Page 335 - SAHCS HIVMed Journal Vol 20 No 1 2019
P. 335
Page 4 of 7 Original Research
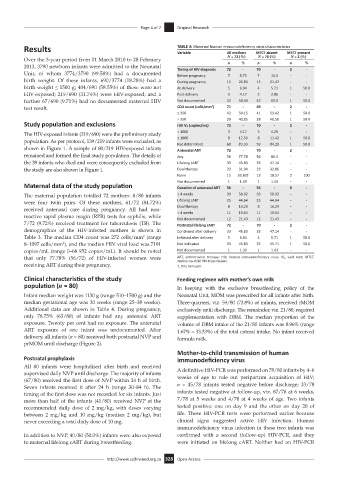
Results TABLE 3: Maternal human immunodeficiency virus characteristics
Variable All mothers MTCT absent MTCT present
Over the 3-year period from 01 March 2010 to 28 February N = 72 (%) n N = 70 (%) n N = 2 (%) %
n
%
%
2013, 3790 newborn infants were admitted to the Neonatal Timing of HIV diagnosis 72 - 70 - 2 -
Unit, of whom 3774/3790 (99.58%) had a documented Before pregnancy 7 9.72 7 10.0 - -
birth weight. Of these infants, 690/3774 (18.28%) had a During pregnancy 15 20.83 15 21.42 - -
birth weight ≤ 1500 g; 404/690 (58.55%) of these were not At delivery 5 6.94 4 5.71 1 50.0
HIV-exposed; 219/690 (31.74%) were HIV-exposed; and a Post-delivery 3 4.17 2 2.86 - -
further 67/690 (9.71%) had no documented maternal HIV Not documented 42 58.33 42 60.0 1 50.0
3
test result. CD4 count (cells/mm ) 71 - 69 - 2 -
≤ 350 42 59.15 41 59.42 1 50.0
> 350 29 40.85 28 40.58 1 50.0
Study population and exclusions HIV VL (copies/mL) 72 - 70 - 2 -
< 1000 3 4.17 3 4.29 - -
The HIV-exposed infants (219/690) were the preliminary study
9
8
population. As per protocol, 139/219 infants were excluded, as ≥ 1000 60 12.50 59 11.42 1 1 50.0
84.29
Not determined
83.33
50.0
shown in Figure 1. A sample of 80/219 HIV-exposed infants Antenatal ART 72 - 70 - 2 -
remained and formed the final study population. The details of Any 56 77.78 56 80.0 - -
the 39 infants who died and were consequently excluded from Lifelong cART 33 45.83 33 47.14 - -
the study are also shown in Figure 1. Dual therapy 23 31.94 23 32.86 - -
None 15 20.83† 13 18.57 2 100
Not documented 1 1.39 1 1.43 - -
Maternal data of the study population Duration of antenatal ART 56 - 56 - 0 -
The maternal population totalled 72 mothers: 8/80 infants ≥ 4 weeks 33 58.92 33 58.92 - -
were four twin pairs. Of these mothers, 61/72 (84.72%) Lifelong cART 25 44.64 25 44.64 - -
8
8
received antenatal care during pregnancy. All had non- Dual therapy 11 14.29 11 14.29 - - - -
19.64
19.64
< 4 weeks
reactive rapid plasma reagin (RPR) tests for syphilis, while Not documented 12 21.43 12 21.43 - -
7/72 (9.72%) received treatment for tuberculosis (TB). The Postnatal lifelong cART 72 - 70 - 2 -
demographics of the HIV-infected mothers is shown in Continued after delivery 33 45.83 33 47.14 - -
Table 3. The median CD4 count was 272 cells/mm (range Initiated after delivery 5 6.94 4 5.71 1 50.0
3
8–1097 cells/mm ), and the median HIV viral load was 7191 Not indicated 33 45.83 32 45.71 1 50.0
3
copies/mL (range 0–68 952 copies/mL). It should be noted Not documented 1 1.39 1 1.43 - -
that only 77.78% (56/72) of HIV-infected women were ART, antiretroviral therapy; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; VL, viral load; MTCT,
mother-to-child HIV-transmission.
receiving ART during their pregnancy. †, One twin pair.
Clinical characteristics of the study Feeding regimen with mother’s own milk
population (n = 80) In keeping with the exclusive breastfeeding policy of the
Infant median weight was 1130 g (range 510–1500 g) and the Neonatal Unit, MOM was prescribed for all infants after birth.
median gestational age was 30 weeks (range 25–38 weeks). Three-quarters, viz. 59/80 (73.8%) of infants, received rMOM
Additional data are shown in Table 4. During pregnancy, exclusively until discharge. The remainder, viz. 21/80, required
only 78.75% (63/80) of infants had any antenatal ART supplementation with DBM. The median proportion of the
exposure. Twenty per cent had no exposure. The antenatal volume of DBM intake of the 21/80 infants was 8.96% (range
ART exposure of one infant was undocumented. After 1.67% – 33.33%) of the total enteral intake. No infant received
delivery, all infants (n = 80) received both postnatal NVP and formula milk.
prMOM until discharge (Figure 2).
Mother-to-child transmission of human
Postnatal prophylaxis immunodeficiency virus
All 80 infants were hospitalised after birth and received A definitive HIV-PCR was performed on 78/80 infants by 4–6
supervised daily NVP until discharge. The majority of infants
(67/80) received the first dose of NVP within 24 h of birth. weeks of age to rule out peripartum acquisition of HIV;
Seven infants received it after 24 h (range 30–84 h). The n = 45/78 infants tested negative before discharge; 33/78
timing of the first dose was not recorded for six infants. Just infants tested negative at follow-up, viz. 67/78 at 6 weeks,
more than half of the infants (41/80) received NVP at the 7/78 at 5 weeks and 4/78 at 4 weeks of age. Two infants
recommended daily dose of 2 mg/kg, with doses varying tested positive: one on day 9 and the other on day 20 of
between 2 mg/kg and 10 mg/kg (median 2 mg/kg), but life. These HIV-PCR tests were performed earlier because
never exceeding a total daily dose of 10 mg. clinical signs suggested active HIV infection. Human
immunodeficiency virus infection in these two infants was
In addition to NVP, 40/80 (50.0%) infants were also exposed confirmed with a second (follow-up) HIV-PCR, and they
to maternal lifelong cART during breastfeeding. were initiated on lifelong cART. Neither had an HIV-PCR
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 328 Open Access