Page 398 - HIVMED_v21_i1.indb
P. 398
Page 3 of 5 Original Research
TABLE 1: Characteristics of the cohort of 503 neonates with confirmed human immunodeficiency virus infection.
Variable Pre-birth EID (2013–2015) (n = 150) Post-birth EID (2016–2017) (n = 353) p
n % n %
Gender (female) 101 67.3 217 61.5 0.450
Number of initiations 135 90 333 94.3 0.081
Age at start of ART (days)† 5.00 0.00–16.8 7.00 0.00–15.3 0.598
Baseline CD4 T-lymphocyte counts† 228 141–375 229 0.685–558 0.002
Pre-treatment viral load† 558 000 969–1040 000 124 46.0–3440 0.046
Died (number or %) 7 4.7 9 2.5 0.226
Lost to follow-up (number or %) 72 48 124 35.1 0.0067
Transferred (number or %) 19 12.7 48 13.6 0.779
ART, antiretroviral therapy; EID, early infant diagnosis.
†, Median (interquartile range).
Discussion
% tested % ini ated % Suppressed
90:90:90 In this retrospective analysis of all HIV-infected neonates
99 diagnosed within the first 4 weeks of age and initiated on ART
100 72 72 90 in eThekwini district over 5 years, we found a significant
% of HIV-exposed infants 70 15 14 12 10 38 33 ART with the introduction of routine birth EID; however, viral
90
increase in the percentage of neonates diagnosed and initiating
80
60
suppression at 1 year after ART initiation remained low.
50
40
30
Achieving the WHO 90:90:90 targets for the infant treatment
20
10
0
infants. Because of a lack of evidence, the WHO conditionally
2013 0 2014 0 2015 2 2016 6 2017 10 cascade is vital for improving the outcomes of HIV-infected
recommends the addition of birth testing to existing EID
Years
strategies to identify HIV infection in HIV-exposed infants. In
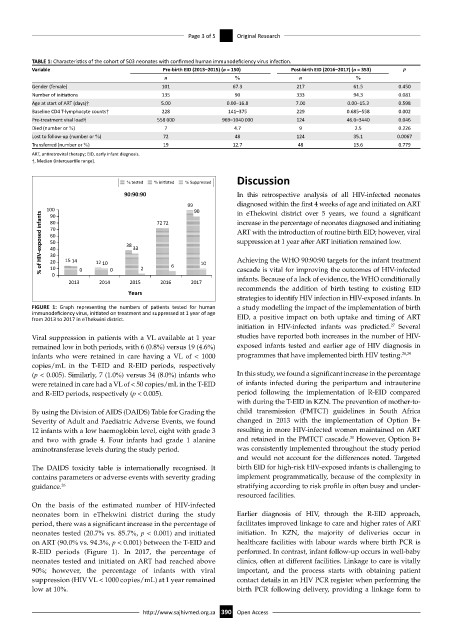
FIGURE 1: Graph representing the numbers of patients tested for human a study modelling the impact of the implementation of birth
immunodeficiency virus, initiated on treatment and suppressed at 1 year of age
from 2013 to 2017 in eThekwini district. EID, a positive impact on both uptake and timing of ART
initiation in HIV-infected infants was predicted. Several
27
Viral suppression in patients with a VL available at 1 year studies have reported both increases in the number of HIV-
remained low in both periods, with 6 (0.8%) versus 19 (4.6%) exposed infants tested and earlier age of HIV diagnosis in
infants who were retained in care having a VL of < 1000 programmes that have implemented birth HIV testing. 28,29
copies/mL in the T-EID and R-EID periods, respectively
(p < 0.005). Similarly, 7 (1.0%) versus 34 (8.0%) infants who In this study, we found a significant increase in the percentage
were retained in care had a VL of < 50 copies/mL in the T-EID of infants infected during the peripartum and intrauterine
and R-EID periods, respectively (p < 0.005). period following the implementation of R-EID compared
with during the T-EID in KZN. The prevention of mother-to-
By using the Division of AIDS (DAIDS) Table for Grading the child transmission (PMTCT) guidelines in South Africa
Severity of Adult and Paediatric Adverse Events, we found changed in 2013 with the implementation of Option B+
12 infants with a low haemoglobin level, eight with grade 3 resulting in more HIV-infected women maintained on ART
30
and two with grade 4. Four infants had grade 1 alanine and retained in the PMTCT cascade. However, Option B+
aminotransferase levels during the study period. was consistently implemented throughout the study period
and would not account for the differences noted. Targeted
The DAIDS toxicity table is internationally recognised. It birth EID for high-risk HIV-exposed infants is challenging to
contains parameters or adverse events with severity grading implement programmatically, because of the complexity in
guidance. 26 stratifying according to risk profile in often busy and under-
resourced facilities.
On the basis of the estimated number of HIV-infected
neonates born in eThekwini district during the study Earlier diagnosis of HIV, through the R-EID approach,
period, there was a significant increase in the percentage of facilitates improved linkage to care and higher rates of ART
neonates tested (20.7% vs. 85.7%, p < 0.001) and initiated initiation. In KZN, the majority of deliveries occur in
on ART (90.0% vs. 94.3%, p < 0.001) between the T-EID and healthcare facilities with labour wards where birth PCR is
R-EID periods (Figure 1). In 2017, the percentage of performed. In contrast, infant follow-up occurs in well-baby
neonates tested and initiated on ART had reached above clinics, often at different facilities. Linkage to care is vitally
90%; however, the percentage of infants with viral important, and the process starts with obtaining patient
suppression (HIV VL < 1000 copies/mL) at 1 year remained contact details in an HIV PCR register when performing the
low at 10%. birth PCR following delivery, providing a linkage form to
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 390 Open Access