Page 82 - SAHCS HIVMed Journal Vol 20 No 1 2019
P. 82
Page 2 of 4 Case Report
HIV drug resistance testing and third-line resistance tests conducted during the course of patient
response management.
A genotypic resistance test was performed on 31 March 2015 She was started on third-line ART in August 2015. She has
after second-line ART failure. Results of the test were had challenges with treatment adherence because of the
interpreted using the Stanford HIV drug resistance guide. We high pill burden, and received 3TC monotherapy as a
found four major protease inhibitor (PI) resistance-associated holding therapy from March 2017 (VL was 255 397 copies/
mutations (RAMs), that is, M46I, I54V, L76V and V82A. The mL) to January 2018. She was treated for pulmonary
PI RAMs conferred high-level resistance to atazanavir (ATV), tuberculosis (TB) from 08 August 2017 to 23 January 2018.
lopinavir, indinavir and saquinavir. The TB diagnosis was made based on loss of weight and
suggestive chest X-ray findings. She improved clinically
There were three nucleoside reverse transcriptase (NRTI) on TB treatment, and after completing 6 months of therapy,
RAMs, that is, M41L, M184V and T215F, and three non- she recommenced third-line therapy with ritonavir-
NRTI RAMs, that is, A98G, K103N and E138A. The RAMs boosted darunavir, lamivudine and dolutegravir (DTG).
conferred intermediate resistance to abacavir, zidovudine, She came daily to the clinic for a nurse to observe her and
stavudine, didanosine and rilpivirine. There was high- to take third-line medicines for 16 weeks, but her VL
level resistance to emtricitabine, lamivudine, efavirenz remained very high.
and nevirapine. The virus had low-level resistance to
tenofovir and etravirine. Table 2 summarises results of the An integrase strand transfer inhibitor (INSTI) resistance
test was then performed on 14 June 2018. Results showed
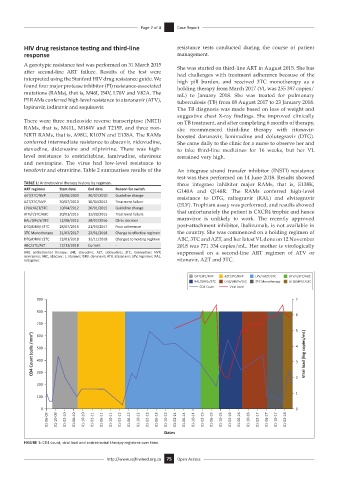
TABLE 1: Antiretroviral therapy history by regimen. three integrase inhibitor major RAMs, that is, E138K,
ART regimen Start date End date Reason for switch G140A and Q148R. The RAMs conferred high-level
d4T/3TC/NVP 28/08/2009 30/07/2010 Guideline change resistance to DTG, raltegravir (RAL) and elvitegravir
AZT/3TC/NVP 30/07/2010 10/04/2012 Treatment failure (ELV). Trophism assay was performed, and results showed
LPV/r/AZT/3TC 10/04/2012 20/01/2015 Guideline change
ATV/r/3TC/ABC 20/01/2015 12/08/2015 Treatment failure that unfortunately the patient is CXCR4 trophic and hence
RAL/DRV/r/3TC 12/08/2015 28/07/2016 Clinic decision maraviroc is unlikely to work. The recently approved
DTG/DRV/r/3TC 28/07/2016 21/03/2017 Poor adherence post-attachment inhibitor, ibalizumab, is not available in
3TC Monotherapy 21/03/2017 23/01/2018 Change to effective regimen the country. She was commenced on a holding regimen of
DTG/DRV/r/3TC 23/01/2018 12/11/2018 Changed to holding regimen ABC, 3TC and AZT, and her latest VL done on 12 November
ABC/3TC/AZT 12/11/2018 Current - 2018 was 771 334 copies/mL. Her mother is virologically
ART, antiretroviral therapy; d4T, stavudine; AZT, zidovudine; 3TC, lamivudine; NVP, suppressed on a second-line ART regimen of ATV or
nevirapine; ABC, abacavir; r, ritonavir; DRV, darunavir; ATV, atazanavir; LPV, lopinavir; RAL,
raltegravir. ritonavir, AZT and 3TC.
D4T/3TC/NVP AZT/3TC/NVP LPV/r/AZT/3TC ATV/r/3TC/ABC
RAL/DRV/r/3TC DTG/DRV/r/3TC 3TC Monotherapy DTG/DRV/r/3TC
CD4 Count Viral Load
900 7
800
6
700
5
CD4 Count (cells /mm 3 ) 500 4 3 Viral load (log copies/mL)
600
400
300
2
200
1
100
0 0
01-06-09 01-10-09 01-02-10 01-06-10 01-10-10 01-02-11 01-06-11 01-10-11 01-02-12 01-06-12 01-10-12 01-02-13 01-06-13 01-10-13 01-02-14 01-06-14 01-10-14 01-02-15 01-06-15 01-10-15 01-02-16 01-06-16 01-10-16 01-02-17 01-06-17 01-10-17 01-02-18
Dates
FIGURE 1: CD4 count, viral load and antiretroviral therapy regimens over time.
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 75 Open Access