Page 347 - SAHCS HIVMed Journal Vol 20 No 1 2019
P. 347
Page 4 of 8 Original Research
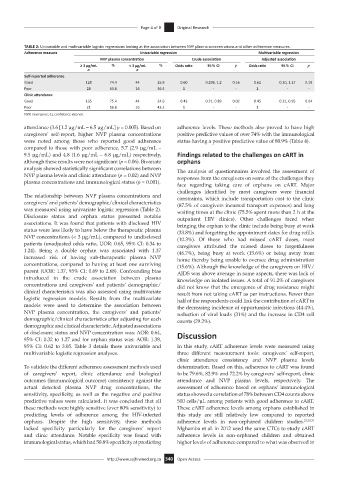
TABLE 2: Univariable and multivariable logistic regressions looking at the association between NVP plasma concentrations and other adherence measures.
Adherence measure Univariable regression Multivariable regression
NVP plasma concentration Crude association Adjusted association
≥ 3 µg/mL % < 3 µg/mL % Odds ratio 95% CI p Odds ratio 95% CI p
n n
Self-reported adherence
Good 128 74.4 44 25.6 0.60 0.298, 1.2 0.16 0.62 0.30, 1.27 0.19
Poor 28 63.6 16 36.4 1 - - 1 - -
Clinic attendance
Good 135 75.4 44 24.6 0.43 0.21, 0.89 0.02 0.45 0.21, 0.95 0.04
Poor 21 56.8 16 43.2 1 - - 1 - -
NVP, nevirapine; CI, confidence interval.
attendance (3.6 [1.2 µg/mL – 6.5 µg/mL] p = 0.005). Based on adherence levels. These methods also proved to have high
caregivers’ self-report, higher NVP plasma concentrations positive predictive values of over 74% with the immunological
were noted among those who reported good adherence status having a positive predictive value of 80.9% (Table 4).
compared to those with poor adherence, 5.7 (2.9 µg/mL –
9.5 µg/mL) and 4.8 (1.6 µg/mL – 6.8 µg/mL) respectively, Findings related to the challenges on cART in
although these results were not significant (p = 0.06). Bivariate orphans
analysis showed statistically significant correlations between The analysis of questionnaires involved the assessment of
NVP plasma levels and clinic attendance (p = 0.02) and NVP responses from the caregivers on some of the challenges they
plasma concentrations and immunological status (p = 0.001).
face regarding taking care of orphans on cART. Major
challenges identified by most caregivers were financial
The relationship between NVP plasma concentrations and constraints, which include transportation cost to the clinic
caregivers’ and patients’ demographic/clinical characteristics (87.5% of caregivers incurred transport expenses) and long
was measured using univariate logistic regression (Table 2). waiting times at the clinic (75.5% spent more than 2 h at the
Disclosure status and orphan status presented notable outpatient HIV clinics). Other challenges faced when
associations. It was found that patients with disclosed HIV bringing the orphan to the clinic include being busy at work
status were less likely to have below the therapeutic plasma (33.8%) and forgetting the appointment dates for drug refills
NVP concentrations (< 3 µg/mL), compared to undisclosed (10.3%). Of those who had missed cART doses, most
patients (unadjusted odds ratio, UOR: 0.65, 95% CI: 0.34 to caregivers attributed the missed doses to forgetfulness
1.24). Being a double orphan was associated with 1.37 (46.7%), being busy at work (15.6%) or being away from
increased risk of having sub-therapeutic plasma NVP home thereby being unable to oversee drug administration
concentrations, compared to having at least one surviving (15.6%). Although the knowledge of the caregivers on HIV/
parent (UOR: 1.37, 95% CI: 0.69 to 2.68). Confounding bias AIDS was above average in some aspects, there was lack of
introduced in the crude association between plasma knowledge on isolated issues. A total of 91.2% of caregivers
concentrations and caregivers’ and patients’ demographic/ did not know that the emergence of drug resistance might
clinical characteristics was also assessed using multivariate result from not taking cART as per instructions. Fewer than
logistic regression models. Results from the multivariate half of the respondents could link the contribution of cART to
models were used to determine the association between the decreasing incidence of opportunistic infections (44.4%),
NVP plasma concentration, the caregivers’ and patients’ reduction of viral loads (31%) and the increase in CD4 cell
demographic/clinical characteristics after adjusting for each counts (29.2%).
demographic and clinical characteristic. Adjusted associations
of disclosure status and NVP concentration was: AOR: 0.64, Discussion
95% CI: 0.32 to 1.27 and for orphan status was: AOR: 1.38,
95% CI: 0.62 to 3.05. Table 3 details these univariable and In this study, cART adherence levels were measured using
multivariable logistic regression analyses. three different measurement tools: caregivers’ self-report,
clinic attendance consistency and NVP plasma levels
To validate the different adherence assessment methods used determination. Based on this, adherence to cART was found
of caregivers’ report, clinic attendance and biological to be 79.6%, 82.9% and 72.2% by caregivers’ self-report, clinic
outcomes (Immunological outcome) consistency against the attendance and NVP plasma levels, respectively. The
actual detected plasma NVP drug concentrations, the assessment of adherence based on orphans’ immunological
sensitivity, specificity, as well as the negative and positive status showed a correlation of 78% between CD4 counts above
predictive values were calculated. It was concluded that all 500 cells/µL among patients with good adherence to cART.
these methods were highly sensitive (over 80% sensitivity) to These cART adherence levels among orphans established in
predicting levels of adherence among the HIV-infected this study are still relatively low compared to reported
orphans. Despite the high sensitivity, these methods adherence levels in non-orphaned children studies. 23,30,31
lacked specificity particularly for the caregivers’ report Mghamba et al. in 2012 used the same CTCs to study cART
and clinic attendance. Notable specificity was found with adherence levels in non-orphaned children and obtained
immunological status, which had 50.8% specificity at predicting higher levels of adherence compared to what was observed in
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 340 Open Access