Page 172 - SAHCS HIVMed Journal Vol 20 No 1 2019
P. 172
Page 3 of 8 Original Research
TABLE 1: Pre-intervention, intervention and post-intervention description of activities conducted at the Lancers Road PHC from 01 September 2011 to 31 December 2015.
Study phase Activity Description of activities
Pre-intervention In-depth file review (IDR) (data not • Assessed baseline clinical management of HIV-positive patients in ART services
Conducted from 01 April 2014 to shown (n = 206) • Evaluated demographics, ART initiation, TB treatment, pregnancy, co-morbidity, psychosocial
30 June 2014 of patients evaluations, visit data and laboratory results
enrolled in the ART
programme from VL and retention in care review • The study team reviewed VL results management and whether clients were retained in care
01 September 2011 to (VLRIC) (n = 1339) • The NHLS computerised system was used to locate VL results not located in client files
31 March 2014 VL management review (VLMR) • Assessed all patients with elevated VL from the VL and retention in care review
(n = 68) • Reviewed clinical management to determine guideline fidelity: follow-up VL testing; adherence
counselling; regimen change and time frames for these actions
Insertion of clinical summary charts • Research clinicians inserted clinical summary sheets in every patient file, management assessed
(n = 1339) • Patients requiring additional intervention were referred to nurse clinicians or sessional medical officers
Intervention Training sessions • Clinic staff were offered guideline-based training, including high VL management, CD4+ testing, pregnancy
01 April 2014–30 April 2015 and postpartum ART management, prophylaxis for opportunistic infections, TB diagnosis and management,
individual client care and preparation for ‘chronic clubs’, and completion of clinical summary charts
• Patient education focused on chronic clubs and viral suppression
• Feedback was given to clinicians managing a client, where appropriate
Clinical summary chart insertion • Nurses introduced clinical summary charts for all other new clients
• ART regimen and duration, due date for blood tests, laboratory results and interventions required were
summarised
• High VLs were flagged for intervention, missing results followed up and plans for stable clients to collect
medication without a clinical visit
Improved laboratory systems • Daily filing of thermal printer results sent through the ticker tape system
• Printing of missing laboratory results from the NHLS website
• Filing of the hard copies of the laboratory results in the client file for clinical management at the
appointment date
VL management system • High VL results flagged for immediate management
• Clients without NHLS blood results were noted to require a VL test at the next visit
• Clients with raised VL results, which were not adequately managed, were called for an appointment
with the clinic doctor within a week
• Unsuppressed VL files were kept in a marked box and not returned to the general filing system until the
client had an undetectable VL result
Follow-up system for missed • Patients with missed appointment dates were flagged for follow-up with the help of community health
appointments and lost to follow-up workers
Chronic club care • Down-referral system to transition stable clients for collection of medication (not requiring clinical
consultation) occurred within the clinic, in preparation for down-referral to a community site
• Basic protocol formulated for patient eligibility, an updated appointment card designed and an
educational message for relevant research staff prepared to create awareness in patients
• Patients eligible for chronic clubs were given dates for medication collection or consultation; using a diary
system those with missing appointments could be identified and contacted to improve retention in care
Post-intervention Improvement in VL testing and access • Available files from the pre-intervention in-depth review were compared to VL testing conducted post-
May 2015—31 December 2015 to VL results (n = 170) intervention
• Assessed improvement in VL testing, including VLs conducted and managed
VL management follow-up (n = 68) • Re-assessed the follow-up management of clients identified with a high VL during the VL and retention
in care review (pre-intervention) between 10 January 2015 and 30 June 2015
Clinical summary chart review • Study team reviewed the uptake of clinical summary sheets on new clients enrolled in the ART programme
(n = 280) • Research clinicians were not routinely involved in the insertion and completion of the clinical summary charts
Down-referral system (chronic clubs) • Eligibility for chronic clubs: patients on ART > 12 months; latest VL result undetectable/low detectable
limit; not currently pregnant or breastfeeding; no recent change in regimen and clinically well
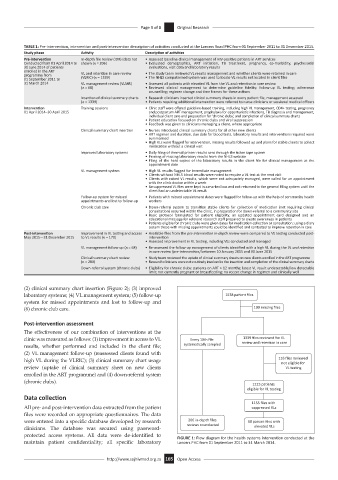
(2) clinical summary chart insertion (Figure 2); (3) improved
laboratory systems; (4) VL management system; (5) follow-up 1538 pa ent files
system for missed appointments and lost to follow-up and
(6) chronic club care. 199 missing files
Post-intervention assessment
The effectiveness of our combination of interventions at the
clinic was measured as follows: (1) improvement in access to VL Every 10th file 1339 files reviewed for VL
results, whether performed and included in the client file; systema cally sampled review and reten on in care
(2) VL management follow-up (reassessed clients found with
high VL during the VLRIC); (3) clinical summary chart usage 116 files reviewed
not eligible for
review (uptake of clinical summary sheet on new clients VL tes ng
enrolled in the ART programme) and (4) down-referral system
(chronic clubs).
1223 pa ents
eligible for VL tes ng
Data collection
1155 files with
All pre- and post-intervention data extracted from the patient suppressed VLs
files were recorded on appropriate questionnaires. The data
were entered into a specific database developed by research 206 in-depth files 68 pa ent files with
clinicians. The database was secured using password- reviews counducted elevated VLs
protected access systems. All data were de-identified to FIGURE 1: Flow diagram for the health systems intervention conducted at the
maintain patient confidentiality; all specific laboratory Lancers PHC from 01 September 2011 to 31 March 2014.
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 165 Open Access