Page 224 - HIVMED_v21_i1.indb
P. 224
Page 6 of 9 Original Research
60 Pre-dialysis Post-dialysis a 2000 Pre-dialysis Post-dialysis b
p = 0.715
p = 0.080
p = 0.001
1500
40
Percentage (%) p = 0.263 (Cells/ul) 1000 p = 0.137
20
500 p = 0.236
p = 0.306
0 0
WCC % CD3 cells % CD4 cells % CD8 cells Abs CD3 count Abs CD4 count Abs CD8 count
Lymphocyte subclasses (Cells/ul)
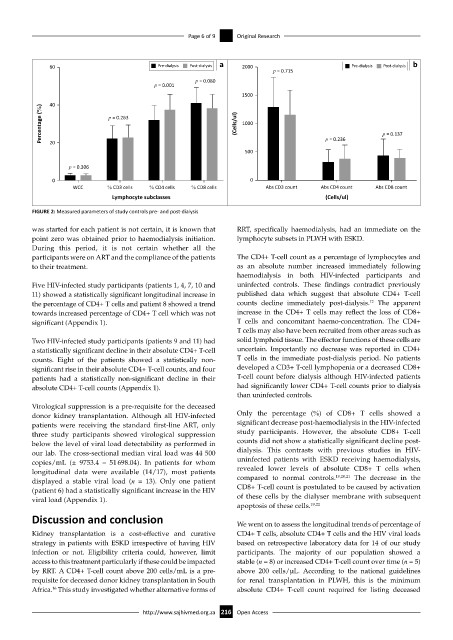
FIGURE 2: Measured parameters of study controls pre- and post-dialysis
was started for each patient is not certain, it is known that RRT, specifically haemodialysis, had an immediate on the
point zero was obtained prior to haemodialysis initiation. lymphocyte subsets in PLWH with ESKD.
During this period, it is not certain whether all the
participants were on ART and the compliance of the patients The CD4+ T-cell count as a percentage of lymphocytes and
to their treatment. as an absolute number increased immediately following
haemodialysis in both HIV-infected participants and
Five HIV-infected study participants (patients 1, 4, 7, 10 and uninfected controls. These findings contradict previously
11) showed a statistically significant longitudinal increase in published data which suggest that absolute CD4+ T-cell
12
the percentage of CD4+ T cells and patient 8 showed a trend counts decline immediately post-dialysis. The apparent
towards increased percentage of CD4+ T cell which was not increase in the CD4+ T cells may reflect the loss of CD8+
significant (Appendix 1). T cells and concomitant haemo-concentration. The CD4+
T cells may also have been recruited from other areas such as
Two HIV-infected study participants (patients 9 and 11) had solid lymphoid tissue. The effector functions of these cells are
a statistically significant decline in their absolute CD4+ T-cell uncertain. Importantly no decrease was reported in CD4+
counts. Eight of the patients showed a statistically non- T cells in the immediate post-dialysis period. No patients
significant rise in their absolute CD4+ T-cell counts, and four developed a CD3+ T-cell lymphopenia or a decreased CD8+
patients had a statistically non-significant decline in their T-cell count before dialysis although HIV-infected patients
absolute CD4+ T-cell counts (Appendix 1). had significantly lower CD4+ T-cell counts prior to dialysis
than uninfected controls.
Virological suppression is a pre-requisite for the deceased
donor kidney transplantation. Although all HIV-infected Only the percentage (%) of CD8+ T cells showed a
patients were receiving the standard first-line ART, only significant decrease post-haemodialysis in the HIV-infected
three study participants showed virological suppression study participants. However, the absolute CD8+ T-cell
below the level of viral load detectability as performed in counts did not show a statistically significant decline post-
our lab. The cross-sectional median viral load was 44 500 dialysis. This contrasts with previous studies in HIV-
copies/mL (± 9753.4 – 51 698.04). In patients for whom uninfected patients with ESKD receiving haemodialysis,
longitudinal data were available (14/17), most patients revealed lower levels of absolute CD8+ T cells when
19,20,21
displayed a stable viral load (n = 13). Only one patient compared to normal controls. The decrease in the
(patient 6) had a statistically significant increase in the HIV CD8+ T-cell count is postulated to be caused by activation
viral load (Appendix 1). of these cells by the dialyser membrane with subsequent
apoptosis of these cells. 19,22
Discussion and conclusion We went on to assess the longitudinal trends of percentage of
Kidney transplantation is a cost-effective and curative CD4+ T cells, absolute CD4+ T cells and the HIV viral loads
strategy in patients with ESKD irrespective of having HIV based on retrospective laboratory data for 14 of our study
infection or not. Eligibility criteria could, however, limit participants. The majority of our population showed a
access to this treatment particularly if these could be impacted stable (n = 8) or increased CD4+ T-cell count over time (n = 5)
by RRT. A CD4+ T-cell count above 200 cells/mL is a pre- above 200 cells/µL. According to the national guidelines
requisite for deceased donor kidney transplantation in South for renal transplantation in PLWH, this is the minimum
16
Africa. This study investigated whether alternative forms of absolute CD4+ T-cell count required for listing deceased
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 216 Open Access