Page 141 - HIVMED_v21_i1.indb
P. 141
Page 3 of 7 Original Research
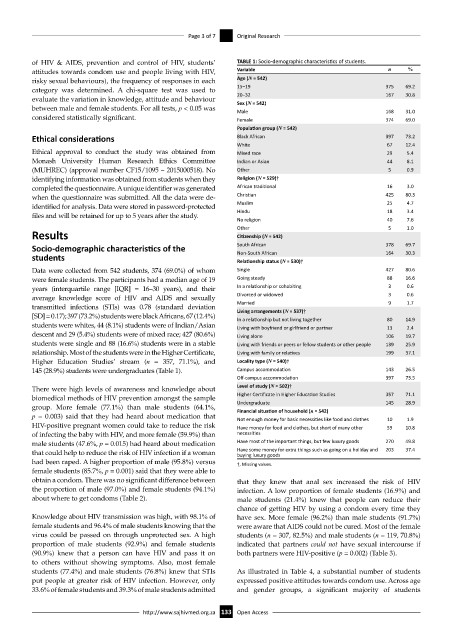
of HIV & AIDS, prevention and control of HIV, students’ TABLE 1: Socio-demographic characteristics of students.
attitudes towards condom use and people living with HIV, Variable n %
risky sexual behaviours), the frequency of responses in each Age (N = 542)
category was determined. A chi-square test was used to 15–19 375 69.2
evaluate the variation in knowledge, attitude and behaviour 20–32 167 30.8
Sex (N = 542)
between male and female students. For all tests, p < 0.05 was Male 168 31.0
considered statistically significant. Female 374 69.0
Population group (N = 542)
Ethical considerations Black African 397 73.2
White 67 12.4
Ethical approval to conduct the study was obtained from Mixed race 29 5.4
Monash University Human Research Ethics Committee Indian or Asian 44 8.1
(MUHREC) (approval number CF15/1095 – 2015000518). No Other 5 0.9
identifying information was obtained from students when they Religion (N = 529)†
completed the questionnaire. A unique identifier was generated African traditional 16 3.0
when the questionnaire was submitted. All the data were de- Christian 425 80.3
identified for analysis. Data were stored in password-protected Muslim 25 4.7
files and will be retained for up to 5 years after the study. Hindu 18 3.4
No religion 40 7.6
Other 5 1.0
Results Citizenship (N = 542)
Socio-demographic characteristics of the South African 378 69.7
Non-South African
30.3
164
students Relationship status (N = 530)†
Data were collected from 542 students, 374 (69.0%) of whom Single 427 80.6
were female students. The participants had a median age of 19 Going steady 88 16.6
years (interquartile range [IQR] = 16–30 years), and their In a relationship or cohabiting 3 0.6
average knowledge score of HIV and AIDS and sexually Divorced or widowed 3 0.6
transmitted infections (STIs) was 0.78 (standard deviation Married 9 1.7
Living arrangements (N = 537)†
[SD] = 0.17); 397 (73.2%) students were black Africans, 67 (12.4%) In a relationship but not living together 80 14.9
students were whites, 44 (8.1%) students were of Indian/Asian Living with boyfriend or girlfriend or partner 13 2.4
descent and 29 (5.4%) students were of mixed race; 427 (80.6%) Living alone 106 19.7
students were single and 88 (16.6%) students were in a stable Living with friends or peers or fellow students or other people 139 25.9
relationship. Most of the students were in the Higher Certificate, Living with family or relatives 199 37.1
Higher Education Studies’ stream (n = 357, 71.1%), and Locality type (N = 540)†
145 (28.9%) students were undergraduates (Table 1). Campus accommodation 143 26.5
Off-campus accommodation 397 73.5
There were high levels of awareness and knowledge about Level of study (N = 502)†
biomedical methods of HIV prevention amongst the sample Higher Certificate in Higher Education Studies 357 71.1
group. More female (77.1%) than male students (64.1%, Undergraduate 145 28.9
Financial situation of household (n = 542)
p = 0.003) said that they had heard about medication that Not enough money for basic necessities like food and clothes 10 1.9
HIV-positive pregnant women could take to reduce the risk Have money for food and clothes, but short of many other 59 10.8
of infecting the baby with HIV, and more female (59.9%) than necessities
male students (47.6%, p = 0.015) had heard about medication Have most of the important things, but few luxury goods 270 49.8
that could help to reduce the risk of HIV infection if a woman Have some money for extra things such as going on a holiday and 203 37.4
buying luxury goods
had been raped. A higher proportion of male (95.8%) versus †, Missing values.
female students (85.7%, p = 0.001) said that they were able to
obtain a condom. There was no significant difference between that they knew that anal sex increased the risk of HIV
the proportion of male (97.0%) and female students (94.1%) infection. A low proportion of female students (16.9%) and
about where to get condoms (Table 2). male students (21.4%) knew that people can reduce their
chance of getting HIV by using a condom every time they
Knowledge about HIV transmission was high, with 98.1% of have sex. More female (96.2%) than male students (91.7%)
female students and 96.4% of male students knowing that the were aware that AIDS could not be cured. Most of the female
virus could be passed on through unprotected sex. A high students (n = 307, 82.5%) and male students (n = 119, 70.8%)
proportion of male students (92.9%) and female students indicated that partners could not have sexual intercourse if
(90.9%) knew that a person can have HIV and pass it on both partners were HIV-positive (p = 0.002) (Table 3).
to others without showing symptoms. Also, most female
students (77.4%) and male students (76.8%) knew that STIs As illustrated in Table 4, a substantial number of students
put people at greater risk of HIV infection. However, only expressed positive attitudes towards condom use. Across age
33.6% of female students and 39.3% of male students admitted and gender groups, a significant majority of students
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 133 Open Access