised in
global healthcare and fiscal problem for Africa. Both are patient evaluation.
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 318 Open Access