Page 215 - SAHCS HIVMed Journal Vol 20 No 1 2019
P. 215
Page 3 of 7 Original Research
Results
A total of 23 HIV-infected patients with cavernous sinus disease
were recruited for analysis. The mean age of the patients was 38
years (Range 22–62 years), and 52% (12/23) were female. Eight Third nerve palsy 0 Fourth nerve palsy
patients were newly diagnosed with HIV infection. The
remainder of the patients were aware of their HIV infection for 3 0
1–6 years. The mean CD4+ count was 390 cells/µL ± 227 (s.d.),
implying mild-to-moderate immunosuppression. However, 3
two patients had severe immunosuppression with CD4+ counts 0
of 24 cells/µL and 70 cells/µL, respectively. The viral load was 9
not readily obtained owing to inadequate records. Four patients
had undetectable viral loads. In three patients, viral loads of
54900 copies/mL, 850 copies/mL and 4992 copies/mL were 1
obtained. Viral loads for the remaining patients were unknown. Sixth nerve palsy
Acute onset of headache was common, but visual symptoms
of diplopia and blurred vision occurred in only 30% of the
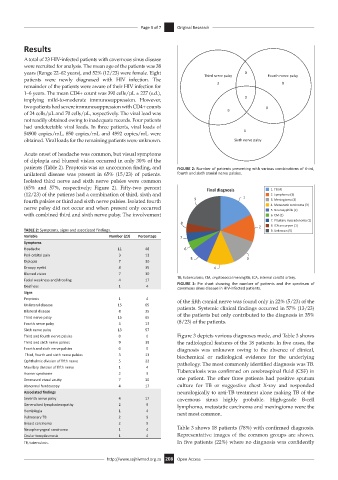
patients (Table 2). Proptosis was an uncommon finding, and FIGURE 2: Number of patients presenting with various combinations of third,
unilateral disease was present in 65% (15/23) of patients. fourth and sixth cranial nerve palsies.
Isolated third nerve and sixth nerve palsies were common
(65% and 57%, respectively; Figure 2). Fifty-two percent Final diagnosis 1. TB (4)
(12/23) of the patients had a combination of third, sixth and 1 2. Lymphoma (3)
fourth palsies or third and sixth nerve palsies. Isolated fourth 9 3. Meningioma (3)
nerve palsy did not occur and when present only occurred 4. Metasta c carcinoma (3)
5. Neurosyphilis (2)
with combined third and sixth nerve palsy. The involvement 6. CM (1)
7. Pituitary macradenoma (1)
8
2 8. ICA aneurysm (1)
TABLE 2: Symptoms, signs and associated findings. 9. Unknown (5)
Variable Number (23) Percentage 7
Symptoms
Headache 11 48 6
Peri-orbital pain 3 13
Diplopia 7 30 5 3
Droopy eyelid 8 35 4
Blurred vision 7 30
Facial weakness and/drooling 4 17 TB, tuberculosis; CM, cryptococcal meningitis; ICA, internal carotid artery.
Deafness 1 4 FIGURE 3: Pie chart showing the number of patients and the spectrum of
cavernous sinus disease in HIV-infected patients.
Signs
Proptosis 1 4 of the fifth cranial nerve was found only in 22% (5/23) of the
Unilateral disease 15 65 patients. Systemic clinical findings occurred in 57% (13/23)
Bilateral disease 8 35
Third nerve palsy 15 65 of the patients but only contributed to the diagnosis in 35%
Fourth nerve palsy 3 13 (8/23) of the patients.
Sixth nerve palsy 13 57
Third and fourth nerve palsies 0 0 Figure 3 depicts various diagnoses made, and Table 3 shows
Third and sixth nerve palsies 9 39 the radiological features of the 18 patients. In five cases, the
Fourth and sixth nerve palsies 0 0 diagnosis was unknown owing to the absence of clinical,
Third, fourth and sixth nerve palsies 3 13 biochemical or radiological evidence for the underlying
Ophthalmic division of fifth nerve 5 22 pathology. The most commonly identified diagnosis was TB.
Maxillary division of fifth nerve 1 4
Horner syndrome 2 9 Tuberculosis was confirmed on cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in
Decreased visual acuity 7 30 one patient. The other three patients had positive sputum
Abnormal fundoscopy 4 17 culture for TB or suggestive chest X-ray and responded
Associated findings neurologically to anti-TB treatment alone making TB of the
Seventh nerve palsy 4 17 cavernous sinus highly probable. High-grade B-cell
Generalised lymphadenopathy 2 9 lymphoma, metastatic carcinoma and meningioma were the
Hemiplegia 1 4 next most common.
Pulmonary TB 2 9
Breast carcinoma 2 9
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma 1 4 Table 3 shows 18 patients (78%) with confirmed diagnosis.
Ocular toxoplasmosis 1 4 Representative images of the common groups are shown.
TB, tuberculosis. In five patients (22%) where no diagnosis was confidently
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 208 Open Access