Page 338 - HIVMED_v21_i1.indb
P. 338
Page 4 of 7 Original Research
Source: Photo taken by author, Saskya Claasens.
FIGURE 1: Proximal onychomycosis affecting four digits.
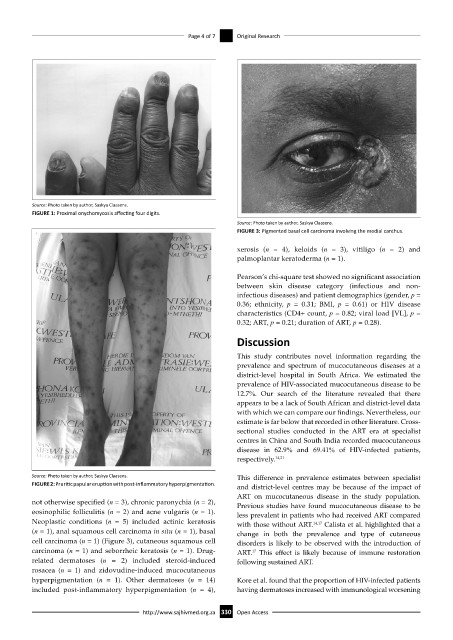
Source: Photo taken by author, Saskya Claasens.
FIGURE 3: Pigmented basal cell carcinoma involving the medial canthus.
xerosis (n = 4), keloids (n = 3), vitiligo (n = 2) and
palmoplantar keratoderma (n = 1).
Pearson’s chi-square test showed no significant association
between skin disease category (infectious and non-
infectious diseases) and patient demographics (gender, p =
0.36; ethnicity, p = 0.31; BMI, p = 0.61) or HIV disease
characteristics (CD4+ count, p = 0.82; viral load [VL], p =
0.32; ART, p = 0.21; duration of ART, p = 0.28).
Discussion
This study contributes novel information regarding the
prevalence and spectrum of mucocutaneous diseases at a
district-level hospital in South Africa. We estimated the
prevalence of HIV-associated mucocutaneous disease to be
12.7%. Our search of the literature revealed that there
appears to be a lack of South African and district-level data
with which we can compare our findings. Nevertheless, our
estimate is far below that recorded in other literature. Cross-
sectional studies conducted in the ART era at specialist
centres in China and South India recorded mucocutaneous
disease in 62.9% and 69.41% of HIV-infected patients,
respectively. 14,21
Source: Photo taken by author, Saskya Claasens. This difference in prevalence estimates between specialist
FIGURE 2: Pruritic papular eruption with post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. and district-level centres may be because of the impact of
ART on mucocutaneous disease in the study population.
not otherwise specified (n = 3), chronic paronychia (n = 2), Previous studies have found mucocutaneous disease to be
eosinophilic folliculitis (n = 2) and acne vulgaris (n = 1). less prevalent in patients who had received ART compared
Neoplastic conditions (n = 5) included actinic keratosis with those without ART. 14,17 Calista et al. highlighted that a
(n = 1), anal squamous cell carcinoma in situ (n = 1), basal change in both the prevalence and type of cutaneous
cell carcinoma (n = 1) (Figure 3), cutaneous squamous cell disorders is likely to be observed with the introduction of
carcinoma (n = 1) and seborrheic keratosis (n = 1). Drug- ART. This effect is likely because of immune restoration
17
related dermatoses (n = 2) included steroid-induced following sustained ART.
rosacea (n = 1) and zidovudine-induced mucocutaneous
hyperpigmentation (n = 1). Other dermatoses (n = 14) Kore et al. found that the proportion of HIV-infected patients
included post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (n = 4), having dermatoses increased with immunological worsening
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 330 Open Access