Page 86 - SAHCS HIVMed Journal Vol 20 No 1 2019
P. 86
Page 2 of 3 Case Report
TABLE 1: Drug resistance report at 12 months.
Drug resistance interpretation: RT ART initiation? ART re-initiation
NRTI Resistance Mutations A62V, K65R, V75I, Y115F, M184V, K219E 1000 000
NNRTI Resistance Mutations L100I, K103N
Other Mutations V90I 100 000
Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors 10 000
abacavir (ABC) High-level Resistance
zidovudine (AZT) Susceptible HIV viral load (log) 1000
emtricitabine (FTC) High-level Resistance 100
lamivudine (3TC) High-level Resistance
tenofovir (TDF) High-level Resistance 10
Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors 1
doravirine (DOR) Intermediate Resistance
efavirenz (EFV) High-level Resistance 01 June 2012 01 June 2013 01 June 2014 01 June 2015
etravirine (ETR) Intermediate Resistance 01 December 2012 01 December 2013 01 December 2014
nevirapine (NVP) High-level Resistance
rilpivirine (RPV) High-level Resistance
Source: Adapted from the Stanford database 2 Date
Note: The drug resistance profile reveals a mixed pattern consisting of the classic XTC-related ART, antiretroviral therapy.
mutation, M184V/I; two TDF-associated mutations, Y115F and K65R; one accessory
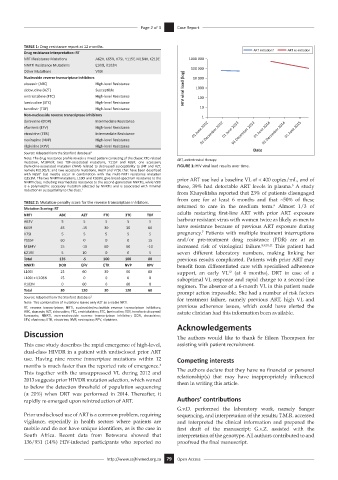
thymidine-associated mutation (TAM) related to decreased susceptibility to d4T and AZT, FIGURE 1: HIV viral load results over time.
namely K219Q/E; and two accessory mutations, A62V and V75I, that have been described
with K65R but mostly occur in combination with the multi-NRTI resistance mutation
3
Q151M. The two NNRTI mutations, L100I and K103N, give broad-spectrum resistance to the prior ART use had a baseline VL of < 400 copies/mL, and of
NNRTI class, including intermediate resistance to the second-generation NNRTIs, while V90I
5
is a polymorphic accessory mutation selected by NNRTIs and is associated with minimal these, 39% had detectable ART levels in plasma. A study
reduction in susceptibility to this class. 2
from Khayelitsha reported that 23% of patients disengaged
from care for at least 6 months and that ~50% of these
TABLE 2: Mutation-penalty score for the reverse transcriptase inhibitors. 6
Mutation Scoring: RT returned to care in the medium term. Almost 1/3 of
NRTI ABC AZT FTC 3TC TDF adults restarting first-line ART with prior ART exposure
A62V 5 5 5 5 5 harbour resistant virus with women twice as likely as men to
K65R 45 -15 30 30 60 have resistance because of previous ART exposure during
7
V75I 5 5 5 5 5 pregnancy. Patients with multiple treatment interruptions
Y115F 60 0 0 0 15 and/or pre-treatment drug resistance (PDR) are at an
M184V 15 -10 60 60 -10 increased risk of virological failure. 8,9,10,11 This patient had
K219E 5 10 0 0 5 seven different laboratory numbers, making linking her
Total 135 -5 100 100 80 previous results complicated. Patients with prior ART may
NNRTI DOR EFV ETR NVP RPV benefit from differentiated care with specialised adherence
L100I 15 60 30 60 60 support, an early VL (at 4 months), DRT in case of a
12
L100I + K103N 15 0 0 0 0 suboptimal VL response and rapid change to a second-line
K103N 0 60 0 60 0 regimen. The absence of a 6-month VL in this patient made
Total 30 120 30 120 60 prompt action impossible. She had a number of risk factors
Source: Adapted from the Stanford database 2 for treatment failure, namely previous ART, high VL and
Note: This combination of mutations leaves only AZT as a viable NRTI.
RT, reverse transcriptase; NRTI, nucleoside/nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors; previous adherence issues, which could have alerted the
ABC, abacavir; AZT, zidovudine; FTC, emtricitabine; 3TC, lamivudine; TDF, tenofovir disoproxil astute clinician had this information been available.
fumarate; NNRTI, non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor; DOR, doravirine;
EFV, efavirenz; ETR, etravirine; NVP, nevirapine; RPV, rilpivirine.
Acknowledgements
Discussion The authors would like to thank Sr Eileen Thompson for
This case study describes the rapid emergence of high-level, assisting with patient recruitment.
dual-class HIVDR in a patient with undisclosed prior ART
use. Having nine reverse transcriptase mutations within 12 Competing interests
months is much faster than the reported rate of emergence.
4
This together with the unsuppressed VL during 2012 and The authors declare that they have no financial or personal
2013 suggests prior HIVDR mutation selection, which waned relationship(s) that may have inappropriately influenced
them in writing this article.
to below the detection threshold of population sequencing
(± 20%) when DRT was performed in 2014. Thereafter, it
rapidly re-emerged upon reintroduction of ART. Authors’ contributions
G.v.D. performed the laboratory work, namely Sanger
Prior undisclosed use of ART is a common problem, requiring sequencing, and interpretation of the results; T.M.R. accessed
vigilance, especially in health sectors where patients are and interpreted the clinical information and prepared the
mobile and do not have unique identifiers, as is the case in first draft of the manuscript; G.v.Z. assisted with the
South Africa. Recent data from Botswana showed that interpretation of the genotype. All authors contributed to and
136/951 (14%) HIV-infected participants who reported no proofread the final manuscript.
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 79 Open Access