Page 90 - SAHCS HIVMed Journal Vol 20 No 1 2019
P. 90
Page 3 of 6 Case Report
a b c
d e f
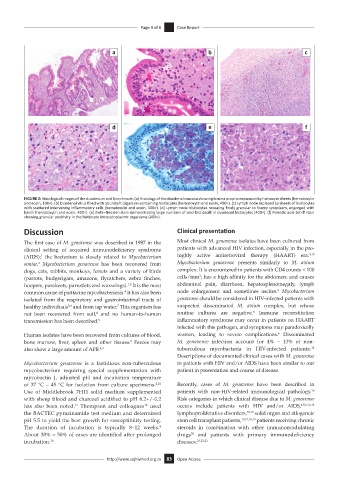
FIGURE 2: Histological images of the duodenum and lymphnode. (a) Histology of the duodenal mucosa showing lamina propria expansion by histiocyte sheets (hematoxylin
and eosin, 100×). (b) Duodenal villus filled with abundant organism-containing histiocytes (hematoxylin and eosin, 400×). (c) Lymph node replaced by sheets of histiocytes
with scattered intervening inflammatory cells (hematoxylin and eosin, 100×). (d) Lymph node histiocytes revealing finely granular to foamy cytoplasm, engorged with
bacilli (hematoxylin and eosin, 400×). (e) Ziehl–Neelsen stain demonstrating large numbers of acid-fast bacilli in duodenal histiocytes (400×). (f) Periodic acid-Schiff stain
showing granular positivity in the histiocyte intracytoplasmic organisms (400×).
Discussion Clinical presentation
The first case of M. genavense was described in 1987 in the Most clinical M. genavense isolates have been cultured from
clinical setting of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome patients with advanced HIV infection, especially in the pre-
1
(AIDS); the bacterium is closely related to Mycobacterium highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) era. 9,10
simiae. Mycobacterium genavense has been recovered from Mycobacterium genavense presents similarly to M. avium
2
dogs, cats, rabbits, monkeys, ferrets and a variety of birds complex: It is encountered in patients with CD4 counts < 100
3
(parrots, budgerigars, amazons, flycatchers, zebra finches, cells/mm ; has a high affinity for the abdomen; and causes
hoopers, parakeets, parrotlets and waxwings). It is the most abdominal pain, diarrhoea, hepatosplenomegaly, lymph
1,3
6
common cause of psittacine mycobacteriosis. It has also been node enlargement and sometimes ascites. Mycobacterium
4
isolated from the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts of genavense should be considered in HIV-infected patients with
healthy individuals and from tap water. This organism has suspected disseminated M. avium complex, but whose
5,6
7
8
not been recovered from soil, and no human-to-human routine cultures are negative. Immune reconstitution
8
transmission has been described. 9 inflammatory syndrome may occur in patients on HAART
infected with this pathogen, and symptoms may paradoxically
6
Human isolates have been recovered from cultures of blood, worsen, leading to severe complications. Disseminated
bone marrow, liver, spleen and other tissues. Faeces may M. genavense infection account for 4% – 13% of non-
8
13
also show a large amount of AFB. 4,9 tuberculous mycobacteria in HIV-infected patients.
Descriptions of documented clinical cases with M. genavense
Mycobacterium genavense is a fastidious non-tuberculous in patients with HIV and/or AIDS have been similar to our
mycobacterium requiring special supplementation with patient in presentation and course of disease.
mycobactin J, adjusted pH and incubation temperature
of 37 °C – 45 °C for isolation from culture specimens. 2,10 Recently, cases of M. genavense have been described in
Use of Middlebrook 7H11 solid medium supplemented patients with non-HIV-related immunological pathology.
10
with sheep blood and charcoal acidified to pH 6.2+/-0.2 Risk categories in which clinical disease due to M. genavense
has also been noted. Thompson and colleagues used occurs include patients with HIV and/or AIDS, 4,5,6,13,14
11
12
the BACTEC pyrazinamide test medium and determined lymphoproliferative disorders, 15,16 solid organ and allogeneic
pH 5.5 to yield the best growth for susceptibility testing. stem cell transplant patients, 10,17,18,19 patients receiving chronic
The duration of incubation is typically 8–12 weeks. steroids in combination with other immunomodulating
8
About 30% – 50% of cases are identified after prolonged drugs and patients with primary immunodeficiency
20
incubation. 10 diseases. 21,22,23
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 83 Open Access