Page 35 - SAHCS HIVMed Journal Vol 20 No 1 2019
P. 35
Page 6 of 26 Guideline
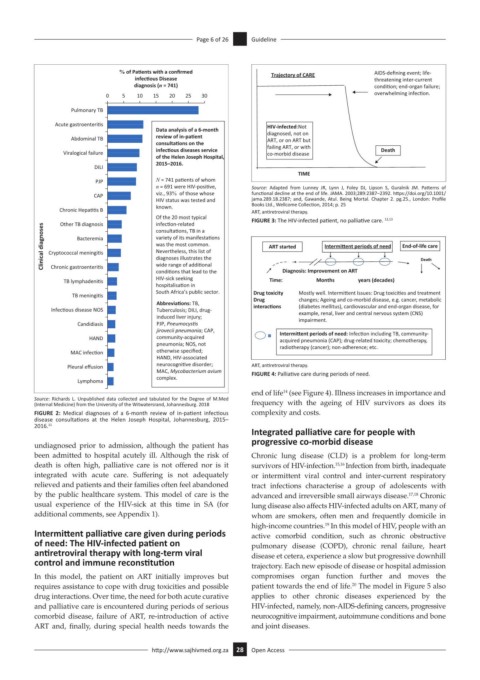
% of Pa ents with a confirmed Trajectory of CARE AIDS-defining event; life-
infec ous Disease threatening inter-current
diagnosis (n = 741) condion; end-organ failure;
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 overwhelming infecon.
Pulmonary TB
Acute gastroenteri s HIV-infected:Not
Data analysis of a 6-month diagnosed, not on
Abdominal TB review of in-pa ent ART, or on ART but
consulta ons on the
infec ous diseases service failing ART, or with Death
Viralogical failure co-morbid disease
of the Helen Joseph Hospital,
2015–2016.
DILI
TIME
PJP N = 741 pa ents of whom
n = 691 were HIV-posi ve, Source: Adapted from Lunney JR, Lynn J, Foley DJ, Lipson S, Guralnik JM. Patterns of
CAP viz., 93% of those whose functional decline at the end of life. JAMA. 2003;289:2387–2392. https://doi.org/10.1001/
HIV status was tested and jama.289.18.2387; and, Gawande, Atul. Being Mortal. Chapter 2. pg.25., London: Profile
Books Ltd., Wellcome Collection, 2014; p. 25
Chronic Hepa s B known. ART, antiretroviral therapy.
Of the 20 most typical FIGURE 3: The HIV-infected patient, no palliative care. 12,13
Other TB diagnosis
infec on-related
Clinical diagnoses Cryptococcal meningi s variety of its manifesta ons ART started Intermi ent periods of need End-of-life care
consulta ons, TB in a
Bacteremia
was the most common.
Nevertheless, this list of
diagnoses illustrates the
wide range of addi onal
Chronic gastroenteri s
condi ons that lead to the Diagnosis: Improvement on ART Death
HIV-sick seeking
TB lymphadeni s Time: Months years (decades)
hospitalisa on in
South Africa’s public sector. Drug toxicity Mostly well. Intermi ent Issues: Drug toxici es and treatment
TB meningi s Drug changes; Ageing and co-morbid disease, e.g. cancer, metabolic
Abbrevia ons: TB,
Infec ous disease NOS Tuberculosis; DILI, drug- interac ons (diabetes mellitus), cardiovascular and end-organ disease, for
example, renal, liver and central nervous system (CNS)
induced liver injury; impairment.
Candidiasis PJP, Pneumocys s
jirovecii pneumonia; CAP, Intermi ent periods of need: Infec on including TB, community-
HAND community-acquired acquired pneumonia (CAP); drug-related toxicity; chemotherapy,
pneumonia; NOS, not radiotherapy (cancer); non-adherence; etc.
MAC infec on otherwise specified;
HAND, HIV-associated
Pleural effusion neurocogni ve disorder; ART, antiretroviral therapy.
MAC, Mycobacterium avium FIGURE 4: Palliative care during periods of need.
complex.
Lymphoma
end of life (see Figure 4). Illness increases in importance and
14
Source: Richards L. Unpublished data collected and tabulated for the Degree of M.Med
(Internal Medicine) from the University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg. 2018 frequency with the ageing of HIV survivors as does its
FIGURE 2: Medical diagnoses of a 6-month review of in-patient infectious complexity and costs.
disease consultations at the Helen Joseph Hospital, Johannesburg, 2015–
2016. 11
Integrated palliative care for people with
undiagnosed prior to admission, although the patient has progressive co-morbid disease
been admitted to hospital acutely ill. Although the risk of Chronic lung disease (CLD) is a problem for long-term
death is often high, palliative care is not offered nor is it survivors of HIV-infection. 15,16 Infection from birth, inadequate
integrated with acute care. Suffering is not adequately or intermittent viral control and inter-current respiratory
relieved and patients and their families often feel abandoned tract infections characterise a group of adolescents with
by the public healthcare system. This model of care is the advanced and irreversible small airways disease. 17,18 Chronic
usual experience of the HIV-sick at this time in SA (for lung disease also affects HIV-infected adults on ART, many of
additional comments, see Appendix 1). whom are smokers, often men and frequently domicile in
high-income countries. In this model of HIV, people with an
19
Intermittent palliative care given during periods active comorbid condition, such as chronic obstructive
of need: The HIV-infected patient on pulmonary disease (COPD), chronic renal failure, heart
antiretroviral therapy with long-term viral disease et cetera, experience a slow but progressive downhill
control and immune reconstitution trajectory. Each new episode of disease or hospital admission
In this model, the patient on ART initially improves but compromises organ function further and moves the
20
requires assistance to cope with drug toxicities and possible patient towards the end of life. The model in Figure 5 also
drug interactions. Over time, the need for both acute curative applies to other chronic diseases experienced by the
and palliative care is encountered during periods of serious HIV-infected, namely, non-AIDS-defining cancers, progressive
comorbid disease, failure of ART, re-introduction of active neurocognitive impairment, autoimmune conditions and bone
ART and, finally, during special health needs towards the and joint diseases.
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 28 Open Access