Page 374 - HIVMED_v21_i1.indb
P. 374
Page 4 of 5 Original Research
mostly patients with anniversary months in December or
VL due Timely VL done
800 January when patients return to family homes outside of the
city during the holidays.
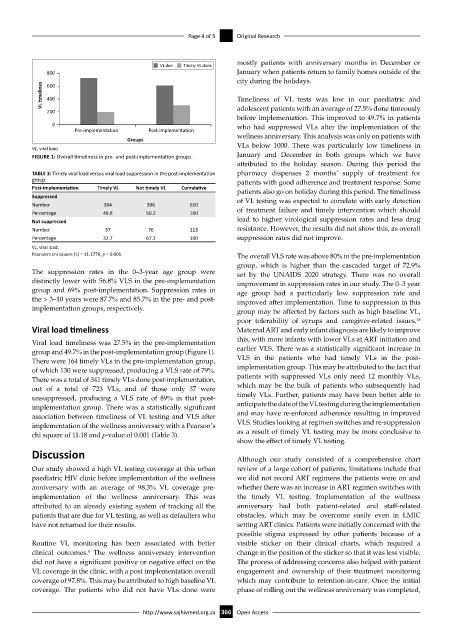
VL melines 400 Timeliness of VL tests was low in our paediatric and
600
200 adolescent patients with an average of 27.5% done timeously
before implementation. This improved to 49.7% in patients
0 who had suppressed VLs after the implementation of the
Pre-implementation Post-implementation
Groups wellness anniversary. This analysis was only on patients with
VL, viral load. VLs below 1000. There was particularly low timeliness in
FIGURE 1: Overall timeliness in pre- and post-implementation groups. January and December in both groups which we have
attributed to the holiday season. During this period the
TABLE 3: Timely viral load versus viral load suppression in the post-implementation pharmacy dispenses 2 months’ supply of treatment for
group. patients with good adherence and treatment response. Some
Post-implementation Timely VL Not timely VL Cumulative patients also go on holiday during this period. The timeliness
Suppressed of VL testing was expected to correlate with early detection
Number 304 306 610
Percentage 49.8 50.2 100 of treatment failure and timely intervention which should
Not suppressed lead to higher virological suppression rates and less drug
Number 37 76 113 resistance. However, the results did not show this, as overall
Percentage 32.7 67.3 100 suppression rates did not improve.
VL, viral load.
Pearson’s chi square (1) = 11.1776; p = 0.001. The overall VLS rate was above 80% in the pre-implementation
group, which is higher than the cascaded target of 72.9%
The suppression rates in the 0–3-year age group were set by the UNAIDS 2020 strategy. There was no overall
distinctly lower with 56.8% VLS in the pre-implementation improvement in suppression rates in our study. The 0–3 year
group and 69% post-implementation. Suppression rates in age group had a particularly low suppression rate and
the > 3–10 years were 87.7% and 85.7% in the pre- and post- improved after implementation. Time to suppression in this
implementation groups, respectively. group may be affected by factors such as high baseline VL,
poor tolerability of syrups and caregiver-related issues.
18
Viral load timeliness Maternal ART and early infant diagnosis are likely to improve
this, with more infants with lower VLs at ART initiation and
Viral load timeliness was 27.5% in the pre-implementation
group and 49.7% in the post-implementation group (Figure 1). earlier VLS. There was a statistically significant increase in
There were 164 timely VLs in the pre-implementation group, VLS in the patients who had timely VLs in the post-
of which 130 were suppressed, producing a VLS rate of 79%. implementation group. This may be attributed to the fact that
There was a total of 341 timely VLs done post-implementation, patients with suppressed VLs only need 12 monthly VLs,
out of a total of 723 VLs, and of those only 37 were which may be the bulk of patients who subsequently had
unsuppressed, producing a VLS rate of 89% in that post- timely VLs. Further, patients may have been better able to
implementation group. There was a statistically significant anticipate the date of the VL testing during the implementation
association between timeliness of VL testing and VLS after and may have re-enforced adherence resulting in improved
implementation of the wellness anniversary with a Pearson’s VLS. Studies looking at regimen switches and re-suppression
chi square of 11.18 and p-value of 0.001 (Table 3). as a result of timely VL testing may be more conclusive to
show the effect of timely VL testing.
Discussion Although our study consisted of a comprehensive chart
Our study showed a high VL testing coverage at this urban review of a large cohort of patients, limitations include that
paediatric HIV clinic before implementation of the wellness we did not record ART regimens the patients were on and
anniversary with an average of 98.3% VL coverage pre- whether there was an increase in ART regimen switches with
implementation of the wellness anniversary. This was the timely VL testing. Implementation of the wellness
attributed to an already existing system of tracking all the anniversary had both patient-related and staff-related
patients that are due for VL testing, as well as defaulters who obstacles, which may be overcome easily even in LMIC
have not returned for their results. setting ART clinics. Patients were initially concerned with the
possible stigma expressed by other patients because of a
Routine VL monitoring has been associated with better visible sticker on their clinical charts, which required a
4
clinical outcomes. The wellness anniversary intervention change in the position of the sticker so that it was less visible.
did not have a significant positive or negative effect on the The process of addressing concerns also helped with patient
VL coverage in the clinic, with a post implementation overall engagement and ownership of their treatment monitoring
coverage of 97.8%. This may be attributed to high baseline VL which may contribute to retention-in-care. Once the initial
coverage. The patients who did not have VLs done were phase of rolling out the wellness anniversary was completed,
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 366 Open Access