Page 278 - HIVMED_v21_i1.indb
P. 278
Page 6 of 10 Original Research
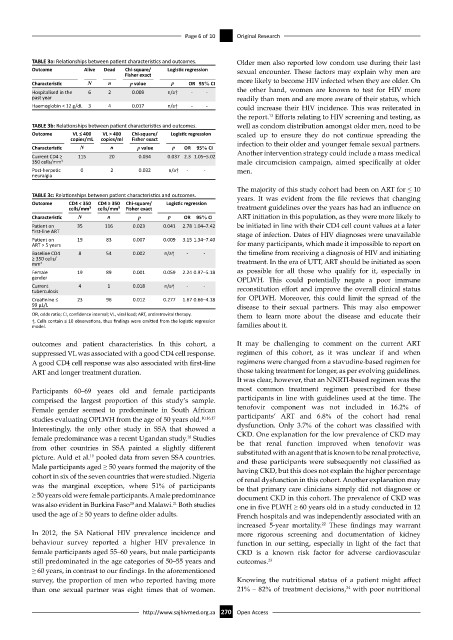
TABLE 3a: Relationships between patient characteristics and outcomes. Older men also reported low condom use during their last
Outcome Alive Dead Chi-square/ Logistic regression sexual encounter. These factors may explain why men are
Fisher exact
Characteristic N n p value p OR 95% CI more likely to become HIV infected when they are older. On
Hospitalised in the 6 2 0.009 n/a† - - the other hand, women are known to test for HIV more
past year readily than men and are more aware of their status, which
Haemoglobin < 12 g/dL 3 4 0.017 n/a† - - could increase their HIV incidence. This was reiterated in
the report. Efforts relating to HIV screening and testing, as
13
TABLE 3b: Relationships between patient characteristics and outcomes. well as condom distribution amongst older men, need to be
Outcome VL ≤ 400 VL > 400 Chi-square/ Logistic regression scaled up to ensure they do not continue spreading the
copies/mL copies/ml Fisher exact
Characteristic N n p value p OR 95% CI infection to their older and younger female sexual partners.
Current CD4 ≥ 115 20 0.034 0.037 2.3 1.05–5.02 Another intervention strategy could include a mass medical
350 cells/mm 3 male circumcision campaign, aimed specifically at older
Post-herpetic 0 2 0.032 n/a† - - men.
neuralgia
The majority of this study cohort had been on ART for ≤ 10
TABLE 3c: Relationships between patient characteristics and outcomes. years. It was evident from the file reviews that changing
Outcome CD4 < 350 CD4 ≥ 350 Chi-square/ Logistic regression
cells/mm³ cells/mm³ Fisher exact treatment guidelines over the years has had an influence on
Characteristic N n p p OR 95% CI ART initiation in this population, as they were more likely to
Patient on 35 116 0.023 0.041 2.78 1.04–7.42 be initiated in line with their CD4 cell count values at a later
first-line ART stage of infection. Dates of HIV diagnoses were unavailable
Patient on 19 83 0.007 0.009 3.15 1.34–7.40
ART > 5 years for many participants, which made it impossible to report on
Baseline CD4 8 54 0.002 n/a† - - the timeline from receiving a diagnosis of HIV and initiating
≥ 350 cells/ treatment. In the era of UTT, ART should be initiated as soon
mm 3
Female 19 89 0.001 0.059 2.24 0.97–5.18 as possible for all those who qualify for it, especially in
gender OPLWH. This could potentially negate a poor immune
Current 4 1 0.018 n/a† - - reconstitution effort and improve the overall clinical status
tuberculosis
Creatinine ≤ 23 96 0.012 0.277 1.67 0.66–4.18 for OPLWH. Moreover, this could limit the spread of the
99 µL/L disease to their sexual partners. This may also empower
OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; VL, viral load; ART, antiretroviral therapy. them to learn more about the disease and educate their
†, Cells contain ≤ 10 observations, thus findings were omitted from the logistic regression
model. families about it.
outcomes and patient characteristics. In this cohort, a It may be challenging to comment on the current ART
suppressed VL was associated with a good CD4 cell response. regimen of this cohort, as it was unclear if and when
A good CD4 cell response was also associated with first-line regimens were changed from a stavudine-based regimen for
ART and longer treatment duration. those taking treatment for longer, as per evolving guidelines.
It was clear, however, that an NNRTI-based regimen was the
Participants 60–69 years old and female participants most common treatment regimen prescribed for these
comprised the largest proportion of this study’s sample. participants in line with guidelines used at the time. The
Female gender seemed to predominate in South African tenofovir component was not included in 16.2% of
studies evaluating OPLWH from the age of 50 years old. 10,16,17 participants’ ART and 6.8% of the cohort had renal
Interestingly, the only other study in SSA that showed a dysfunction. Only 3.7% of the cohort was classified with
female predominance was a recent Ugandan study. Studies CKD. One explanation for the low prevalence of CKD may
18
from other countries in SSA painted a slightly different be that renal function improved when tenofovir was
substituted with an agent that is known to be renal protective,
picture. Auld et al. pooled data from seven SSA countries. and these participants were subsequently not classified as
19
Male participants aged ≥ 50 years formed the majority of the having CKD, but this does not explain the higher percentage
cohort in six of the seven countries that were studied. Nigeria of renal dysfunction in this cohort. Another explanation may
was the marginal exception, where 51% of participants be that primary care clinicians simply did not diagnose or
≥ 50 years old were female participants. A male predominance document CKD in this cohort. The prevalence of CKD was
was also evident in Burkina Faso and Malawi. Both studies one in five PLWH ≥ 60 years old in a study conducted in 12
21
20
used the age of ≥ 50 years to define older adults. French hospitals and was independently associated with an
increased 5-year mortality. These findings may warrant
22
In 2012, the SA National HIV prevalence incidence and more rigorous screening and documentation of kidney
behaviour survey reported a higher HIV prevalence in function in our setting, especially in light of the fact that
female participants aged 55–60 years, but male participants CKD is a known risk factor for adverse cardiovascular
still predominated in the age categories of 50–55 years and outcomes.
23
≥ 60 years, in contrast to our findings. In the aforementioned
survey, the proportion of men who reported having more Knowing the nutritional status of a patient might affect
24
than one sexual partner was eight times that of women. 21% – 82% of treatment decisions, with poor nutritional
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 270 Open Access