Page 125 - HIVMED_v21_i1.indb
P. 125
Page 34 of 34 Guideline
Appendix 4: Psychosocial and mental health interventions
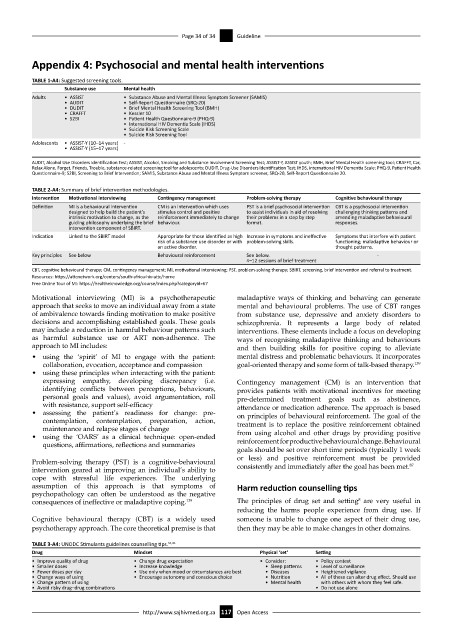
TABLE 1-A4: Suggested screening tools.
Substance use Mental health
Adults • ASSIST • Substance Abuse and Mental Illness Symptom Screener (SAMIS)
• AUDIT • Self-Report Questionnaire (SRQ-20)
• DUDIT • Brief Mental Health Screening Tool (BMH)
• CRAFFT • Kessler 10
• S2BI • Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9)
• International HIV Dementia Scale (IHDS)
• Suicide Risk Screening Scale
• Suicide Risk Screening Tool
Adolescents • ASSIST-Y (10–14 years) -
• ASSIST-Y (15–17 years)
AUDIT, Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test; ASSIST, Alcohol, Smoking and Substance Involvement Screening Test; ASSIST-Y, ASSIST youth; BMH, Brief Mental Health screening tool; CRAFFT, Car,
Relax Alone, Forget, Friends, Trouble, substance-related screening tool for adolescents; DUDIT, Drug-Use Disorders Identification Test; IHDS, international HIV Dementia Scale; PHQ-9, Patient Health
Questionnaire-9; S2BI, Screening to Brief Intervention; SAMIS, Substance Abuse and Mental Illness Symptom screener, SRQ-20, Self-Report Questionnaire 20.
TABLE 2-A4: Summary of brief intervention methodologies.
Intervention Motivational interviewing Contingency management Problem-solving therapy Cognitive behavioural therapy
Definition MI is a behavioural intervention CM is an intervention which uses PST is a brief psychosocial intervention CBT is a psychosocial intervention
designed to help build the patient’s stimulus control and positive to assist individuals in aid of resolving challenging thinking patterns and
intrinsic motivation to change, as the reinforcement immediately to change their problems in a step by step amending maladaptive behavioural
guiding philosophy underlying the brief behaviour. format. responses.
intervention component of SBIRT.
Indication Linked to the SBIRT model Appropriate for those identified as high Increase in symptoms and ineffective Symptoms that interfere with patient
risk of a substance use disorder or with problem-solving skills. functioning; maladaptive behaviour or
an active disorder. thought patterns.
Key principles See below Behavioural reinforcement See below. -
4–12 sessions of brief treatment
CBT, cognitive behavioural therapy; CM, contingency management; MI, motivational interviewing; PST, problem-solving therapy; SBIRT, screening, brief intervention and referral to treatment.
Resources: https://attcnetwork.org/centers/south-africa-hiv-attc/home
Free Online Tour of MI: https://healtheknowledge.org/course/index.php?categoryid=67
Motivational interviewing (MI) is a psychotherapeutic maladaptive ways of thinking and behaving can generate
approach that seeks to move an individual away from a state mental and behavioural problems. The use of CBT ranges
of ambivalence towards finding motivation to make positive from substance use, depressive and anxiety disorders to
decisions and accomplishing established goals. These goals schizophrenia. It represents a large body of related
may include a reduction in harmful behaviour patterns such interventions. These elements include a focus on developing
as harmful substance use or ART non-adherence. The ways of recognising maladaptive thinking and behaviours
approach to MI includes: and then building skills for positive coping to alleviate
• using the ‘spirit’ of MI to engage with the patient: mental distress and problematic behaviours. It incorporates
collaboration, evocation, acceptance and compassion goal-oriented therapy and some form of talk-based therapy.
139
• using these principles when interacting with the patient:
expressing empathy, developing discrepancy (i.e. Contingency management (CM) is an intervention that
identifying conflicts between perceptions, behaviours, provides patients with motivational incentives for meeting
personal goals and values), avoid argumentation, roll pre-determined treatment goals such as abstinence,
with resistance, support self-efficacy attendance or medication adherence. The approach is based
• assessing the patient’s readiness for change: pre- on principles of behavioural reinforcement. The goal of the
contemplation, contemplation, preparation, action, treatment is to replace the positive reinforcement obtained
maintenance and relapse stages of change
• using the ‘OARS’ as a clinical technique: open-ended from using alcohol and other drugs by providing positive
questions, affirmations, reflections and summaries reinforcement for productive behavioural change. Behavioural
goals should be set over short time periods (typically 1 week
or less) and positive reinforcement must be provided
Problem-solving therapy (PST) is a cognitive-behavioural 87
intervention geared at improving an individual’s ability to consistently and immediately after the goal has been met.
cope with stressful life experiences. The underlying
assumption of this approach is that symptoms of Harm reduction counselling tips
psychopathology can often be understood as the negative
8
consequences of ineffective or maladaptive coping. 139 The principles of drug set and setting are very useful in
reducing the harms people experience from drug use. If
Cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) is a widely used someone is unable to change one aspect of their drug use,
psychotherapy approach. The core theoretical premise is that then they may be able to make changes in other domains.
TABLE 3-A4: UNODC Stimulants guidelines counselling tips. 51,91
Drug Mindset Physical ‘set’ Setting
• Improve quality of drug • Change drug expectation • Consider: • Policy context
• Smaller doses • Increase knowledge • Sleep patterns • Level of surveillance
• Fewer doses per day • Use only when mood or circumstances are best • Diseases • Heightened vigilance
• Change ways of using • Encourage autonomy and conscious choice • Nutrition • All of these can alter drug effect. Should use
• Change pattern of using • Mental health with others with whom they feel safe.
• Avoid risky drug–drug combinations • Do not use alone
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 117 Open Access