Page 244 - HIVMED_v21_i1.indb
P. 244
Page 6 of 9 Review Article
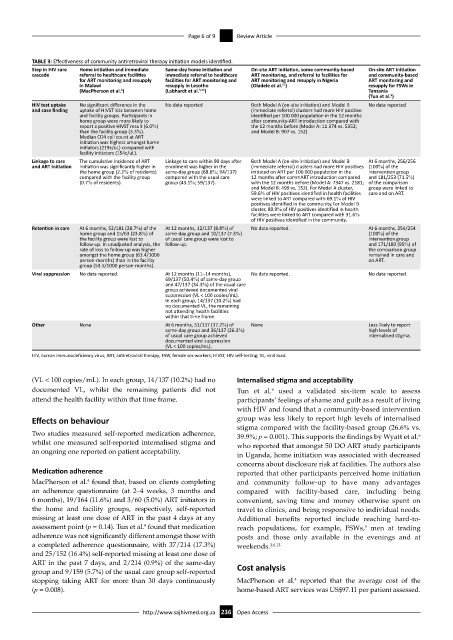
TABLE 3: Effectiveness of community antiretroviral therapy initiation models identified.
Step in HIV care Home initiation and immediate Same-day home initiation and On-site ART initiation, some community-based On-site ART initiation
cascade referral to healthcare facilities immediate referral to healthcare ART monitoring, and referral to facilities for and community-based
for ART monitoring and resupply facilities for ART monitoring and ART monitoring and resupply in Nigeria ART monitoring and
11
in Malawi resupply in Lesotho (Oladele et al. ) resupply for FSWs in
(MacPherson et al. ) 4 (Labhardt et al. 3,12 ) Tanzania
9
(Tun et al. )
HIV test uptake No significant difference in the No data reported Both Model A (on-site initiation) and Model B No data reported
and case finding uptake of HIVST kits between home (immediate referral) clusters had more HIV positive
and facility groups. Participants in identified per 100 000 population in the 12 months
home group were more likely to after community-ART introduction compared with
report a positive HIVST result (6.0%) the 12 months before (Model A: 11 374 vs. 5352;
than the facility group (3.3%). and Model B: 907 vs. 152)
Median CD4 cell count at ART
initiation was highest amongst home
initiators (219c/uL) compared with
facility initiators (154c/uL).
Linkage to care The cumulative incidence of ART Linkage to care within 90 days after Both Model A (on-site initiation) and Model B At 6 months, 256/256
and ART initiation initiation was significantly higher in enrolment was higher in the (immediate referral) clusters had more HIV positives (100%) of the
the home group (2.2% of residents) same-day group (68.6%; 94/137) initiated on ART per 100 000 population in the intervention group
compared with the facility group compared with the usual care 12 months after commART introduction compared and 181/253 (71.5%)
(0.7% of residents). group (43.1%; 59/137). with the 12 months before (Model A: 7347 vs. 2181; of the comparison
and Model B: 499 vs. 152). For Model A cluster, group were linked to
59.6% of HIV positives identified in health facilities care and on ART.
were linked to ART compared with 69.1% of HIV
positives identified in the community.For Model B
cluster, 80.9% of HIV positives identified in health
facilities were linked to ART compared with 31.6%
of HIV positives identified in the community.
Retention in care At 6 months, 52/181 (28.7%) of the At 12 months, 12/137 (8.8%) of No data reported. At 6 months, 254/254
home group and 15/63 (23.8%) of same-day group and 10/137 (7.3%) (100%) of the
the facility group were lost to of usual care group were lost to intervention group
follow-up. In unadjusted analysis, the follow-up. and 171/180 (95%) of
rate of loss to follow-up was higher the comparison group
amongst the home group (63.4/1000 remained in care and
person-months) than in the facility on ART.
group (53.5/1000 person-months).
Viral suppression No data reported. At 12 months (11–14 months), No data reported. No data reported.
69/137 (50.4%) of same-day group
and 47/137 (34.3%) of the usual care
group achieved documented viral
suppression (VL < 100 copies/mL).
In each group, 14/137 (10.2%) had
no documented VL, the remaining
not attending health facilities
within that time frame.
Other None At 6 months, 51/137 (37.2%) of None Less likely to report
same-day group and 36/137 (26.3%) high levels of
of usual care group achieved internalised stigma.
documented viral suppression
(VL < 100 copies/mL).
HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; ART, antiretroviral therapy; FSW, female sex workers; HIVST, HIV self-testing; VL, viral load.
(VL < 100 copies/mL). In each group, 14/137 (10.2%) had no Internalised stigma and acceptability
documented VL, whilst the remaining patients did not Tun et al. used a validated six-item scale to assess
9
attend the health facility within that time frame. participants’ feelings of shame and guilt as a result of living
with HIV and found that a community-based intervention
Effects on behaviour group was less likely to report high levels of internalised
stigma compared with the facility-based group (26.6% vs.
Two studies measured self-reported medication adherence, 39.9%; p = 0.001). This supports the findings by Wyatt et al.
6
whilst one measured self-reported internalised stigma and who reported that amongst 50 DO ART study participants
an ongoing one reported on patient acceptability. in Uganda, home initiation was associated with decreased
concerns about disclosure risk at facilities. The authors also
Medication adherence reported that other participants perceived home initiation
MacPherson et al. found that, based on clients completing and community follow-up to have many advantages
4
an adherence questionnaire (at 2–4 weeks, 3 months and compared with facility-based care, including being
6 months), 19/164 (11.6%) and 3/60 (5.0%) ART initiators in convenient, saving time and money otherwise spent on
the home and facility groups, respectively, self-reported travel to clinics, and being responsive to individual needs.
missing at least one dose of ART in the past 4 days at any Additional benefits reported include reaching hard-to-
assessment point (p = 0.14). Tun et al. found that medication reach populations, for example, FSWs, men at trading
9
9
adherence was not significantly different amongst those with posts and those only available in the evenings and at
a completed adherence questionnaire, with 37/214 (17.3%) weekends. 3,6,13
and 25/152 (16.4%) self-reported missing at least one dose of
ART in the past 7 days, and 2/214 (0.9%) of the same-day Cost analysis
group and 9/159 (5.7%) of the usual care group self-reported
stopping taking ART for more than 30 days continuously MacPherson et al. reported that the average cost of the
4
(p = 0.008). home-based ART services was US$97.11 per patient assessed.
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 236 Open Access