Page 89 - SAHCS HIVMed Journal Vol 20 No 1 2019
P. 89
Page 2 of 6 Case Report
a b c
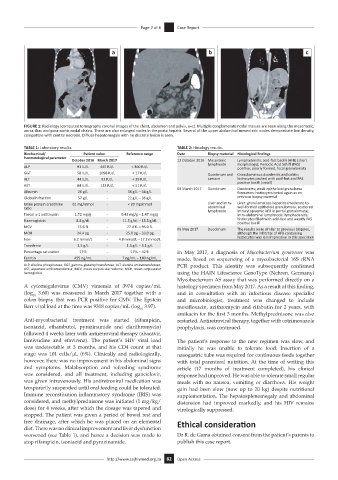
FIGURE 1: Radiology (computed tomography coronal images of the chest, abdomen and pelvis, a–c). Multiple conglomerate nodal masses are seen along the mesenteric,
aorta, iliac and para-aortic nodal chains. There are also enlarged nodes in the porta hepatis. Several of the upper abdominal mesenteric nodes demonstrate low density,
compatible with central necrosis. Diffuse hepatomegaly with no discrete lesion is seen.
TABLE 1: Laboratory results. TABLE 2: Histology results.
Biochemical/ Patient value Reference range Date Biopsy material Histological findings
haematological parameter
October 2016 March 2017 12 October 2016 Mesenteric Lymphadenitis; acid-fast bacilli (AFB) (short
ALP 91 IU/L 445 IU/L < 300 IU/L lymphnode morphology); Periodic Acid Schiff (PAS)
positive; poorly formed, focal granulomata
GGT 58 IU/L 1098 IU/L < 17 IU/L Duodenum and Granulomatous duodenitis and colitis;
ALT 44 IU/L 92 IU/L < 39 IU/L caecum histiocytes packed with acid-fast and PAS
AST 84 IU/L 132 IU/L < 51 IU/L positive bacilli (small)
Albumin 20 g/L - 38 g/L – 54 g/L 08 March 2017 Duodenum Duodenitis; weak epithelioid granuloma
formation; histiocytes noted again as on
Globulin fraction 57 g/L - 22 g/L – 36 g/L previous biopsy material
Urine protein:creatinine 61 mg/mmol - < 20 mg/mmol Liver and intra- Liver: granulomatous hepatitis (moderate to
ratio abdominal well-formed epitheloid granulomata; scattered
lymphnode
intracytoplasmic AFB in portal granulomata);
Faecal α-1 antitrypsin 1.72 mg/g - 0.43 mg/g – 1.47 mg/g intra-abdominal lymphnode: lymphadenitis;
Haemoglobin 8.8 g/dL - 11.5 g/dL – 15.5 g/dL histiocytes filled with acid-fast and weakly PAS
positive bacilli
MCV 75.6 fL - 77.0 fL – 95.0 fL 06 May 2017 Duodenum The results were similar to previous biopsies,
MCH 24.4 pg - 25.0 pg – 33.0 pg although the infiltrate of AFB containing
Iron 6.2 mmol/L - 4.8 mmol/L – 17.2 mmol/L histiocytes was less impressive in this specimen
Transferrin 1.5 g/L - 1.3 g/L – 3.1 g/L
Percentage saturation 17% - 17% – 42% In May 2017, a diagnosis of Mycobacterium genavense was
Ferritin 495 ng/mL - 7 ng/mL – 140 ng/mL made, based on sequencing of a mycobacterial 16S rRNA
ALP, alkaline phosphatase; GGT, gamma-glutamyl transferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; PCR product. This identity was subsequently confirmed
AST, aspartate aminotransferase; MCV, mean corpuscular volume; MCH, mean corpuscular
hemoglobin. using the HAIN Lifescience GenoType (Nehren, Germany)
Mycobacterium AS assay that was performed directly on a
A cytomegalovirus (CMV) viraemia of 3974 copies/mL histology specimen from May 2017. As a result of this finding,
(log 3.60) was measured in March 2017 together with a and in consultation with an infectious disease specialist
10
colon biopsy that was PCR positive for CMV. The Epstein and microbiologist, treatment was changed to include
Barr viral load at the time was 9318 copies/mL (log 3.97). moxifloxacin, azithromycin and rifabutin for 2 years, with
10
amikacin for the first 3 months. Methylprednisone was also
Anti-mycobacterial treatment was started (rifampicin, restarted. Antiretroviral therapy, together with cotrimoxazole
isoniazid, ethambutol, pyrazinamide and clarithromycin) prophylaxis, was continued.
followed 4 weeks later with antiretroviral therapy (abacavir,
lamivudine and efavirenz). The patient’s HIV viral load The patient’s response to the new regimen was slow, and
was undetectable at 3 months, and his CD4 count at that initially he was unable to tolerate food. Insertion of a
stage was 101 cells/μL (6%). Clinically and radiologically, nasogastric tube was required for continuous feeds together
however, there was no improvement in his abdominal signs with total parenteral nutrition. At the time of writing this
and symptoms. Malabsorption and refeeding syndrome article (17 months of treatment completed), his clinical
was considered, and all treatment, including ganciclovir, response had improved. He was able to tolerate small regular
was given intravenously. His antiretroviral medication was meals with no nausea, vomiting or diarrhoea. His weight
temporarily suspended until oral feeding could be tolerated. gain had been slow (now up to 20 kg) despite nutritional
Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS) was supplementation. The hepatosplenomegaly and abdominal
considered, and methylprednisone was initiated (1 mg/kg/ distension had improved markedly, and his HIV remains
dose) for 4 weeks, after which the dosage was tapered and virologically suppressed.
stopped. The patient was given a period of bowel rest and
free drainage, after which he was placed on an elemental Ethical consideration
diet. There was no clinical improvement and liver dysfunction
worsened (see Table 1), and hence a decision was made to Dr R. de Gama obtained consent from the patient’s parents to
stop rifampicin, isoniazid and pyrazinamide. publish this case report.
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 82 Open Access