Page 407 - HIVMED_v21_i1.indb
P. 407
Page 7 of 13 Original Research
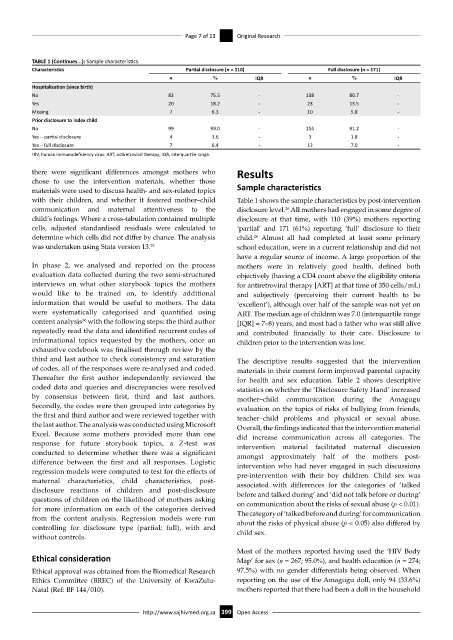
TABLE 1 (Continues...): Sample characteristics.
Characteristics Partial disclosure (n = 110) Full disclosure (n = 171)
n % IQR n % IQR
Hospitalisation (since birth)
No 83 75.5 - 138 80.7 -
Yes 20 18.2 - 23 13.5 -
Missing 7 6.3 - 10 5.8 -
Prior disclosure to index child
No 99 99.0 - 156 91.2 -
Yes – partial disclosure 4 3.6 - 3 1.8 -
Yes – full disclosure 7 6.4 - 12 7.0 -
HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; ART, antiretroviral therapy; IQR, interquartile range.
there were significant differences amongst mothers who Results
chose to use the intervention materials, whether those
materials were used to discuss health- and sex-related topics Sample characteristics
with their children, and whether it fostered mother–child Table 1 shows the sample characteristics by post-intervention
communication and maternal attentiveness to the disclosure level. All mothers had engaged in some degree of
26
child’s feelings. Where a cross-tabulation contained multiple disclosure at that time, with 110 (39%) mothers reporting
cells, adjusted standardised residuals were calculated to ‘partial’ and 171 (61%) reporting ‘full’ disclosure to their
determine which cells did not differ by chance. The analysis child. Almost all had completed at least some primary
26
was undertaken using Stata version 13. 35 school education, were in a current relationship and did not
have a regular source of income. A large proportion of the
In phase 2, we analysed and reported on the process mothers were in relatively good health, defined both
evaluation data collected during the two semi-structured objectively (having a CD4 count above the eligibility criteria
interviews on what other storybook topics the mothers for antiretroviral therapy [ART] at that time of 350 cells/mL)
would like to be trained on, to identify additional and subjectively (perceiving their current health to be
information that would be useful to mothers. The data ‘excellent’), although over half of the sample was not yet on
were systematically categorised and quantified using ART. The median age of children was 7.0 (interquartile range
content analysis with the following steps: the third author [IQR] = 7–8) years, and most had a father who was still alive
36
repeatedly read the data and identified recurrent codes of and contributed financially to their care. Disclosure to
informational topics requested by the mothers, once an children prior to the intervention was low.
exhaustive codebook was finalised through review by the
third and last author to check consistency and saturation The descriptive results suggested that the intervention
of codes, all of the responses were re-analysed and coded. materials in their current form improved parental capacity
Thereafter the first author independently reviewed the for health and sex education. Table 2 shows descriptive
coded data and queries and discrepancies were resolved statistics on whether the ‘Disclosure Safety Hand’ increased
by consensus between first, third and last authors. mother–child communication during the Amagugu
Secondly, the codes were then grouped into categories by evaluation on the topics of risks of bullying from friends,
the first and third author and were reviewed together with teacher–child problems and physical or sexual abuse.
the last author. The analysis was conducted using Microsoft Overall, the findings indicated that the intervention material
Excel. Because some mothers provided more than one did increase communication across all categories. The
response for future storybook topics, a Z-test was intervention material facilitated maternal discussion
conducted to determine whether there was a significant amongst approximately half of the mothers post-
difference between the first and all responses. Logistic intervention who had never engaged in such discussions
regression models were computed to test for the effects of pre-intervention with their boy children. Child sex was
maternal characteristics, child characteristics, post- associated with differences for the categories of ‘talked
disclosure reactions of children and post-disclosure before and talked during’ and ‘did not talk before or during’
questions of children on the likelihood of mothers asking on communication about the risks of sexual abuse (p < 0.01).
for more information on each of the categories derived The category of ‘talked before and during’ for communication
from the content analysis. Regression models were run about the risks of physical abuse (p < 0.05) also differed by
controlling for disclosure type (partial; full), with and
without controls. child sex.
Most of the mothers reported having used the ‘HIV Body
Ethical consideration Map’ for sex (n = 267; 95.0%), and health education (n = 274;
Ethical approval was obtained from the Biomedical Research 97.5%) with no gender differentials being observed. When
Ethics Committee (BREC) of the University of KwaZulu- reporting on the use of the Amagugu doll, only 94 (33.6%)
Natal (Ref: BF 144/010). mothers reported that there had been a doll in the household
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 399 Open Access