Page 192 - HIVMED_v21_i1.indb
P. 192
Page 5 of 7 Original Research
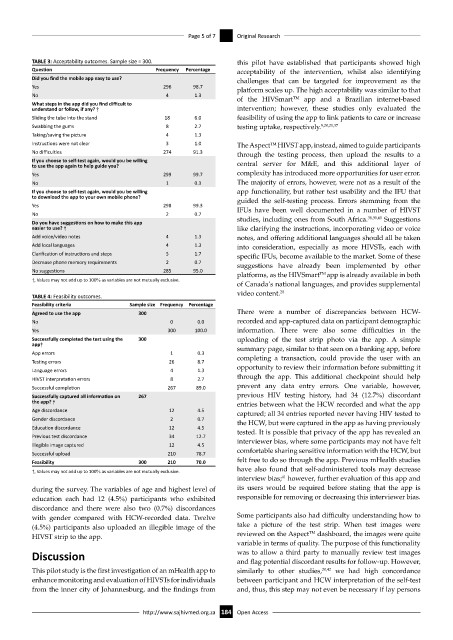
TABLE 3: Acceptability outcomes. Sample size = 300. this pilot have established that participants showed high
Question Frequency Percentage acceptability of the intervention, whilst also identifying
Did you find the mobile app easy to use? challenges that can be targeted for improvement as the
Yes 296 98.7 platform scales up. The high acceptability was similar to that
No 4 1.3 of the HIVSmart app and a Brazilian internet-based
TM
What steps in the app did you find difficult to
understand or follow, if any? † intervention; however, these studies only evaluated the
Sliding the tube into the stand 18 6.0 feasibility of using the app to link patients to care or increase
Swabbing the gums 8 2.7 testing uptake, respectively. 9,20,21,37
Taking/saving the picture 4 1.3
Instructions were not clear 3 1.0 The Aspect HIVST app, instead, aimed to guide participants
TM
No difficulties 274 91.3 through the testing process, then upload the results to a
If you choose to self-test again, would you be willing
to use the app again to help guide you? central server for M&E, and this additional layer of
Yes 299 99.7 complexity has introduced more opportunities for user error.
No 1 0.3 The majority of errors, however, were not as a result of the
If you choose to self-test again, would you be willing app functionality, but rather test usability and the IFU that
to download the app to your own mobile phone? guided the self-testing process. Errors stemming from the
Yes 298 99.3 IFUs have been well documented in a number of HIVST
No 2 0.7 38,39,40
Do you have suggestions on how to make this app studies, including ones from South Africa. Suggestions
easier to use? † like clarifying the instructions, incorporating video or voice
Add voice/video notes 4 1.3 notes, and offering additional languages should all be taken
Add local languages 4 1.3 into consideration, especially as more HIVSTs, each with
Clarification of instructions and steps 5 1.7 specific IFUs, become available to the market. Some of these
Decrease phone memory requirements 2 0.7 suggestions have already been implemented by other
No suggestions 285 95.0 platforms, as the HIVSmart TM app is already available in both
†, Values may not add up to 100% as variables are not mutually exclusive.
of Canada’s national languages, and provides supplemental
TABLE 4: Feasibility outcomes. video content. 20
Feasibility criteria Sample size Frequency Percentage
Agreed to use the app 300 There were a number of discrepancies between HCW-
No 0 0.0 recorded and app-captured data on participant demographic
Yes 300 100.0 information. There were also some difficulties in the
Successfully completed the test using the 300 uploading of the test strip photo via the app. A simple
app† summary page, similar to that seen on a banking app, before
App errors 1 0.3
Testing errors 26 8.7 completing a transaction, could provide the user with an
Language errors 4 1.3 opportunity to review their information before submitting it
HIVST interpretation errors 8 2.7 through the app. This additional checkpoint should help
Successful completion 267 89.0 prevent any data entry errors. One variable, however,
Successfully captured all information on 267 previous HIV testing history, had 34 (12.7%) discordant
the app? † entries between what the HCW recorded and what the app
Age discordance 12 4.5 captured; all 34 entries reported never having HIV tested to
Gender discordance 2 0.7 the HCW, but were captured in the app as having previously
Education discordance 12 4.5 tested. It is possible that privacy of the app has revealed an
Previous test discordance 34 12.7 interviewer bias, where some participants may not have felt
Illegible image captured 12 4.5
Successful upload 210 78.7 comfortable sharing sensitive information with the HCW, but
Feasibility 300 210 70.0 felt free to do so through the app. Previous mHealth studies
have also found that self-administered tools may decrease
†, Values may not add up to 100% as variables are not mutually exclusive.
interview bias; however, further evaluation of this app and
41
during the survey. The variables of age and highest level of its users would be required before stating that the app is
education each had 12 (4.5%) participants who exhibited responsible for removing or decreasing this interviewer bias.
discordance and there were also two (0.7%) discordances
with gender compared with HCW-recorded data. Twelve Some participants also had difficulty understanding how to
(4.5%) participants also uploaded an illegible image of the take a picture of the test strip. When test images were
TM
HIVST strip to the app. reviewed on the Aspect dashboard, the images were quite
variable in terms of quality. The purpose of this functionality
Discussion was to allow a third party to manually review test images
and flag potential discordant results for follow-up. However,
This pilot study is the first investigation of an mHealth app to similarly to other studies, 20,42 we had high concordance
enhance monitoring and evaluation of HIVSTs for individuals between participant and HCW interpretation of the self-test
from the inner city of Johannesburg, and the findings from and, thus, this step may not even be necessary if lay persons
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 184 Open Access