Page 277 - HIVMED_v21_i1.indb
P. 277
Page 5 of 10 Original Research
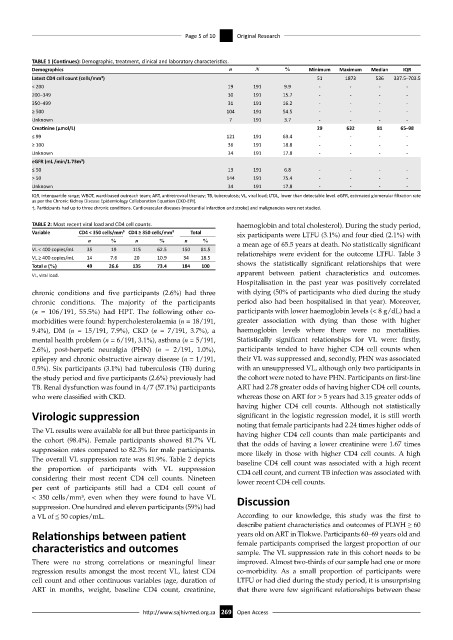
TABLE 1 (Continues): Demographic, treatment, clinical and laboratory characteristics.
Demographics n N % Minimum Maximum Median IQR
Latest CD4 cell count (cells/mm³) 51 1873 536 337.5 ̶ 703.5
< 200 19 191 9.9 - - - -
200–349 30 191 15.7 - - - -
350–499 31 191 16.2 - - - -
≥ 500 104 191 54.5 - - - -
Unknown 7 191 3.7 - - - -
Creatinine (µmol/L) 29 632 81 65 ̶ 98
≤ 99 121 191 63.4 - - - -
≥ 100 36 191 18.8 - - - -
Unknown 34 191 17.8 - - - -
eGFR (mL /min/1.73m³)
≤ 50 13 191 6.8 - - - -
> 50 144 191 75.4 - - - -
Unknown 34 191 17.8 - - - -
IQR, interquartile range; WBOT, ward-based outreach team; ART, antiretroviral therapy; TB, tuberculosis; VL, viral load; LTDL, lower than detectable level. eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate
as per the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration Equation (CKD-EPI).
†, Participants had up to three chronic conditions. Cardiovascular diseases (myocardial infarction and stroke) and malignancies were not studied.
TABLE 2: Most recent viral load and CD4 cell counts. haemoglobin and total cholesterol). During the study period,
Variable CD4 < 350 cells/mm³ CD4 ≥ 350 cells/mm³ Total six participants were LTFU (3.1%) and four died (2.1%) with
n % n % n % a mean age of 65.5 years at death. No statistically significant
VL < 400 copies/mL 35 19 115 62.5 150 81.5 relationships were evident for the outcome LTFU. Table 3
VL ≥ 400 copies/mL 14 7.6 20 10.9 34 18.5
Total n (%) 49 26.6 135 73.4 184 100 shows the statistically significant relationships that were
VL, viral load. apparent between patient characteristics and outcomes.
Hospitalisation in the past year was positively correlated
chronic conditions and five participants (2.6%) had three with dying (50% of participants who died during the study
chronic conditions. The majority of the participants period also had been hospitalised in that year). Moreover,
(n = 106/191, 55.5%) had HPT. The following other co- participants with lower haemoglobin levels (< 8 g/dL) had a
morbidities were found: hypercholesterolaemia (n = 18/191, greater association with dying than those with higher
9.4%), DM (n = 15/191, 7.9%), CKD (n = 7/191, 3.7%), a haemoglobin levels where there were no mortalities.
mental health problem (n = 6/191, 3.1%), asthma (n = 5/191, Statistically significant relationships for VL were: firstly,
2.6%), post-herpetic neuralgia (PHN) (n = 2/191, 1.0%), participants tended to have higher CD4 cell counts when
epilepsy and chronic obstructive airway disease (n = 1/191, their VL was suppressed and, secondly, PHN was associated
0.5%). Six participants (3.1%) had tuberculosis (TB) during with an unsuppressed VL, although only two participants in
the study period and five participants (2.6%) previously had the cohort were noted to have PHN. Participants on first-line
TB. Renal dysfunction was found in 4/7 (57.1%) participants ART had 2.78 greater odds of having higher CD4 cell counts,
who were classified with CKD. whereas those on ART for > 5 years had 3.15 greater odds of
having higher CD4 cell counts. Although not statistically
Virologic suppression significant in the logistic regression model, it is still worth
noting that female participants had 2.24 times higher odds of
The VL results were available for all but three participants in having higher CD4 cell counts than male participants and
the cohort (98.4%). Female participants showed 81.7% VL that the odds of having a lower creatinine were 1.67 times
suppression rates compared to 82.3% for male participants. more likely in those with higher CD4 cell counts. A high
The overall VL suppression rate was 81.9%. Table 2 depicts baseline CD4 cell count was associated with a high recent
the proportion of participants with VL suppression CD4 cell count, and current TB infection was associated with
considering their most recent CD4 cell counts. Nineteen lower recent CD4 cell counts.
per cent of participants still had a CD4 cell count of
< 350 cells/mm³, even when they were found to have VL Discussion
suppression. One hundred and eleven participants (59%) had
a VL of ≤ 50 copies/mL. According to our knowledge, this study was the first to
describe patient characteristics and outcomes of PLWH ≥ 60
Relationships between patient years old on ART in Tlokwe. Participants 60–69 years old and
characteristics and outcomes female participants comprised the largest proportion of our
sample. The VL suppression rate in this cohort needs to be
There were no strong correlations or meaningful linear improved. Almost two-thirds of our sample had one or more
regression results amongst the most recent VL, latest CD4 co-morbidity. As a small proportion of participants were
cell count and other continuous variables (age, duration of LTFU or had died during the study period, it is unsurprising
ART in months, weight, baseline CD4 count, creatinine, that there were few significant relationships between these
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 269 Open Access