Page 21 - HIVMED_v21_i1.indb
P. 21
Page 3 of 8 Guideline
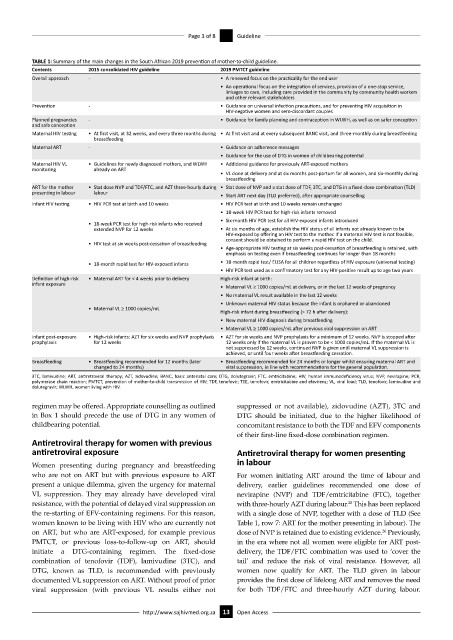
TABLE 1: Summary of the main changes in the South African 2019 prevention of mother-to-child guideline.
Contents 2015 consolidated HIV guideline 2019 PMTCT guideline
Overall approach - • A renewed focus on the practicality for the end user
• An operational focus on the integration of services, provision of a one-stop service,
linkages to care, including care provided in the community by community health workers
and other relevant stakeholders
Prevention - • Guidance on universal infection precautions, and for preventing HIV acquisition in
HIV-negative women and sero-discordant couples
Planned pregnancies - • Guidance for family planning and contraception in WLWH, as well as on safer conception
and safe conception
Maternal HIV testing • At first visit, at 32 weeks, and every three months during • At first visit and at every subsequent BANC visit, and three-monthly during breastfeeding
breastfeeding
Maternal ART - • Guidance on adherence messages
• Guidance for the use of DTG in women of childbearing potential
Maternal HIV VL • Guidelines for newly diagnosed mothers, and WLWH • Additional guidance for previously ART-exposed mothers
monitoring already on ART
• VL done at delivery and at six months post-partum for all women, and six-monthly during
breastfeeding
ART for the mother • Stat dose NVP and TDF/FTC, and AZT three-hourly during • Stat dose of NVP and a stat dose of TDF, 3TC, and DTG in a fixed-dose combination (TLD)
presenting in labour labour
• Start ART next day (TLD preferred), after appropriate counselling
Infant HIV testing • HIV PCR test at birth and 10 weeks • HIV PCR test at birth and 10 weeks remain unchanged
• 18-week HIV PCR test for high-risk infants removed
• Six-month HIV PCR test for all HIV-exposed infants introduced
• 18-week PCR test for high-risk infants who received
extended NVP for 12 weeks • At six months of age, establish the HIV status of all infants not already known to be
HIV-exposed by offering an HIV test to the mother. If a maternal HIV test is not feasible,
consent should be obtained to perform a rapid HIV test on the child.
• HIV test at six weeks post-cessation of breastfeeding
• Age-appropriate HIV testing at six weeks post-cessation of breastfeeding is retained, with
emphasis on testing even if breastfeeding continues for longer than 18 months
• 18-month rapid test for HIV-exposed infants • 18-month rapid test/ ELISA for all children regardless of HIV exposure (universal testing)
• HIV PCR test used as a confirmatory test for any HIV-positive result up to age two years
Definition of high-risk • Maternal ART for < 4 weeks prior to delivery High-risk infant at birth:
infant exposure
• Maternal VL ≥ 1000 copies/mL at delivery, or in the last 12 weeks of pregnancy
• No maternal VL result available in the last 12 weeks
• Unknown maternal HIV status because the infant is orphaned or abandoned
• Maternal VL ≥ 1000 copies/mL
High-risk infant during breastfeeding (> 72 h after delivery):
• New maternal HIV diagnosis during breastfeeding
• Maternal VL ≥ 1000 copies/mL after previous viral suppression on ART
Infant post-exposure • High-risk infants: AZT for six weeks and NVP prophylaxis • AZT for six weeks and NVP prophylaxis for a minimum of 12 weeks. NVP is stopped after
prophylaxis for 12 weeks 12 weeks only if the maternal VL is proven to be < 1000 copies/mL. If the maternal VL is
not suppressed by 12 weeks, continued NVP is given until maternal VL suppression is
achieved, or until four weeks after breastfeeding cessation.
Breastfeeding • Breastfeeding recommended for 12 months (later • Breastfeeding recommended for 24 months or longer whilst ensuring maternal ART and
changed to 24 months) viral suppression, in line with recommendations for the general population.
3TC, lamivudine; ART, antiretroviral therapy; AZT, zidovudine; BANC, basic antenatal care; DTG, dolutegravir; FTC, emtricitabine; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; NVP, nevirapine; PCR,
polymerase chain reaction; PMTCT, prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV; TDF, tenofovir; TEE, tenofovir, emtricitabine and efavirenz; VL, viral load; TLD, tenofovir, lamivudine and
dolutegravir; WLWH, women living with HIV.
regimen may be offered. Appropriate counselling as outlined suppressed or not available), zidovudine (AZT), 3TC and
in Box 1 should precede the use of DTG in any women of DTG should be initiated, due to the higher likelihood of
childbearing potential. concomitant resistance to both the TDF and EFV components
of their first-line fixed-dose combination regimen.
Antiretroviral therapy for women with previous
antiretroviral exposure Antiretroviral therapy for women presenting
Women presenting during pregnancy and breastfeeding in labour
who are not on ART but with previous exposure to ART For women initiating ART around the time of labour and
present a unique dilemma, given the urgency for maternal delivery, earlier guidelines recommended one dose of
VL suppression. They may already have developed viral nevirapine (NVP) and TDF/emtricitabine (FTC), together
resistance, with the potential of delayed viral suppression on with three-hourly AZT during labour. This has been replaced
25
the re-starting of EFV-containing regimens. For this reason, with a single dose of NVP, together with a dose of TLD (See
women known to be living with HIV who are currently not Table 1, row 7: ART for the mother presenting in labour). The
on ART, but who are ART-exposed, for example previous dose of NVP is retained due to existing evidence. Previously,
26
PMTCT, or previous loss-to-follow-up on ART, should in the era where not all women were eligible for ART post-
initiate a DTG-containing regimen. The fixed-dose delivery, the TDF/FTC combination was used to ‘cover the
combination of tenofovir (TDF), lamivudine (3TC), and tail’ and reduce the risk of viral resistance. However, all
DTG, known as TLD, is recommended with previously women now qualify for ART. The TLD given in labour
documented VL suppression on ART. Without proof of prior provides the first dose of lifelong ART and removes the need
viral suppression (with previous VL results either not for both TDF/FTC and three-hourly AZT during labour.
http://www.sajhivmed.org.za 13 Open Access