Page 403 - HIVMED_v21_i1.indb
P. 403
Page 3 of 13 Original Research
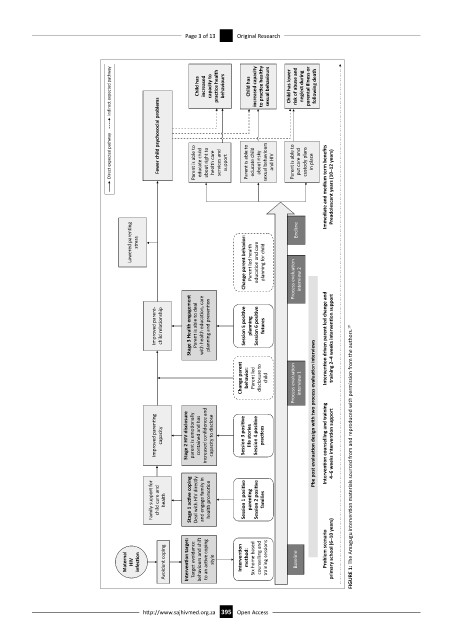
Indirect expected pathway Child has increased capacity to prac ce health behaviours Child has increased capacity to prac ce healthy sexual behaviours Child has lower risk of abuse and neglect during parental illness or following death
Direct expected pathway Fewer child psychosocial problems Parent is able to educate child about right to health care services and support Parent is able to educate child about risky sexual behaviours and HIV Parent is able to put care and custody plans in place Immediate and medium term benefits Preadolescent years (10–12 years)
Lowered paren ng stress Change parent behavior: Parent led health educa on and care planning for child Process evalua on Endline interview 2
Improved parent- child rela onship Stage 3 Health engagement Parent is able to deal with health educa on, care planning and preven on Session 5 posi ve planning Session 6 posi ve futures Interven on driven parent led change and training 2–4 weeks interven on support
Change parent behavior: Parent led disclosure to child Process evalua on interview 1
Improved paren ng capacity Stage 2 HIV disclosure parent is emo onally contained and has increased confidence and capacity to disclose Session 3 posi ve life stories Session 4 posi ve prac ces Pbe post evalua on design with two process evalua on interviews Interven on counselling and training 4–6 weeks interven on support FIGURE 1: The Amagugu intervention materials sourced from and reproduced with permission from the authors. 10
Family support for child care and health Stage 1 ac ve coping Deal with HIV directly and engage family in health promo on Session 1 posi ve paren ng Session 2 posi ve families
Maternal HIV infec on Avoidant coping Interven on target: Target avoidance behaviours and shi to an ac ve coping style Interven on method: Six home based counselling and training sessions Baseline Problem scenario primary school (6–10 years)
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 395 Open Access