Page 247 - SAHCS HIVMed Journal Vol 20 No 1 2019
P. 247
Page 3 of 5 Original Research
and blue colour, respectively. In both groups, reactive TABLE 3: CD4 count: Effect of CD4 count on malignant lesions.
lymphoid hyperplasia was found in 77% of patients. Variable CD4 count (cells/mm ) 3 Total
Actinomycosis was found in 12% of patients in the HIV- ≤ 200 ÿ 200
infected group, while in the HIV-uninfected patients, it was Malignant lesion 2 5 7
observed in 11% of patients. Benign lesion 27 73 100
Total 29 78 107
Chi square = 0.008; p = 0.928.
Chi-square test of independence
to have malignant tonsillar pathology than HIV-uninfected
The majority of patients (both HIV-positive and negative)
had benign pathology of their tonsils. In the HIV-infected patients. The Wald tests showed that only age significantly
patients, eight patients (9.3%) had a malignant pathology. In predicted the presence of malignant pathology (p = 0.017).
the HIV-uninfected group, six patients (8.1%) had a malignant HIV infection did not influence the risk of developing
pathology. We concluded that there was no statistical malignant pathology (p = 0.586). This result is in accordance
evidence that HIV infection conferred an increased risk for with the chi-square test in Table 3.
the development of malignant tonsillar disease (see Table 1 3
and Table 2). Patients with a lower CD4 count (< 200 cells/mm ) would be
expected to have more severe HIV disease and, therefore, a
greater chance of having an HIV-associated malignancy. In
Logistic regression was performed to test the effects of age our study, a low CD4 count did not appear to affect the
and HIV infection on the presence of malignant lesions. The occurrence of malignant lesions (p = 0.928).
results indicated that when controlling for the effect of age in
the model, HIV-infected patients are 1.380 times more likely Discussion
We reviewed 160 tonsillectomy specimens. The most common
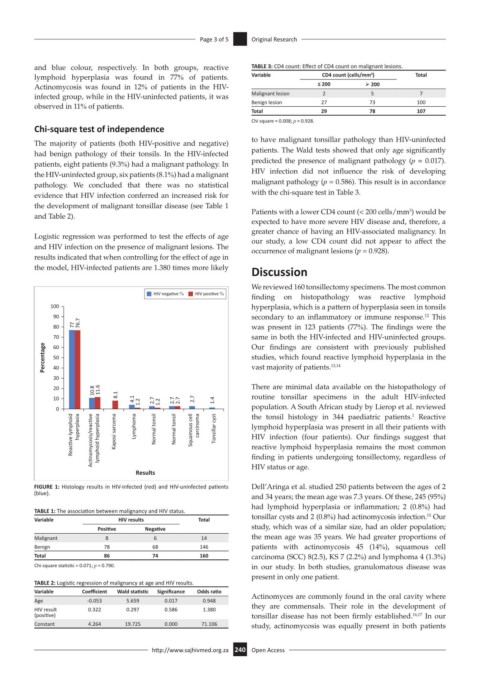
HIV nega ve % HIV posi ve %
finding on histopathology was reactive lymphoid
100 hyperplasia, which is a pattern of hyperplasia seen in tonsils
90 secondary to an inflammatory or immune response. This
12
80 77 76.7 was present in 123 patients (77%). The findings were the
70 same in both the HIV-infected and HIV-uninfected groups.
Our findings are consistent with previously published
Percentage 60 studies, which found reactive lymphoid hyperplasia in the
50
13,14
vast majority of patients.
40
30
20 10.8 11.6 There are minimal data available on the histopathology of
10 8.1 4.1 1.2 2.7 1.2 2.7 2.7 2.7 1.4 routine tonsillar specimens in the adult HIV-infected
0 population. A South African study by Lierop et al. reviewed
the tonsil histology in 344 paediatric patients. Reactive
1
Reac ve lymphoid hyperplasia Ac nomycosis/reac ve lymphoid hyperplasia Kaposi sarcoma Lymphoma Normal tonsil Normal tonsil Squamous cell carcinoma Tonsillar cyst lymphoid hyperplasia was present in all their patients with
HIV infection (four patients). Our findings suggest that
reactive lymphoid hyperplasia remains the most common
HIV status or age.
Results finding in patients undergoing tonsillectomy, regardless of
FIGURE 1: Histology results in HIV-infected (red) and HIV-uninfected patients Dell’Aringa et al. studied 250 patients between the ages of 2
(blue).
and 34 years; the mean age was 7.3 years. Of these, 245 (95%)
had lymphoid hyperplasia or inflammation; 2 (0.8%) had
TABLE 1: The association between malignancy and HIV status. 15
Variable HIV results Total tonsillar cysts and 2 (0.8%) had actinomycosis infection. Our
Positive Negative study, which was of a similar size, had an older population;
Malignant 8 6 14 the mean age was 35 years. We had greater proportions of
Benign 78 68 146 patients with actinomycosis 45 (14%), squamous cell
Total 86 74 160 carcinoma (SCC) 8(2.5), KS 7 (2.2%) and lymphoma 4 (1.3%)
Chi-square statistic = 0.071; p = 0.790. in our study. In both studies, granulomatous disease was
present in only one patient.
TABLE 2: Logistic regression of malignancy at age and HIV results.
Variable Coefficient Wald statistic Significance Odds ratio Actinomyces are commonly found in the oral cavity where
Age -0.053 5.659 0.017 0.948
HIV result 0.322 0.297 0.586 1.380 they are commensals. Their role in the development of
(positive) tonsillar disease has not been firmly established. 16,17 In our
Constant 4.264 19.725 0.000 71.106 study, actinomycosis was equally present in both patients
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 240 Open Access