Page 229 - HIVMED_v21_i1.indb
P. 229
Page 2 of 11 Review Article
3
200 to 350 cells/mm . In addition, all pregnant women and
3
persons with Stage 3 and 4 infection were offered ART. In Records obtained through database search Google
scholar = 89, Ebscohorst = 101, Cochrane 9,
2010, the threshold was raised to CD4 < 350 c/mm for all Iden fica on Embase 23 and PubMed = 71 (n = 293)
3
irrespective of clinical stage. By June 2013, the threshold
4,5
was further increased to CD4 < 500/cells/mm for all children
3
Records remained aer 79
> 5 years and adults irrespective of stage/symptoms. In Total records obtained duplicates removed (n = 214)
6
2015, the WHO and numerous international organisations Screening (n = 293)
removed the CD4 threshold and recommended ART to all
regardless of CD4 cell count and clinical stage. Data from Records excluded on the basis of
7
two highly influential randomised controlled clinical trials, tles and abstracts (n = 187)
the START and TEMPRANO studies, underpinned this Eligibility Ar cles remaining aer tle
decision. Both demonstrated survival advantage to those on and abstract screening (n = 27)
ART irrespective of clinical stage or CD4 count. This led to Ar cles excluded because
8,9
the introduction by all international agencies, including the they focused on drug
WHO, of the policy of ‘universal test and treat (UTT)’. The Inclusion Full texts ar cles included in regimen changes not policy
WHO estimates that if these recommendations are adopted final review (n = 16) implementa ons changes aer
reading manuscripts (n = 11)
globally, 21 million deaths and 28 million new infections
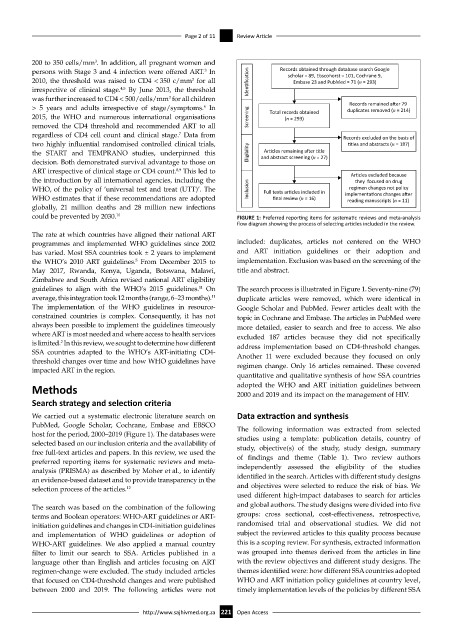
could be prevented by 2030. 10 FIGURE 1: Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analysis
flow diagram showing the process of selecting articles included in the review.
The rate at which countries have aligned their national ART
programmes and implemented WHO guidelines since 2002 included: duplicates, articles not centered on the WHO
has varied. Most SSA countries took ± 2 years to implement and ART initiation guidelines or their adoption and
the WHO’s 2010 ART guidelines. From December 2015 to implementation. Exclusion was based on the screening of the
5
May 2017, Rwanda, Kenya, Uganda, Botswana, Malawi, title and abstract.
Zimbabwe and South Africa revised national ART eligibility
guidelines to align with the WHO’s 2015 guidelines. On The search process is illustrated in Figure 1. Seventy-nine (79)
11
11
average, this integration took 12 months (range, 6–23 months). duplicate articles were removed, which were identical in
The implementation of the WHO guidelines in resource- Google Scholar and PubMed. Fewer articles dealt with the
constrained countries is complex. Consequently, it has not topic in Cochrane and Embase. The articles in PubMed were
always been possible to implement the guidelines timeously more detailed, easier to search and free to access. We also
where ART is most needed and where access to health services excluded 187 articles because they did not specifically
is limited. In this review, we sought to determine how different address implementation based on CD4-threshold changes.
2
SSA countries adapted to the WHO’s ART-initiating CD4- Another 11 were excluded because they focused on only
threshold changes over time and how WHO guidelines have regimen change. Only 16 articles remained. These covered
impacted ART in the region.
quantitative and qualitative synthesis of how SSA countries
Methods adopted the WHO and ART initiation guidelines between
2000 and 2019 and its impact on the management of HIV.
Search strategy and selection criteria
We carried out a systematic electronic literature search on Data extraction and synthesis
PubMed, Google Scholar, Cochrane, Embase and EBSCO The following information was extracted from selected
host for the period, 2000–2019 (Figure 1). The databases were studies using a template: publication details, country of
selected based on our inclusion criteria and the availability of study, objective(s) of the study, study design, summary
free full-text articles and papers. In this review, we used the of findings and theme (Table 1). Two review authors
preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-
analysis (PRISMA) as described by Moher et al., to identify independently assessed the eligibility of the studies
an evidence-based dataset and to provide transparency in the identified in the search. Articles with different study designs
selection process of the articles. 12 and objectives were selected to reduce the risk of bias. We
used different high-impact databases to search for articles
The search was based on the combination of the following and global authors. The study designs were divided into five
terms and Boolean operators: WHO-ART guidelines or ART- groups: cross sectional, cost-effectiveness, retrospective,
initiation guidelines and changes in CD4-initiation guidelines randomised trial and observational studies. We did not
and implementation of WHO guidelines or adoption of subject the reviewed articles to this quality process because
WHO-ART guidelines. We also applied a manual country this is a scoping review. For synthesis, extracted information
filter to limit our search to SSA. Articles published in a was grouped into themes derived from the articles in line
language other than English and articles focusing on ART with the review objectives and different study designs. The
regimen-change were excluded. The study included articles themes identified were: how different SSA countries adopted
that focused on CD4-threshold changes and were published WHO and ART initiation policy guidelines at country level,
between 2000 and 2019. The following articles were not timely implementation levels of the policies by different SSA
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 221 Open Access