Page 384 - SAHCS HIVMed Journal Vol 20 No 1 2019
P. 384
Page 3 of 6 Original Research
TABLE 1: Participant characteristics (N = 385).
Characteristic Frequency N. gonorrhoeae
n % IQR
Median age, years 41 - 35–47
Marital status C. trachomas
Married 171 44.4 -
Widowed 103 26.8 - Sexually transmi ed infec ons T. vaginalis
Divorced/separated 62 16.1 -
Single 49 12.7 - Syphilis Ab
CD4+ cell count (cells/μL), median (IQR) 503 - 347–655
Viral load HSV-2
< 1000 copies/mL 347 97.5
< 50 copies/mL 324 91.0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60
Duration on ART, years, median (IQR) 6.2 - 3.2–9.0 Percentage
Sexual history
Age at sexual debut, years, median (IQR) 19 - 17–21 HSV, Herpes simplex virus; AB, antibody.
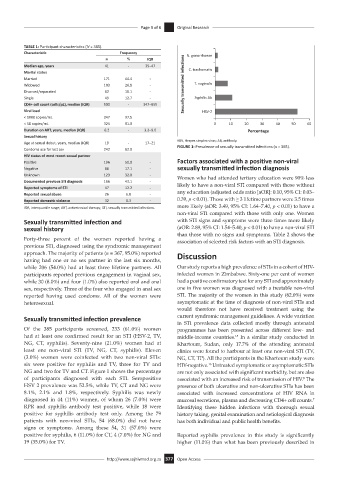
Condoms use for last sex 242 62.9 FIGURE 1: Prevalence of sexually transmitted infections (n = 365).
HIV status of most recent sexual partner
Positive 196 50.0 - Factors associated with a positive non-viral
Negative 66 17.1 - sexually transmitted infection diagnosis
Unknown 123 32.0 - Women who had attended tertiary education were 90% less
Documented previous STI diagnosis 166 43.1 - likely to have a non-viral STI compared with those without
Reported symptoms of STI 47 12.2 -
Reported sexual abuse 26 6.8 - any education (adjusted odds ratio [aOR]: 0.10, 95% CI: 0.03–
Reported domestic violence 32 8.3 - 0.39, p < 0.01). Those with ≥ 3 lifetime partners were 3.5 times
IQR, interquartile range; ART, antiretroviral therapy; STI, sexually transmitted infections. more likely (aOR: 3.49, 95% CI: 1.64–7.40, p < 0.01) to have a
non-viral STI compared with those with only one. Women
Sexually transmitted infection and with STI signs and symptoms were three times more likely
sexual history (aOR: 2.89, 95% CI: 1.54–5.40, p < 0.01) to have a non-viral STI
than those with no signs and symptoms. Table 2 shows the
Forty-three percent of the women reported having a association of selected risk factors with an STI diagnosis.
previous STI, diagnosed using the syndromic management
approach. The majority of patients (n = 367, 95.0%) reported Discussion
having had one or no sex partner in the last six months,
while 206 (54.0%) had at least three lifetime partners. All Our study reports a high prevalence of STIs in a cohort of HIV-
participants reported previous engagement in vaginal sex, infected women in Zimbabwe. Sixty-one per cent of women
while 30 (8.0%) and four (1.0%) also reported oral and anal had a positive confirmatory test for any STI and approximately
sex, respectively. Three of the four who engaged in anal sex one in five women was diagnosed with a treatable non-viral
reported having used condoms. All of the women were STI. The majority of the women in this study (62.0%) were
heterosexual. asymptomatic at the time of diagnosis of non-viral STIs and
would therefore not have received treatment using the
Sexually transmitted infection prevalence current syndromic management guidelines. A wide variation
in STI prevalence data collected mostly through antenatal
Of the 385 participants screened, 233 (61.0%) women programmes has been presented across different low- and
had at least one confirmed result for an STI (HSV-2, TV, middle-income countries. In a similar study conducted in
15
NG, CT, syphilis). Seventy-nine (21.0%) women had at Khartoum, Sudan, only 17.7% of the attending antenatal
least one non-viral STI (TV, NG, CT, syphilis). Eleven clinics were found to harbour at least one non-viral STI (TV,
(3.0%) women were coinfected with two non-viral STIs: NG, CT, TP). All the participants in the Khartoum study were
six were positive for syphilis and TV, three for TV and HIV-negative. Untreated symptomatic or asymptomatic STIs
16
NG and two for TV and CT. Figure 1 shows the percentage are not only associated with significant morbidity, but are also
of participants diagnosed with each STI. Seropositive associated with an increased risk of transmission of HIV. The
8
HSV 2 prevalence was 52.5%, while TV, CT and NG were presence of both ulcerative and non-ulcerative STIs has been
8.1%, 2.1% and 1.8%, respectively. Syphilis was newly associated with increased concentrations of HIV RNA in
diagnosed in 44 (11%) women, of whom 26 (7.0%) were mucosal secretions, plasma and decreasing CD4+ cell counts.
7
RPR and syphilis antibody test positive, while 18 were Identifying these hidden infections with thorough sexual
positive for syphilis antibody test only. Among the 79 history taking, genital examination and aetiological diagnosis
patients with non-viral STIs, 54 (68.0%) did not have has both individual and public health benefits.
signs or symptoms. Among these 54, 31 (57.0%) were
positive for syphilis, 6 (11.0%) for CT, 4 (7.0%) for NG and Reported syphilis prevalence in this study is significantly
19 (35.0%) for TV. higher (11.0%) than what has been previously described in
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 377 Open Access