Page 391 - HIVMED_v21_i1.indb
P. 391
Page 7 of 11 Original Research
TABLE 7: Independent t-tests for adolescent HIV self-management across categories of viral suppression and adherence.
AdHIVSM-35 n Mean SD T DF p
VL suppressed < 50
Yes 197 80.56 9.52 2.376 305 0.02
No 110 77.90 9.22 - - -
Adherent (Likert item 1 – last missed dose)
Yes 130 82.43 9.04 4.435 336 <0.001
No 208 77.91 9.19 - - -
Adherent (Likert item 2 – average adherence)
Yes 160 81.97 9.21 4.444 336 <0.001
No 178 77.54 9.08 - - -
Consistent condom use
Yes, using condoms every time 46 81.15 8.59 1.947 95 0.05
No, inconsistent condom use 51 77.58 9.38 - - -
Multiple sexual partners
Yes, more than one partner 27 77.86 9.73 –1.187 78 0.24
One partner only 53 80.44 8.95 - - -
Source: Based on Crowley T. The development of an instrument to measure adolescent HIV self-management in the context of the Western Cape, South Africa. [unpublished thesis]. Cape town:
Stellenbosch University; 2018
AdHIVSM, adolescent HIV self-management; SD, standard deviation; DF, degrees of freedom.
community, knowing the names of one’s ARVs or one’s
Proximal
VL, showing interest in understanding one’s VL and Process outcomes Distal outcomes
remembering to take treatment (not relying on other people
to remind them). The sub-scales with the lowest mean
percentage scores were Biomedical management and Coping Non- –0.14*
adherent
and self-regulation (Table 6). Participants who indicated that –0.34** behaviour Health-
they did not know how they were infected had significantly related
lower self-management scores compared to those who knew quality of
life
(t[115.15] = –2.299, p = 0.02).
Adolescent 0.45**
HIV Self-
Adolescent HIV self-management had a correlation management
coefficient of medium strength with HRQoL (r = 0.450, 0.17* –0.08
p < 0.01) and a negative correlation with non-adherent –0.03 –0.09
behaviour (r = –0.249, p < 0.01). The sub-scale of self-
management with the strongest correlation with HRQoL Sexual risk
was Goals and facilitation, which includes setting goals, but *, p < 0.05 behaviour 0.15* Viral load log
**, p < 0.01
importantly, obtaining support from family, friends and
healthcare workers. Participation or being actively involved
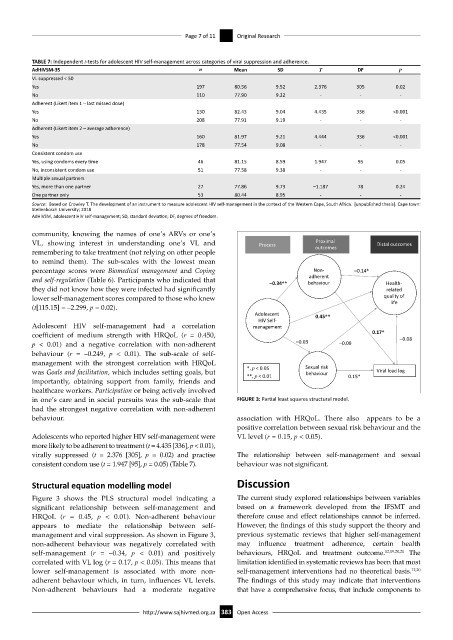
in one’s care and in social pursuits was the sub-scale that FIGURE 3: Partial least squares structural model.
had the strongest negative correlation with non-adherent
behaviour. association with HRQoL. There also appears to be a
positive correlation between sexual risk behaviour and the
Adolescents who reported higher HIV self-management were VL level (r = 0.15, p < 0.05).
more likely to be adherent to treatment (t = 4.435 [336], p < 0.01),
virally suppressed (t = 2.376 [305], p = 0.02) and practise The relationship between self-management and sexual
consistent condom use (t = 1.947 [95], p = 0.05) (Table 7). behaviour was not significant.
Structural equation modelling model Discussion
Figure 3 shows the PLS structural model indicating a The current study explored relationships between variables
significant relationship between self-management and based on a framework developed from the IFSMT and
HRQoL (r = 0.45, p < 0.01). Non-adherent behaviour therefore cause and effect relationships cannot be inferred.
appears to mediate the relationship between self- However, the findings of this study support the theory and
management and viral suppression. As shown in Figure 3, previous systematic reviews that higher self-management
non-adherent behaviour was negatively correlated with may influence treatment adherence, certain health
self-management (r = –0.34, p < 0.01) and positively behaviours, HRQoL and treatment outcome. 12,19,20,21 The
correlated with VL log (r = 0.17, p < 0.05). This means that limitation identified in systematic reviews has been that most
lower self-management is associated with more non- self-management interventions had no theoretical basis. 12,20
adherent behaviour which, in turn, influences VL levels. The findings of this study may indicate that interventions
Non-adherent behaviours had a moderate negative that have a comprehensive focus, that include components to
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 383 Open Access